Adult dosages Flashcards
Corticosteroids
Pt with severe asthma attack
or
severe allergy/anapylaxis
Hydrocortisone:
200-500mg IVI slowly
(5mg/kg)
Salbutamol
Premature/obstructed labour/prolapsed cord
Maintenance infusion?
Dilute
2 mg [4 x 500 mcg/ml] into 200 ml N/S (10mcg/ml solution)
Start with 10 mcg/min.
May increase by 10 mcg/min every 10 min to a max of 45 mcg/min
Lorazepam
Pt with active convulsions
Initial dose?
If not terminated by intial dose?
Maximum dose?

2-4mg slowly IVI
If required an additional 4mg IVI may be administered after 10 minutes
Titrate to effect (use the lowest effective dosage)
Maximum 8mg/12hours
Lignocaine Hydrochloride (Lidocaine) (Systemic)
Endotracheal Intubation Sequence
(for raised ICP)
Specifically indicated for patients who may already have an element of raised intracranial pressure, the addition to which would compromise the patient
administer 1.5mg/kg 3 minutes before intubation
Thiamine Hydrochloride
Pt with suspected Wernicke’s encephalopathy
100 mg IVI bolus, slowly
Magnesium Sulphate
Pt in cardiac arrest unresponsive to conventional therapy
1-2g (2 to 4ml of a 50% solution)
Dilute 1g/2ml vial to 10ml sterile water = 10% solution
Give slowly, not exceeding 1.5ml/min, with continuous careful monitoring
Salbutamol
Pt in obstructed labour
IV Bolus dose and rate?
Slow IV
100-250 mcg IV
Administer
1ml/min until:
- Total of 250mcg/10min has been given, i.e. 10ml
- Mother’s heart rate >120bpm
- Contraction cease
Dextrose 50%
Pt in hypoglycemic coma
10g (20ml of a 50% solution) slowly IVI
Repeat
every 5 minutes should blood glucose remain
First give 100mg Thiamine if available and indicated
Glyceryl Trinitrate
Pt with cardiac chest pain
One tablet sublingual
OR
one spray (without inhaling) onto oral mucosa
(preferably sublingual)
Repeat
every 5 minutes until pain is relieved, or max dose taken
Maximum of 3 sprays/tablets
- Terminate administration if systolic blood pressure:
- -Decreased by more than 10% in a normotensive patient -Decreases by more than 30% in a hypertensive patient -Measures lower than 90mmHg
Lignocaine Hydrochloride (Lidocaine) (Systemic)
Pt with chest pains, BP 80/60mmHg, HR 92, with arrhythmia
loading dose?
When must the bolus dose be terminated?

Loading dose:
1mg/kg slowly IVI
Bolus doses must be terminated when either:
- A maximum of 3mg/kg has been administered, or
- The blood pressure drops by >10%, or
- Ventricular arrhythmia ceases, or -
Signs of toxicity develop
Thiamine Hydrochloride
Pt with suspected thiamine deficiency (eg alcoholims, malnourishment)
Dose prior IV 50% Dextrose administration
100 mg IVI bolus, slowly
Atropine Sulphate
Pt with refractory symptomatic bradycardia
First dose?
0.5mg IVI push
Midazolam
- Adult dose -
Maintenance Infusion for a transfer of a 100kg intubated pt on mechanical ventilator
How many mls/hour if using 200mls NS?
(maximum recommended dose)
0.03mg/kg/hr-0.1mg/kg/hr
VR = SR/SS x VS
VR=(0.1mgx100)/15mg x 200ml
VR=133mls/hr
when used in combination with narcotic analgesics
Adrenaline
Pt in cardiac arrest
Intravenous:
1 mg IVI push
Tracheal:
2 mg diluted with 10 ml of water for injection preferred
Repeat every 3-5 minutes
Flumazenil
Pt overdosed on Valium (benzodiazepine) and is only responding to pain and breathing at a rate of 10/min.
Intitial dose?

Initial bolus:
0.2mg slowly IVI over 15 seconds
Magnesium Sulphate
Pt with convulsions in toxaemia of pregnancy
Infusion dose and rate?
3g in 200ml 0.9% sodium chloride solution
at a rate not exceeding 3ml/min
Lignocaine Hydrochloride (Lidocaine) (Systemic)
80kg male pt with stable BP, no chest pain, HR of 180 and the following ECG rhythm. Amiodarone is not available
loading dose?
When must bolus dose be terminated?
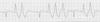
Loading dose:
1mg/kg slowly IVI
Bolus doses must be terminated when either:
- A maximum of 3mg/kg has been administered, or
- The blood pressure drops by >10%, or
- Ventricular arrhythmia ceases, or
- Signs of toxicity develop
Sodium Bicarbonate 8.5%
Pt in cardiac arrest due to suspected cocaine overdose
1ml/kg (8.5%) slowly IVI with free flowing line
Lignocaine Hydrochloride (Lidocaine) (Systemic)
Pt in cardiac arrest with the following arrhythmia.
(Amiodarone is not available)
Bolus dose?
Repeat dose?
Maxium total dose?

Administer a bolus dose of
1mg/kg IVI/IO push
0.5mg/kg IVI/IO (or 1 mg/kg ET) every 5 minutes
Maximumm total bolus dose
3 mg/kg IVI
Following successful defibrillation, follow with maintenance infusion
Naloxone Hydrochloride
- Adult dose-
- 0.4mg slowly IVI/IMI (0.1mg/kg)
- Repeat every 5 minutes, up to 2mg
- Should 2mg fail to elicit the desired response, then overdose with agents other than opiods should be considered
Flumazenil
Pt overdosed on Valium (benzodiazepine), responds only to pain and has a RR 10/min. You have already administered a bolus of 0.2mg IVI
Repeat dose?
(Include max dose that can be administered)

Repeat:
0.1mg at 1 minute intervals
Max dose:
1mg
Metoclopramide Monohydrochloride
Pt that is feeling nauseous and is vomitting

>60 kg:
10 mg slowly IVI/IMI
< 60 kg:
5 mg slowly IVI/IMI
Calcium Chloride 10%
Pt with Verapamil (calcium channel blocker) overdose

10ml of calcium chloride 10% solution, slowly IVI
If being administered pre-arrest, administer at 1ml/min
Magnesium Sulphate
Pregnant female convulsing (toxemia of pregnancy)
Bolus dose?

2-4g of a 10% solution given very slowly,
with careful monitoring not exceeding 1.5ml/min
(10% solution is obtained by diluting the 1g/2ml vial to 10ml with sterile water)