Adrenal Disease Flashcards
Describe the basic anatomy of the adrenal gland [6]
- Composed of adrenal medulla and cortex:
- Adrenal Cortex:
- Zona glomerulosa → aldosterone (salt)
- Zona fasciculata → cortisol (sugar)
- Zona reticularis → androgens (sex)
- Adrenal medulla
- Composed chromograffin cells
- Release catecholamines
Renin is the major regulator of aldosterone production. When is it activated and what effects does it have? [4]
- Activated in response to ↓blood pressure
- Leads to production of angiotensin II which causes direct and indirect methods of BP elevation:
- Direct = vasoconstriction
- Indirect = aldosterone release
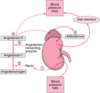
Describe the regulation of cortisol and androgen production

What are the typical signs and symptoms of Cushing’s Syndrome? [12]
- Euphoria (through sometimes depression or psychotic symptoms, and emotional lability)
- Weight gain
- Hirsutism
- Proximal myopathy
- Plethora (red cheeks)
- Moon facies
- Hypertension
- Bruising
- Striae (red/purple)
- Buffalo hump
- Thinning of skin
- Muscle wasting in arms and legs

What tests are used for the diagnosis of Cushing’s Syndrome? [8]
- 24hr urinary free cortisol
- Urine cortisol : creatinine ratio x3
- Dexamethasone suppression test
- Either overnight or low dose test over 48hrs
- Plasma cortisol should be undetectable in normal circumstances
- If it is a pituitary problem, cortisol will suppress to <50%
- No response in ectopic ACTH
- Late night salivary cortisol
- Should be undetectable or very low normally
- Plasma ACTH
- If low, the problem is in the adrenals
- High dose dexamethasone suppression test
- CRH test
- Exaggerated response in pituitary disease
- No response in ectopic ACTH
- Imaging
- Adrenal CT or MRI
- Pituitary MRI only detects 50% of ACTH producing pituitary tumours
- Optimal imaging for ectopic tumours unclear (CT/PET/MRI)
What are the causes of Cushing’s Syndrome? [8]
- ACTH dependent
- Pituitary adenoma (68%) Cushing Disease
- Ectopic ACTH
- Ectopic CRH
- ACTH independent
- Adrenal adenoma
- Adrenal carcinoma
- Nodular hyperplasia
What condition is caused by adrenal insufficiency? [1]
Addison’s disease
What are the signs and symptoms of Addison’s disease? [8]
- Anorexia, weight loss
- Fatigue/lethargy
- Dizziness
- Low BP
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Skin pigmentation
What investigations are used for diagnosis of Addison’s disease and what values are indicative of the disease? [5]
- “suspicious biochemistry”
- ↓Na2+
- ↑K+
- Short synACTHen test
- Measure plasma cortisol before and 30mins after IV ACTH injection
- Normal:
- Baseline >250nmol/L
- Post-ACTH >480nmol/L
- ACTH levels
- Should be significantly elevated (↑↑)
- Causes skin pigmentation
- Renin/aldosterone levels
- ↑↑ renin
- ↓ aldosterone
- Adrenal autoantibodies
What is congenital adrenal hyperplasia? [3]
- Autosomal recessive disorder
- Range of genetic disorders relating to defects in steroidogenic genes
- Most common = CYP21 (21 alpha hydroxylase)
How does congenital adrenal hyperplasia present in…
- females? [1]
- males? [4]
- Presentation in females:
- Ambiguous genitalia
- Presentation in males:
- Adrenal crisis
- Hypotension
- Hyponatraemia
- Early virilisation
How do you treat congenital adrenal hyperplasia? [2]
- mineralocorticoid replacement and
- glucocorticoid replacement
What is late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia and what is the basic pathogenesis behind it? [3]
- Partial 21 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency
- Maintain cortisol within normal range
- Increased ACTH drive leads to increased 17 OPH and adrenal androgens
How does late onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) typically present? [3]
- Oligomenorrhoea
- Hirsutism
- Reduced fertility
How do you diagnose late onset CAD? [2]
synACTHen test with 17OHP
Define primary aldosteronism (Conn’s Syndrome) and what is it usually associated with? [3]
- Excess production of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels
- Commonest “secondary” cause of hypertension
- 40% adenoma
- 60% bilateral hyperplasia
- Hypokalaemia present in less than 50% of cases
What investigations are used to diagnose primary aldosteronism and what results would make you suscipious? [5]
- Aldosterone-renin ratio (ARR) is the best screening tool
- If increased, then consider further testing
- Saline suppression test
- 2L saline over 4hrs
- 4hr aldosterone >270pmol/l highly suspicious
What is the immediate management of primary aldosteronism? [5]
-
Stop medications if possible
- Definitely stop β-blockers and MR antagonists
- Alternative drugs include:
- α-blockers
- Verapamil
- Hydralazine
Describe the management options for primary aldosteronism (PA)? [8]
- Surgical
- Unilateral laparoscopic adrenalectomy
- Only if adrenal adenoma
- Cure of hypokalaemia
- Cures hypertension in 30-70% of cases
- Medical
- Use MR antagonists
- Spironolactone or eplerenone
Define pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma [2]
- Pheochromocytoma:
- Rare tumour affecting the adrenal medulla
- Paraganglioma:
- Extra-adrenal neural crest cells (e.g. sympathetic ganglia)
What are the typical signs & symptoms of pheochromocytoma? [13]
- Hypertension (intermittent in 50%)
- Episodes of:
- headache,
- palpitations,
- pallor
- sweating
- Also,
- tremor,
- anxiety,
- nausea,
- vomiting,
- chest or abdominal pain
- Crises last 15 minutes
- Often well in between crises
Phaeochromocytoma is treated surgically. What pre-operative treatment must be given first? [7]
- Alpha-blockade initially
- Phenoxybenzamine or doxazosin
- Aim for SBP <120mmHg if possible
- Postural drop
- Then beta blocker if tachycardic
- Labetalol or bisoprolol
- Encourage salt intake
Define an adrenal incidentaloma [1]
Incidentally discovered adrenal lesion discovered through diagnostic imaging for unrelated condition, without prior suspicion of tumour/disease
Describe the 2 types of adrenal incidentaloma [2]
-
Malignancy:
- Imaging characteristics
- Size <4cm
- Low Housfield units on non-contrast CT
- <10HU
- Lipid rich
- No further scan
- Imaging characteristics
- Dynamic scan:
- Adenoma rapid wash out
-
Functional:
- Aldosterone
- Cortisol
- Androgens
- Catecholamines


