Additional Info Flashcards
(40 cards)
What reflections are absent from the simple lattice structure XRD pattern?
None
What reflections are absent from the body centered lattice structure XRD pattern?
(h+k+l) is odd
What reflections are absent from the face centered lattice structure XRD pattern?
h, k, and l are mixed, odd and even
What reflections are absent from the diamond lattice structure XRD pattern?
h, k, and l are mixed; or (h+k+l)=4n+2
What is the expression of Bragg condition?

Name the seven crystal structures.
Cubic, tetragonal, orthorhombic, rhombohedral, monoclinic, triclinic, hexagonal
Name the four types of lattice structures.
Simple, base-centered, body-centered, and face-centered.
What is the resolution of an optical microscope?
200 nm
What is the formula for the resolution of an optical microscope?
(0.61*lambda)/NA
What is the formula for the depth of field of an optical microscope?
(2R) / [tan(alpha)]
What is the resolution of a TEM?
0.1 nm
What is the resolution of a SEM?
1 nm
What are the lateral and vertical resolutions of a STM?
Lateral: 0.1 nm
Vertical: 0.01 nm
What are the lateral and vertical resolutions of a AFM?
Lateral: 1 nm
Vertical: 0.1 nm
What is the formula for oscilation frequency?

What is the formula for reduced mass?
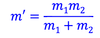
What are the types of vibrations that contribute to a 3 atom molecules’ 9 degrees of freedom (specify the number of degrees of each type).
Symmetric Stretching (x 1)
Asymmetric Stretching (x 1)
Bending (x 1)
Translational (x 3)
Rotational (x 3)
Which vibration[s] type[s] of the following molecule will be visible on an IR spectrum?

Asymmetric stretching
Bending
Which type[s] of vibration[s] will be visible on a Raman spetrum of the following molecule?

Symmetric stretching
Which type[s] of vibration[s] will be visible on a Raman spetrum of the following molecule?

Symmetric Stretching
Asymmetric Stretching
Bending
Which vibration[s] are visible on the IR spectrum of the following molecule?

Symmetric Stretching
Asymmetric Stretching
Bending
Identify the unit cell of the honeycomb lattice (small dots) and the rectangular lattice (big dots). And what are the unit vector lengths of the two types of unit cells?

Honeycomb is hexagonal unit cell with edge length √3 angstroms.
Rectangular cell has edge lengths 2√3 and 3 angstroms

What is the typical energy and wavelength of visible light in an optical microscope?
Energy: ~ 2 eV
Wavelength: ~ 600 nm
What is the typical energy and wavelength of electrons in a SEM?
Energy: ~ 10 keV
Wavelength: ~ 0.1 angstom













