Acute care q-bank Flashcards
Name the toxidrome: mydriasis, HTN, tachycardia, hyperactive DTRs, hyperthermic, dysphoria or anxiety / panic / hallucinations / depersonalization
hallucinogen intoxication ie: LSD, PCP
Name the toxidrome: mydriasis, HTN, tachycardia, hyperthermia, dry mouth, sweating, paranoid ideation, impulsivity, hyperactivity, convulsions
Amphetamines
Name the toxidrome: excitement, restlessness, euphoria, increased motor activity, decreased sense of fatigue, increased tremors, convulsive movements, increased HR/T/BP
Cocaine
How do you declare brain-death in a newborn >36 weeks gestational age and <30 days?
2 clinical exams (CN exam and apnea tests) more than 24h apart with the first exam done at > 48h of life
How do you declare brain-death in a 1 month to 1 year old?
2 separate clinical exam (CN exam and apnea test), no fixed interval between exams
How do you declare brain-death in a child or adolescent > 1 year old?
2 separate exam (CN + apnea test), but apnea test can be done concurrently
What is the caveat to declaring brain death in a hypoxic event at any age?
You must delay the exam 24 hours
What are the three components to a clinical brain death examination?
irreversible coma / unresponsiveness absence of brainstem reflexes apnea
What are the brainstem reflexes that are assessed in brain death?
pupillary light reflex oculocephalic reflex corneal reflex oculovestibular reflex gag and cough reflex
Name 6 indications for hospitalization for burns
>15% of TBSA any 3rd degree face/hands/perineum/genitals/major joints electrical or chemical burns inhalational injury inadequate home or social environment child abuse or neglect complex pre-existing medical condition associated injuries
How do you calculate fluid resuscitation in burns?
Maintenance IVF + Parkland: Ringers lactate (4mL x kg x % BSA) with 1/2 of fluids over first 8 hours and remaining 1/2 over next 16 hours
What toxidrome does TCA overdose present with?
Anticholinergic & lethargy / coma / myoclonic jerks / seizures & CVS refractory hypotension, QRS prolongation
How do you manage TCA overdoses?
Monitor ECG closely for QRS duration Gastric decontamination with activated charcoal in some Supportive treatment: - sodium bicarbonate antidote for QRS >/= 110msec, ventricular dysrhythmia, hypotension - hypertonic saline, lidocaine, lipid emulsion therapy for refractory arrhythmias - vasopressor therapy - benzodiazepines for seizures
What does anticholinergic syndrome look like?
(HOT) Fever, Tachycardia (RED) Flushing ( DRY) Urinary retention, Dry mucous membranes, Absent bowel sounds (BLIND) Dilated pupils (MAD) Altered mental status
What are features of a second degree burn?
Painful Wet blisters and bullae
What are features of a third degree burn?
White waxy and dry eschar No blanching, no bleeding Insensate
Name three negative prognostic factors in a submersion injury
Submersion >10 minutes Failure to respond to CPR after 25 minutes Hyperglycemia in the ED Absence of pupillary light response Apnea Deep coma
What are the features of an organophosphate overdose?
DUMBBELS Diarrhea/defecation Urination Miosis Bronchospasm Bradycardia Emesis Lacrimation Salivation
What is the management of organophosphate overdose?
Decontamination (remove clothing, wash, activated charcoal +/-) Atropine +/- Pralidoxime IVF
What test to order if suspecting alcohol overdose and how to treat?
Alcohols cause increased osmolar gap (measured osmolality minus calculated osmolality) Treat with fomepizole, ethanol or sodium bicarb in severe acidosis.
How do you calculate osmolarity?
2xNa + BUN + glucose
How do you calculate the anion gap?
Na - (Cl+HCO3)
What’s the antidote for anticholinergic ingestions?
Physostigmine Physostigmine is a carbamate which inhibits the enzyme acetylcholinesterase and prolongs the central and peripheral effects of acetylcholine
What is the toxic metabolite in methanol poisoning?
Formic acid it block mitochondrial respiration
What is the minimum length of time of observation an asymptomatic near-drowning?
8 hours - in a review, no injuries occurred after 7hrs; resp distress and pulmonary edema develop between 4-8hrs afterwards - perform CXR prior to d/c
What kind of reaction: face and neck involvement manifesting as torticollis, retrocollis, oculogyric crisis, or tongue protrusion with potentially life-threatening presentations with laryngospasm and airway compromise
Acute dystonic reaction
What class do the following fall under? gasoline, propellants, motor oils, lighter fluid, lamp oils
hydrocarbons
What are the most serious consequences of hydrocarbon ingestion?
chemical pneumonitis (aspiration leads to inactivation of type II pneumocytes)
What is sudden sniffing death?
Some volatile hydrocarbons sensitize the myocardium to the effects of endogenous catecholamines and can result in dysrhythmias examples: toluene, propellants, refrigerants and volatile nitrites, all commonly abused by inhalation
What are the clinical manifestations of hydrocarbon ingestion?
-transient mild CNS depression -coughing with aspiration -CXRs start off normal and by 6 hrs will have developed abnormalities including aspiration pneumonitis, pneumatoceles develop 2-3 weeks after exposure
Treatment for hydrocarbon intoxication?
Supportive standard mechanical ventilation, HFOV, ECMO PRN
What are treatment options for CSE PRE-hospital? (acc to CPS)
Lorazepam PO/PR Midazolam PO/IN Diazepam PR
Give an example of a H1 agonist
Cetirixine Diphenhydramine
Give an example of a H2 agonist
Ranitidine
Outline ‘first tier’ ICP management strategies
Head of bed elevation Sedation and analgesia Osmolar agents: NaCl 3% (4-6ml/kg, Serum Osm <360mOsm/L), Mannitol Intubation and controlled mechanical ventilation Neuromuscular blockade CSF drainage
Outline ‘second tier’ ICP management strategies
Barbituate infusion Decompressive craniectomy Mild hypothermia Hyperventilation Lumbar CSF drainage
What are the ECG findings of pulmonary embolus?
S1Q3T3 RBBB RV strain Right axis deviation Right atrial enlargement
Describe the tools and techniques for tension pneumothorax drainage
18-20 Fr needle catheter connected through tubing to a three-way stopcock and 60mL syringe top of the child’s third rib (second intercostal space) in the midclavicular line or 4th rib anterior axillary line
Management of pulseless v-tach?
Shock-shock-epi-shock- amio 2J/kg then 4 J/kg then 0.01mg/kg 1:10,000
Whats a sulfonylurea? What to consider with ingestion?
Oral DM2 drug. Sulfonylureas work by enhancing endogenous insulin secretion. Duration of hypoglycaemic action can last up to 24h.
How to treat glyburide ingestion?
-Dextrose, oral okay if only mild symptoms. Try to avoid repeated boluses or infusion since can also increase insulin excretion. -Octreotide (somatostatin analog) inhibits insulin release
What are contraindications to ketamine?
<3 months old, schizophrenia, conditions where increased BP are hazardous, ie: glaucoma hypersensitivity or allergy
How to calculate ETT size?
uncuffed: 4 + (age/4) cuffed: 3.5 + (age/4)
What toxidrome does a gravol ingestion cause?
Anticholinergic syndrome
Name three meds for reducing blood pressure in a HTN emergency
labetalol sodium nitroprusside nicardipine
What are the three tenets of informed consent? (CPS)
1) appropriate information 2) decision-making capacity 3) voluntariness
What finding can help identify serotonin syndrome?
hyperreflexia
What are management options for serotonin syndrome?
Discontinue offending agent Benzodiazepines in mild cases Intubation, sedation, and paralysis in patients with severe manifestations Consider cyproheptadine
What are the features on CT of an epidural bleed
elliptical
What are the features on CT of a subdural bleed?
crescentic, follows contour of brain
What are characteristic features of Reye syndrome?
vomiting, hepatic dysfunction, confusion, seizures, coma (increased ICP!) - especially with influenza A and varicella - aspirin ingestion
What are features of lightning injury?
cutaneous feathering CVS: cardiac arrest, HTN, PVCs, Vfib CNS: cerebral edema, hemorrhage, seizures, mood changes rhabdomyolysis myoglobinuria
Perinatal acquisition of perineal warts can appear up until what age?
3 YEARS
Which bite wounds should get antibiotics?
antibiotics should be administered to all victims of human bites all but the most trivial of dog, cat, and rat bite injuries, regardless of whether there is evidence of infection.
If you have a clean and minor wound with <3 doses of Tdap or uncertain, what do you do?
Give vaccine
If you have a big wound with <3 doses or Tdap or uncertain, what do you do?
Give vaccine and TIG
If you have received at least 3 doses of Tdap and have a big wound, what do you do?
If last tetanus was not within 5 years, give booster.
If you have received at least 3 doses of Tdap and have a clean minor wound, what do you do?
Only give booster if >10 years since last.
What should you think of with the following history? vesicles with sun exposure and hypopigmented flat scars with mild trauma
Porphyria cutanea tarda or pseudo-porphyria secondary to Naproxen
Name side effects of Risperdal
Increased appetite Weight gain Elevated blood sugar secondary to insulin resistance Dyslipidemia (high TG, low HDL) Blood pressure changes Electrocardiogram (EKG) changes, such as prolongation of QTc Fatigue and drowsiness Dizziness Drooling Liver function abnormalities (AST.ALT) Blood dyscrasias Increase in prolactin (of unknown clinical significance) Less common, but serious, side effects include dystonic reactions, tardive dyskinesia, akathisia
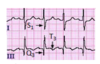
S1Q3T3
signs of pulmonary embolus


