Acquired Macular Disease Flashcards
Age-related macular hole ( FTMH)
- Who are prone? Male or Female?
- Age?
- How do they present with?
- Usually female
- In 60s or 70s
- Present with
- severe impairment of central vision
- asymptomatic deterioration, first noticed when the other eye is closed
Age-related macular hole
Pathogenesis ? What structures involved?
Photoreceptors are displaced due to centrifugal force, probably c/b abnormal attachment of the vitreous and fovea
Traction occurs pulling anterior and posteriorly
Age-related macular hole
Stages?
Causes several stages
- a. Impending
b. Occult - Early
- Established
- Greater than 400μm
Macular hole
stages Stage 1a - Impending
Characteristics?
(3)
Characterized by
- flattening of the umbo
- yellow foveolar spot
- loss of the foveolar reflex.
Rarely seen clinically
Usually detected in a patient with a FTMH in the other eye
Macular hole – stages Stage 1b - Occult
- Vision defect?
- What do you see around fovea?
- Will it resolve?
- Patient c/o mild decrease in VA or metamorphopsia
- Yellow ring seen around the fovea
- About 50% of stage 1 holes resolve following spontaneous separation of the vitreous and fovea

Macular hole – stages Stage 2 – Early FTMH
Size of defect area?
How long does it take to progress from stage 1 to 2?
Defect area is less than 400μm in diameter
Can take 1-2 weeks to several months to progress from stage 1 to 2

Macular hole – stages Stage 3 – Established FTMH
Size of defect? Thickness?
Stage 3 – Established FTMH
Full thickness defect more than 400μm in diameter

Macular hole – stages Stage 4 – Greater than 400μm
Size of defect?
Appreance?
Effect on VA?
- Round defect more than 400μm in diameter
- Yellowish deposits within the round defect
- VA eventually stabilises as the hole reaches its maximum size

Macular hole - diagnosis
- Name of simple test diagnosing macular hole? ( Gross diagnosis)
- Procedure
- How patients with macular hole report?

- Watzke-Allen test
- Projecting a narrow slit beam over the centre of the hole both vertically and horizontally
- Patient with a macular hole will report that the beam is thinned or broken
Patients with a pseudohole or cyst see a beam of uniform thickness which is distorted or bent
Macular hole - diagnosis
What is the most useful diagnosis tool?
OCT is useful to diagnose and determine the stage of macular holes

Is FFA useful in diagnosis of Macular hole? Why?
Macular hole - diagnosis
- FFA
- Not so useful
- Shows hyperfluorescence which looks similar to:
–Cysts
–Pseudo-holes

Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR)
- Aka?
- Definition?
- Pathogenesis?
- Affect one or both eyes?
- Nature of this condition?
- Who does it mainly affect?
- Aggravated ( worsen) by?
- AKA: central serous chorioretinopathy
- Sporadic ( infrequent, periodic) disorder of outer blood-retina barrier
- Sensory retina around the macula becomes detached
- Usually affects one eye only
- Self-limiting
- Mainly affects young/middle-aged men with “type A personality”
- Aggravated by
–Emotional stress
–Hypertension
–Alcohol
–Reflux
CSR - signs
Round/oval detachment of sensory retina at the macula
OCT shows elevation of the retinal layer from the RPE
Separated by optically empty zone

CSR - course
Short - Prolonged - Chronic

CYSTOID MACULAR OEDEMA
- Caused by?
- Any short term effect?
- If long standing, can cause what?
- Damange reversible?
- C/b accumulation of fluid in the outer plexiform and inner nuclear layers of the retina
Fluid-filled cysts form - No short-term effects
- If long-standing, can lead to large cavities at the fovea
- Irreversible damage to central vision

CMO - presentation
- Patient presentation depends on ?
- VA affected?
- Patient c/o?
- Patient presentation depends on aetiology
- VA could be affected by a pre-existing condition which has caused the CMO
- If no pre-existing disease:
patient c/o:
- impaired central vision &
- positive central scotoma

CMO – Slit-lamp signs ?
Fovea?
Retina?
On slit-lamp examination you see:
- loss of the foveal depression
- thickening of the retina
- multiple cysts

CMO – OCT signs
Retina?
Macula?
Fovea?
Hyporeflective spaces within the retina
Overall macular thickening
Loss of foveal depression

CMO – FFA signs
- Arteriovenous phase?
- Late phase?
-
Arteriovenous phase:
Small hyperfluorescent spots
Caused by early leakage -
Late phase:
‘flower-petal’ pattern of hyperfluorescence
Caused by accumulation of dye within cystic spaces

CMO Causes

High myopia
•What’s the definition of high myopia?
6.00D or more
Axial length greater than 26mm
Excessive elongation- changes to everything
Pathological myopia: elongating and stretching soccer ball into a football => Everything is afffected
High Myopia
Pathological or degenerative myopia is characterized by ?
Secondary changes to which structures?
Pathological or degenerative myopia is characterized by:
progressive and excessive anteroposterior elongation of the globe
- Associated with secondary changes involving the: sclera, retina, choroid and optic nerve head
Degenerative myopia

Tigroid appearance ( Tiger-stripe shape)
Brecks in Bruch’s membrane
Lacquer cracks
Due to diffuse attenuation of RPE with visibility of large choroidal vessels
Sign?

Degenerative Myopia
Focal choroidal atrophy and titled disc
Optic nerve more rounded/ovally
white= sclera
Black= retinal pigment
Visibility of larger choroidal vessles and evetually sclera
Sign?

Ruptures in RPE Brunch’s membrane
Choriocapillaris complex
Fine, irregular yellow line branching & corssing @ Posterior pole
Lacquer crack ?
Sign?

Choroidal neovascularisation
Atrophy
Lacquer cracks
Sign?

Subretinal coin haemorrhage
Sign?

Degenerative myopia
Fuch’s spot
Degenerative myopia
Any impact on visual acuity
Impede on macula
If out in periphery - not going to complain as much

Angioid streaks
- What is it?
- Cause?
- Apperance?
- Location?
- Pattern? in relation to disc?
Angioid streaks
- Crack-like ruptures in Bruch’s membrane
- Occurs as a result of thickened, calcified and abnormally brittle collagenous and elastic portion of Bruch membrane
- Linear, grey/dark red lesions with irregular edges
- Lie beneath normal retinal vessels
- Communicate in a ring-like way around the disc and radiate outwards

Angioid streaks
FFA sign?
Cause by?
Angioid streaks
•Hyperflurescence is seen on FFA
- C/b window defects in the RPE
- FFA is mostly used to detect CNV
Angioid streaks
Sign on fundus?

•Optic disc drusen are commonly found
•Choroidal rupture following minor ocular trauma causes subretinal haemorrhage
–Eyes with angioid streaks are very fragile!

Solar retinopathy
- What is it?
- Effect on VA?
Solar retinopathy
- Retinal injury caused by photochemical effects of solar radiation by directly or indirectly viewing the sun (eclipse retinopathy)
- Patient presents within 1-4 hours of solar exposure with
–unilateral or bilateral central VA ↓
–small central scotoma
Solar retinopathy
Sign on fundus?
Resolve?
Solar retinopathy
- Fundus shows
Small yellow or red foveolar spot
Fades within a few weeks
Spot is replaced by a sharply defined foveolar defect with irregular borders or a lamellar hole
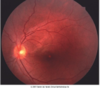
Sign?

Phototoxic maculopathy
Yellow spot on macula
Burned a hole in both fovea
OCT below= resolve !

Case study
62 y/o female
3/52 history of decreased VA
VA RE = 6/18

Stage 1B macular hole
Fundus shows cystic appearance at the fovea
OCT shows elevation at the foveal level
Remaining retina bridges over the fovea

Case study
69 y/o female
C/o decreased VA worse in the RE, for past few months
VA RE = 6/60
Diagnosis?

Full thickness macular hole
Full-thickness hole confirmed on OCT
•Loss of retinal tissue at the fovea

Case study
42 y/o male
C/o progressive central vision loss RE over past 1/12
Diagnosis?

Central Serous Retinopathy
Dilated fundus exam shows diminished foveal reflex
FFA shows pinpoint leak inferior to the fovea

Patient with psuedo-phakic LE
•VA LE = 6/9

Drusen
Fundus exam shows drusen
FFA shows late staining of the areas of drusen
OCT shows altered foveal contour

45 y/o female
Referred for evaluation central visual distortion in RE for 6/12
VA RE = 6/7.5
Diagnosis?

Angioid Streaks
OCT shows normal neurosensory retina and normal foveal contour
Choroid on the RHS shows irregularity

60 y/o female
C/o decreased VA RE 1/12 post cataract Sx & IOL insertion
VA RE = 6/30
Diagnosis?

CMO



