Acquired Brain Injury EXAM 1 Flashcards
Traumatically induced structural injury and/or phsyiologic disruption of brain function as a result of an external force that is indicated by new onset or worsening of at least one of the following clinical signs immediately following the event
- any pd of loss of dec’d lvls of consiousness
- any loss of memory for events immediately BEFORE or AFTER injury
- any alteration in mental state @ the time of the injury
- confusion, disorientation, slow thinking, etc..
-
Neuro. deficits that may/may not be transient
- weakness, LOB, change in vision, praxis, paresis/plegia, sensory loss, aphasia
- Intracranial lesion
Epidemiology of TBI
- CDC–> 1.7 mill people/yr
- TBI is a contributing factor to a third (30.5%) of all injury related deaths in the US
- avg age onset is 30
- HIGHEST incidence b/w 15-24
-
ADULTS
-
MOST FREQ–> MVA
- falls
- trauma
-
MOST FREQ–> MVA
-
CHILDREN
- MOST FREQ–> abuse

Types of TBI:
- Concussion
- Open/Penetrating Injury
- Closed
Types of TBI: Concussion
- Transient (1 day) deficit
- evidenced LT consequences
TBI: Open/Penetrating Injury
- Dura is compromised
- deficits are focal
- risk of infection
TBI: Closed
- diffuse (widespread) deficits
- Dura mater: structural support w/ sharp edges
Coup-Contrecoup
“Impact”
MVA–Whiplash
Coup is the head/brain going FORWARD injury
Contrecoup is the head/brain going BACKWARD injury
See pic!!!

Skull Fxs are HIGHLY correlated w/:
ICHs
Skull Fx: Two types
- Non-Displaced (linear)
- Depressed/Displaced
* depressed==caved in
* displaced==shards of bone into brain
- Depressed/Displaced
Primary Brain Damage (3)
- Focal
- Diffuse
- Assoc’d Hemorrhage
Focal Primary Brain damage has a _______ site
Specific site
Focal Primary brain damage caused by __________ or _______ @ impact
Distortion or laceration
Focal primary brain damage can be the impact of the ______ on ______
impact of brain on the dura/bone
Diffuse Primary Brain damage ===>
Axonal shearing
remember diffuse==widespread
Primary brain damage can have this assoc’d w/ it
hemorrhage
ICH associated w/ TBI can be in 3 places:
- Epidural–outside dura
- Subdural–b/w dura and brain
- Intracerebral –in deep brain
CARDINAL sign of Epidural ICH
Concussion
Epidural ICH
- skull fx assoc’d w/ superficial vessel laceration
- Lucid interval:
- Concussion–> lucidity–> decline
Subdural ICH
- Bleeding from vessels b/w dura and brain
- Accel/Decel injuries
- HIGH mortality rate******
Intracerebral ICHs
- Contusion deep brain
- Coup/Contrecoup injury
Diffuse Axonal Injury
What is going on here???
Axonal Shearing
see pic!!!

MOST COMMON STRUCTURAL ABNORMALITY IN TBI
Axonal shearing from Diffuse Axonal Injury
Axonal shearing deficits?
minor–> fatal
Axonal shearing and skull fx’s?
Can occur in the absence of Skull fx
Secondary Brain Damage: 2 Subtypes
- System Brain Damage
- Intracranial Brain Damage
Secondary Brain Damage: Systemic
-
arterial hypoxemia
- airway obstruction/trauma
- brain loses ability to autoreg. vasodilation
- DEC cerebral perfusion==hypoxia
Secondary Brain Damage: Intracranial
- Cytotoxic edema
- inflammation
- Vasogenic edema
- inflammation
- Inc’d ICP
- from 5-10 mmHg
Brain shift + Herniation is considered…..
NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY!
Brain shift and herniation: 4 types
- Uncal herniation
- Central herniation
What is an Uncal herniation ?
Temporal lobe gets pushed DOWNward thru temporal notch compressing the BS
What is a Central herniation?
SAME as Uncal herniation
but diencephalon @ risk
What is a Subfalcial herniation?
*remember Falx cerebri
Expanding frontal lobe lesion
What is a Cerebellar herniation ?
Cerebellar edema pushes the cerebellar tonsils DOWNward thru foramen magnum
BS compressed
Associated Ortho. cond’s w/ TBI and skull fx
- Occult SCI
- SCI and TBI common together
- Temporal fx
- Myositis ossificans/HO
- contractures
- hypERtonia common
- trauma
Blast Induced Traumatic Brain Injury
See table
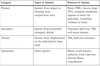
Blast induced TBI: Primary
Types of injuries
injuries from impact or shearing from overpressure wave
Blast induced TBI: Primary
Patterns of Injuries
Brain (TBI), viscera, lungs (PE), tymp. memb. rupture or inner ear patho (vestibular, cochlear, BOTH)
Blast Induced TBI: Secondary
Types of injuries
Injuries from projectiles
shrapnel, debris
Blast Induced TBI: Secondary
Patterns of Injuries
Fx’s, limb loss, TBI, soft-tissue injuries
Blast Induced TBI: Tertiary
Types of Injuries
Injuries from displacement of the indiv. by blast wind
Blast induced TBI: Tertiary
Patterns of injury
TBI, limb loss, fx’s
Blast induced TBI: Quaternary
types of injuries
other types of injuries
Blast induced TBI: Quaternary
patterns of injury
burns, crush inj’s, asphyxia, toxin exposure, chronic illness exacerbation
What are the lvls of Alertness?
- Normal consciousness
- coma
- stupor
- obtundity
- delirium
alterness: normal arousal/cognition
Norm consciousness
alterness: unresponsive to stimuli
coma
alertness: arousal only by vigorous stimuli
Stupor
alertness: slow responses to stimuli
delayed resp.
Obtundity
alertness: misinterpretation of stimuli
Delirium
What are 3 measures used to measure Arousal and Cognition?
- Orientation
- Glasgow Coma Scale
- Rancho los Amigos Scale of Cognitive Functioning
Testing Orientation
A+O *3
what is this?
- A= Alert
- O= Orientation
- *3
- Person
- Place
- Time
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale
GCS
- Done in field AND @ 24hrs
- Predictive, NOT localizing
THREE components to the GCS
- eye opening
- Best motor response
- Best verbal response
GCS grading
3-15
GCS: 8 or LESS ===>
Coma
*NOTE: score of 8 or LESS correlates w/ need for LT care
GCS: Eye opening scale
- 4= spont. eye opening
- 3= open to command
- 2= open to painful stimuli
- sternal rub
- nail bed press.
- 1= No response
GCS: Best MOTOR response
- 6= obeys command
- 5= localizes
- 4= w/draws
- 3= Decorticate (flex) posturing
- 2= Decerebrate (ext, all the e’s) posturing
- WORSE vs. decorticate
- 1= No response
GCS: Best VERBAL Response
- 5= Oriented
- 4= responsive BUT disoriented
- 3= inappropriate
- 2= Moans
- 1= No response
GCS score range
3-15
*8 or LESS defines coma
*8 or LESS correlates w/ need for LT care
Rancho Los Amigos Scale for Cognitive Functioning
*Listed out*
- I= No response
- coma lvl
- II= Genarlized response
- coma lvl
- III= Localized response
- coma lvl
- IV= Confused- agitated
- V= Confused- inappropriate
- VI= Confused- appropriate
- VII= Automatic Appropriate
- VIII= Puroseful Appropriate
Rancho lvl 1
No response
*coma lvl
indiv. in deep coma and does NOT respond to ANY outside stim. (verbal, touch)
Rancho lvl 2
generalized response
*coma lvl
indiv. sleeps most of the time, awake for only brief pds.
responses and body mvmts are reflexive and non-purposeful
Rancho lvl 3
Localized response
*coma lvl
indiv. is alert for more than brief pds
he/she reacts to commands incosistently, BUT resp’s are specific to the type of stim. (touch may produce a w/drawal)
Rancho lvl 4
Confused-Agitated
indiv’s behavior shows marked confusion and agitation as awareness inc’s
behavior may be aggressive and inappropriate, and speech incoherent
individual is NOT able to participate in Tx due to lack of attention, and cannot perform ADLs (brush teeth, eat)
Rancho lvl 5
Confused- Inappropriate
indiv. shows INconsistent ability to follow commands, but LT memory is returning
well-known skills such as eating return, however, complex tasks are difficult as are NEW skills and concentration
Rancho lvl 6
Confused-Appropriate
indiv. begins demonstrating goal-directed behavior w/ assistance
individual is now aware of their diff’s and familiar people
retention of re-learned skills is improved, and can be used in other situations
Rancho lvl 7
Automatic Appropriate
indiv. performs ADLs w/ more ease and is able to learn NEW skills
noticeable impairment still exists in ST memory and problem solving ability
Rancho lvl 8
Purposeful Appropriate
indiv is able to function w/in the community even w/ continued impairment in cognitive ability, and social and emotional ability
Frontal Lobe Syndrome
*Think of what happened to Phineas Gage!!!
- Exacerbation of premorbid behaviors
- Emotional lability
- unstable mood
- Disinhibition
- Loss of executive function
- Highly distractible
- Confabulation***
- making up stories
- memory gaps
Memory Changes: Amnesia
3 types
- Retrograde
- Anterograde
- Post-traumatic
Retrograde Amnesia:
Think “before”
- Loss/disturbance memories for events that occured before an event
-
EX:
- after person suffers brain damage MVA, he/she may be unable to remember events that occured before the BI, such as being in the car
Anterograde Amnesia:
Think “after”
- Loss/disturbance memory events that occur after an event
- EX: after person suffers brain damage from head injury, he/she may be unable to remember events that occur AFTER BI, such as being in hospital
Post-traumatic Amnesia
think “forming memories”
- inability to form consistent day-day memories
- often actively confused/disoriented
Concussion aka
Silent Epidemic
Concussions—-Silent Epidemic
Some data…
- CDC–> concussions resulting in LOC acct for 8-19% concussions
- w/ 1.6 to 3.8 mill concussions occurring ea. yr
- only 1/2 recognized/reported
- NOTE: # of people w/ TBI not seen in ED or receive no care is unknown
FACTS: Concussion
- Concussions per every 100,000 games and/or practice collegiate lvl:
- Football-27
- Ice hockey-25
- Men’s soccer- 25
- Women’s soccer- 24
- Wrestling- 20
- Women’s basketball- 15
- Men’s basketball- 12
What about helmets
*concussion
DO NOT protect from accel/decel forces
ONLY FOCAL INJURY (or the traumatic initial blow) NOT the coup/contrecoup
S/S Concussion
Thinking/Remembering
Physical
Emotion/Mood
Sleep
***SEE PIC

S/S concussion: Thinking/Remembering
- diff thinking clearly
- feel slowed down
- diff concentrating
- diff remembering new info
S/S concussion: Physical
- HA–fuzzy/blurry vision
- Nausea or vomiting early on, dizziness
- sensitive to noise/light—balance probs
- tired, no energy
S/S concussion: Emo/Mood
- irritable
- sad
- MORE emo
- nervous/anxious
S/S concussion: Sleep
- sleep more than usual
- sleep less than usual
- trouble falling asleep
IMMEDIATE signs concussion
w/in secs to mins***
*I.S.G.D.E.M.A
- Impaired attention
- vacant stare, delayed resp., inability to focus
- Slurred or incoherent speech
- Gross incoordination
- Disorientation
- Emotional rxns out of proportion
- Memory deficits
- Any loss of consciousness
LATER signs of concussion
*w/in hrs to days
- persistent HA 71%
- dizziness/vertigo 55%
- poor attn and concentration 57%
- memory dysf 43%
- nausea/vomiting
- fatigue easily 50%
- irritability
- intolerance bright lights 47%
- intolerance loud noises
- anxiety/depress.
- sleep disturbances
Concussion aka
“Bell Ringer”
“Got your bell rung”
Bell Ringer facts :
- Study showed 64 high school football players w/ concussions “resolving” w/in 15mins by sideline tests
- avg time for full recovery by neurocog. testing is 7 days
- IF asymptomatic by 5mins returned to neurocog. baseline by day 4
How would you define Post-concussive syndrome from minor head trauma?
NO skull fx OR ICH
unconscious for <2 hours
Post-concussive syndrome from minor head trauma S/S
- persistent HAs 25%
- anxiety 19%
- insomnia 15%
- non-specific dizziness 14%
- Others
- fatigue, HA, poor concentration, memory disorder, irritability, spatial disorientation
Post-concussive Vestibular dysf.
*PT wheelhouse!!!
- s/s include:
- vertigo
- dizziness
- imbalance
- dizziness or imbalance 2* to mild TBI ranges 24%-83%
- vestib s/s can last >6 months
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
what about it????
Controversy b/w this and having ALS
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
CTE
What did they find w/ this and ALS?
- Neuropath. study of athletes (12) w/ mult. concussions
- 2 dx’d w/ ALS
- neuropath studies demonstrate CTE
- abnormal tau PRO ID’d
- 3 athletes w/ CTE ALSO developed progressive motor neuron disease w/ profound weakness, atrophy, spasticity, and fasciculations several yrs BEFORE death


