9/10 - Chemistry of Anti-HT's Flashcards
Selective B1-Adrenergic Antagonist
Features
PARA substituent = B1 Selective
3A-2B-E-M
Atenolol + Acebutolol + Alprenolol
Betaxolol + Bisoprolol
Esmolol
METOPROLOL

What Drug & What Class?

VERAPAMIL
Calcium Channel Blocker
PhenylAlkylAmine = PAA

What Drug?

CAPTOPRIL
look at the:
SULFA GROUP
essential for chelating the ZINC ion of the enzyme
- *Lead Compound for ARBs**
- *ImidazoleAcetic Acid = Lead Compound**
Correlation with AT2:
Tyr 4
PHENYL RING
mimics the:
Tyr 4
side chain of AT2

Diltiazem
Drug Class & PK/PD
BenzoThiazepine = BTZ
Calcium Channel Blocker
- *Single (+) Enantiomer**
- *Fast Onset** due to HIGH LIPID Solubility
Extensive Metabolism into ACTIVE:
DaAcetyl-Diltiazem

What Drug?

AZILSARTAN MEDOXOMIL
ProDrug –> completely metabolized @ Intestinal Wall
- *Tetrazole Ring** –> REPLACED by a OXO-OXADIAZOLE RING
- LESS ACIDIC*
better control of 24 hour SBP than other ARB’s
Better AT1 Binding
&
DISSOCIATES more SLOWLY
vs other ARBS

What is normally on the
RING?
&
What site does it bind to?

DiCarboxylate-Containing ACE-Inhibitors
Ring:
CarboCyclic AA** –> **S2’ Site
needed for the terminal peptide residue
VARIES for each ACE-I
Cyclic + -COOH

Which B-Blockers have
INTRINSIC SYMPATHOMIMETIC ACTIVITY
(ISA)?
What FEATURE do we look for?
ISA = C-A-PP
Carteolol - Acebutolol - Pindolol - Penbutolol
- *NH_ or _OH** @ Meta/Para of Phenyl Ring
- via metabolic biotransformation*
allowing them to:
Partially Stimulate the B-Receptor

What Drug & Class?

DILTIAZEM
Calcium Channel Blocker
BTZ** = **BenzoThiAzePine
Benzo = Benzyne
Thio = Sulfur
Aza = Nitrogen
Pine = 7 membered ring

Verapamil
Metabolism

More Active S (-) Isomer –> rapidly N-demethylated by
CYP3A4
in intestine & liver into:
NORVERAPAMIL (~20% potency of Verapamil)
Verapamil is also a substrate of:
P-GLYCOPROTEIN EFFLUX TRANSPORTER
which will drastically
INCREASE Intestinal Absorption or other P-gp substrates
like digoxin, in a dose-dependent manner
SAR of 1,4-DHPs
What is preferred on the X group?

BULKY GROUP in Ortho / Meta
in order to
LOCK conformation of the 1,4-DHP so that:
2 RINGS are PERPENDICULAR to one another
X:
Nifedipine / Nosoldipine = 2-NO2
Amlodipine = 2-Cl

CCB’s
Mechanism of Action
with the exception of BEPRIDIL:
CCBs are selective for:
L-Type High-Voltage-Activated Calcium Channels
Most effective when membrane depolarization is:
Longer / More Intense / More Frequent
USE-DEPENDENCY
indicate that CCBs prefer to interact with theire receptors in the
CA channel in either the states of either:
OPEN**or**INACTIVE
- *What drugs are**
- *Centrally Acting a2-agonists?**
L-MethylDopa** + **Clonidine** + **Guanfacine** + **Guanabenz
Clonidine
metabolized in liver –> glucuronide/sulfate conjugates
Guanfacine
more selective for a2 receptor > clonidine or guanabenz
liver metabolized –> glucoronide/sulfate/mercapturic acid
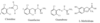
1,4-DHP SAR
R6 or C6
changes

- *R6** can tolerate
- *LARGER SUBSTITUENTS**
Since Amlodipine = Enhanced Potency

SARs of ARBs
Eprosartan
ACIDIC GROUP
needed to mimic the Tyr4 Phenol
CARBOXYLATE GROUP** @ **ORTHO POSITION
for optimal activity
THIENYL METHYL SIDE CHAIN
provided a better mimic of Phe 8

SAR of CAPTOPRIL
Methyl Group Stereoconfiguration
important –> mimics the L-Amino Acid
SULFA GROUP
essential for chelating the ZINC ion
but also produced:
SKIN RASH + TASTE DISTURBANCE

What Drug?

CANDESARTAN CILEXETIL
&
Olmesartan Medoxomil
both are:
rapidly & completely metabolizeed @ INTESTINAL WALL
= PRODRUG
to increase oral bioavailability
Oxygen-Carbon-Oxygen = Good Leaving Group

ACE-Independent Pathways
Avoid Renin & ACE
Cathepsin G
Trypsin
Kallikrein
Chymase

Discovery of PROPRANOLOL

Non-Selective B-Adrenergic Antagonist
Isoproternol
replaced the catechol –> CHLORINE = Sympatholytic Agent (DCI)
Pronethalol (R-isomer)
ELONGATION of ETHYLAMINE by an OXYMETHYLENE BRIDGE
& placement @ C1 POSITION of the Naphthyl Group
- *PROPRANOLOL**
- *S- Isomer Active**

Newer 1,4-DHPs
R vs S

Replacement @ C3 or C5
Ester –> NO2
Produces a pair of STEREOISOMERS with Opposite actions
R (-)- PN202-791 blocks the calcium channel
R - Block
S (+)- PN202-791 activates the calcium channel
by stabilizing the channel in the open state during depolarization
potential use for the S (+) isomer for Congestive Heart Failure
Lead Compound for ARBs
ImidazoleAcetic Acid
Correlation with AT2:
His 6
IMIDAZOLE RING
overlaps with the:
His 6
side chain

Diltiazem = BTZ
Where does it enter?
&
Binding Site?
1,4-DHPs & Diltiazem enter from the
EXTRACELLULAR SIDE
Binding of Diltiazem or 1,4-DHP in the ALLOSTERIC interacting site:
INHIBIT’s the binding of VERAPAMIL
Diltiazem + 1,4-DHPs = POSITIVE ALLOSTERIC EFFECTORS
enhance the binding of each other
1,4-DHP
Essential SAR’s
- *Ester Groups_ @ _C3_ & _C5**
- replacement with another group –> ENANTIOMERIC isomers*
O** or **M-substituted Phenyl Ring** @ **C4 Position
provides optimal CCB activity = 90*
Size of Substituent X is important
sufficient BULK –> to LOCK conformation of 1,4-DHP
so that
2 Rings are PERPENDICULAR to ONE ANOTHER

What Drug & Class?

METOPROLOL
Selective B1-Adrenergic Antagonist
Para-Substituent








































