7A Flashcards
(23 cards)
what is monohybrid inheritance?
inheritance of a characteristic controlled by a single gene
monohybrid crosses
shows the likelihood of the different alleles of that gene being inherited by their offspring
phenotypic ratios
the phenotypic ratio is the ratio of different phenotypes in the offspring - although sometimes you won’t get the predicted ratio, as the alleles could be codominant or sex-linked
what is a Punnett square?
a way of showing a genetic diagram
what is co-dominance?
both alleles are expressed in their phenotype as neither alleles are recessive (E.g. sickle cell anaemia - a mutation in the haemoglobin gene)
monohybrid cross of two heterozygous parents, what ratio do you expect?
1 : 2 : 1
Dihybrid
the inheritance of two genes simultaneously (E.g. flowers colour and leaf shape)
multiple allele crosses
multiple alleles crossed, E.g. blood types O, A, B, AB - crossing a parent with alleles A O, and a parent with alleles B O, gives a expected ratio of 1 : 1 : 1 : 1
with heterozygous Dihybrid crosses, the ratio you expect is
9 : 3 : 3 : 1
sex linked characteristics
alleles coding for certain characteristics are located on the sex chromosome
how are men more likely to inherit a sex linked disease? E.g. colour blindness, haemophilia
because the Y chromosome is smaller than the X, it only takes one allele to code for a characteristic, unlike women who need either two recessive alleles (or a dominant) men only need one recessive allele. Y-linked disorders do exist but are less common
when a male without colourblindness and a female carrier have offspring, what do you expect?
only the males in the offspring will be at risk, as the females won’t have the other allele (From their dad) to make them colour blind, they would only be a carrier
linkage of autosomal genes
Genes on the same autosome are said to be linked as they don’t separate during independent segregation (Meiosis 1). Only when crossing over occurs they can be split. The closer the genes are together on the autosome, the more likely they are said to be linked as its less likely crossing over will split them up
linkage of autosomal gene ratio
phenotypic ratio is not like the dihybrid cross (9:3:3:1), but more like the monohybrid cross ratio (3:1) as they’re inherited together, meaning they’re more likely to inherit their parents heterozygous genotype and phenotype
linkage of autosomal gene example: two parents, one homozygous dominant for red eyes and wing length (NNRR) and one homozygous recessive for vestigial wing and purple eyes (nnrr) what offspring and ratio do you expect?
offspring were all heterozygous for normal wing and red eyes (NnRr)
linkage of autosomal gene example 2: the heterozygous parent for normal wing and red eyes (NnRr) was crossed with a homozygous recessive vestigial wing with purple eyes (nnrr) what is the expected ratio of offspring?
1 : 1 : 1 : 1 4 Normal wings, red eyes 4 normal wings, purple eyes 4 vestigial wings, red eyes 4 vestigial wings, purple eyes
what is epistasis?
many different allele can control the same characteristic. this is because the allele of one gene masks/blocks the expression of another allele
what is chi squared?
chi squared is a statistical test used to see if the results of an experiment support a theory
what always is the null hypothesis for a chi squared experiment?
There is no significant difference between the observed and expected results
what is the chi squared formula?
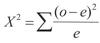
What is a critical value?
The critical value compares the X2 value with the critical values to determine the properbility that the difference between the expected and observed is due to chance
if the chi squared value is larger than the critical value, what do you do?
reject the null hypothesis
if the chi squared value is lower than the critical value, what do you do?
fail to reject (Accept) the null hypothesis


