5 - Inflammatory Dermatoses Flashcards
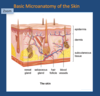
Outline the basic microanatomy of the skin
Epidermis
(between epi and dermis is the basement membrane)
Dermis
- hair follicles
- sebaceous glands
- sweat glands
- collagen
- fibroblasts
- immune cells
- hair follicle + sebaceous gland + erector muscle = pilosebaceous unit
Fat
Fascia
Muscle
Outline the basics of skin histology
In hairy skin, there are hair follicles
Sebaceous glands make sebum which lubricates the hair and contains chemicals which suppress growth of bacteria and fungi
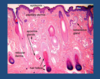
What consititutes the epidermis?
Keratinocytes sit on the basement membrane
- proliferate and move up through epidermis
- differentiate
- make keratin which forms granules
- lose their nuclei
- dead cells at the top
- form stratum corneum (barrier function of skin)
Langherhans Cells = AP cells
Melanocytes = make melanin
Merkel Cells = sensation

What are keratinocytes?
Form the stratum corneum
- dead cells in top layer

Outline the skin histology of the epidermis
Melanocytes are dark ones at bottom and look vaculated
Top-layer = weave-like structure = stratum corneum

Outline the structure of the stratum corneum
Very important for barrier function of the skin
Defects lead to eczema
Filagrin gene mutation common in eczema patients
- skin is genetically predisposed to be dry
Blocks = keratinocytes
Between cells is made up of lipids and proteins
- one of the proteins is called filagrin

What is atopy?
ATOPY
Tendency to develop hypersensitivity
Give examples of atopic diseases
Eczema
- Atopic eczema is:
- common
- relapsing
- remitting
Asthma
Hayfever
What is The Atopic March?
THE ATOPIC MARCH
People who have atopic diseases tend to develop eczema first early in life (peak at around 2 years of age)
Then they develop food allergies
Then they develop asthma
They then develop rhinitis (hayfever)
What is happening is that the eczema and dry skin is causing them to become sensitised to other environmental allergens

What factors lead to atopic eczema?
INTRINSIC FACTORS
- impaired barrier function of skin (could be due to defective filagrin)
- allows for the extrinsic factors
EXTRINSIC FACTORS
- penetration of allergens into the skin
- irritants such as house-dust mite
- taken into skin
- stimulate immune response
- recruitment of inflammatory cells
- IgE produced
- stimualtes mast-cells to degranulate
- inflammation is perpetuated

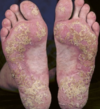
What does this photo show?

Palmar Hyperlinearity
- sign of filagrin gene mutation
- the lines on palms and soles are more prominent and easy to see
- therefore, someone with this sign would be more likely to have eczema than someone else with an itchy rash

What do thes photos show?

Infantile atopic eczema
- acute
- skin is red, raw, weepy and may have blisters
- normally in areas where children rub their skin (e.g. face)
- skin on face is more likely to be sensitised to food allergens
- undefined edges

What is atopic dermatitis?
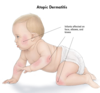
What are the common sites of eczema outbreaks in children and adults?
Sweaty areas predispose to eczema in both children and adults

What does this photo show?

Acute eczema is normally red, weepy and sore
This photo shows chronic eczema
- eczema with lichenification
- lichenification means that the skin markings are much more visible due to lots of scratching of the skin
- lichenification
- erythema
- looks like the skin is becoming thicker
- chronic changes
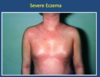
What does this photo show?

Severe Eczema
- erythredermic eczema
- acute eczema (red and weepy) is all over the skin’s surface
- patient is systemically unwell
- should be admitted to hospital
- likely to be staphylococcal infection
- colonises the skin
- perptuates eczema and can also cause infections
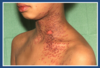
What does this photo show?
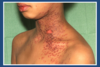
Eczema herpeticum
- HSV infection occuring in eczematous skin
- HSV spreads all over skin’s surface
- blisters breakdown and form ulcers
- patients should be admitted and treated with acyclovir
- if left untreated, could spread in blood and cause herpes encephalitis in the brain
In ecezema, the skin is not performing its barrier function correctly
- predisposed to infection
- staphylococcus aureus
- also, viral infections such as HSV
List the types of eczema
Seborrhoeic
- overgrowth of yeast with eczema
Allergic contact dermatitis
Discoid
Atopic
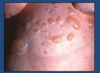
What does this photo show?
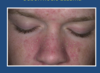
Seborrhoeic Eczema
- different to atopic
- greasy scale with redness
- dandruff when on scalp
- seborrhoeic eczema on other parts of body
- often occurs in naso-labial folds and scalp
Overgrowth of yeast, but can be primary or secondary to the eczema
Not really itchy but more cosmetically a problem