5 - Brainstem Structure and Cranial Nerve Nuclei Flashcards
(36 cards)
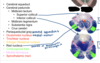
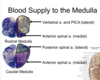
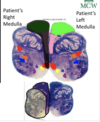
Name each blackened label?


What are the three general areas of the brainstem in a cross-section?
The portion posterior to the ventricular space (blue)
The portion anterior to the ventricular space (green)
Additional structures on the anterior surface (red)
What are the three functions of the brain stem?
Integrative functions
Cranial nerve functions
Conduit functions
Describe the integrative funcitons of the brainstem?
They’re performed by a diffuse nucleus within the core of the brainstem - the reticular formation (yellow) ; this helps to regulate consciousness and contain respiratory and CV centers.

Describe the conduit function of the brainstem?
It serves as a conduit for ascending sensory and descending motor tracts.
What is the motor funciton of the brainstem? What tract does this?
Corticosplinal tract (green) - voluntary movement of limbs

What are the sensory functions of the brainstem? What tracts do this?
Spinothalamic tract (red) - transmits pain and temp information to the brain
Posterior column / Medial Lemniscus (pink) - transmits touch, vibration, pressure, and proprioception to the brain

What are the cranial nerve functions of the brainstem?
Cell bodies of neurons clustered in “nuclei” throughout the brainstem which serve as the origins of motor CNs or as the terminations of sensory CNs.
Describe the developent of the brainstem nuclei?
- NS developes from neural tube
- Neural tube has basal plate (motor) and alar plate (sensory) divided by sulcus limitans
- Brainstem development is similar to spinal cord development
How does the NS develop from the neural tube?
Neural folds come up to make neural crests that eventually meet to form a neural tube that extends.

What are the sensory and motor portions of the spinal cord derived from?
The basal plate (motor) and the alar plate (sensory), which is divided by the sulcus limitans.
Describe the brainstem development?
It’s similar to the development of the spinal cord.
Instead of maintaining the tube-like structure like the sp cd, it opens up and unfolds.
Basal plate stays medial and sensory (alar) plate goes more laterally.
Where are the motor and sensory nuclei each found in the brainstem?
Motor is medial
Sensory sides
Which cranial nerves emerge form the midbrain and above?
Cranial nerves 1-4

What cranial nerve emerges at the mid-pons level?
The trigeminal nerve (V)
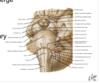
Which cranial nerves exit at the level of the pons?
Cranial nerves 5-8
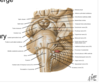
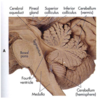
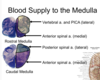
Which cranial nerves exit at the level of the medulla?
Cranial Nerves 9-12.
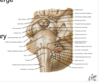
What are cranial nerve nuclei?
Clusters of cell bodies WITHIN the brainstem (bilaterally)
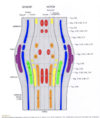
Where would you find the nuclei of somatic motor neurons?
Motor neurons are in the medial portion of brainstem (red portions).

Where would you find nuclei of visceral motor neurons in the brainstem?
Near the medial portion of the brainstem (yellow).
Examples include: edinger-wesphal nucleus, salivatory nucleus, and dorsal motor nucleus of X.

Where would you expect to see visceral sensory, somatic sensory, and special sensory nuclei in the brainstem?
More laterally within the brain stem (green, blue, purple).
Examples include the rostral and caudal nucleus solitarius (gustatory), the trigeminal nuclei, the cochlear nuclei, and the vestibular nuclei.
Which cranial nerve is located within the interpeduncular fossa?
CN III - oculomotor

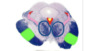
What is located within the midbrain?
Tectum, tegmentum, cerebral aqueduct, CN III, and CN IV

Label the parts of the midbrain