4_EC2 Flashcards
(32 cards)
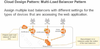
EC2 - Pricing Options
- On-Demand: allow you to pay a fixed rate by the hour (or by the second) with no commitment
-
Reserved Instances: provide you with a capacity reservation, and offer a significant discount on the hourly charge for an instance. 1 Year or 3 Years Terms. It comes with 3 different types:
- Standard RI
- Convertible RI: Change EC2 type
- Scheduled RI: Specify a time schedule for the instances.
-
Spot Instances: enable you to bid whatever price you want for instance capacity, providing for even greater savings if your applications have flexible start and end times
- If you terminate the instance, you pay for the hour
- If AWS terminates the spot instance, you get the hour it was terminated in for free
- Dedicated Hosts: Physical EC2 server dedicated for your use. Dedicated Hosts can help you reduce costs by allowing you to use your existing server-bound software licenses, such as MSDN subscription licenses
EC2 - Pricing Options
- On-Demand: allow you to pay a fixed rate by the hour with no commitment
- Reserved Instances: provide you with a capacity reservation, and offer a significant discount on the hourly charge for an instance. 1 Year or 3 Years Terms.
-
Spot Instances: enable you to bid whatever price you want for instance capacity, providing for even greater savings if your applications have flexible start and end times
- If you terminate the instance, you pay for the hour
- If AWS terminates the spot instance, you get the hour it was terminated in for free
- Dedicated Hosts: Physical EC2 server dedicated for your use. Dedicated Hosts can help you reduce costs by allowing you to use your existing server-bound software licenses, such as MSDN subscription licenses
EC2 - Instance Types
FIGHT DR MC PXZ AU
- F - FPGA
- I - IOPS
- G - Graphics
- H - High Disk Throughput
- T- Cheap general purpose (think T2 micro)
- D - Density
- R - RAM
- M - Main choice for general purpose apps
- C - Compute
- P - Graphics (think Pics)
- X - Extreme memory
- Z - Extreme memory and CPU
- A - Arm-based workload
- U - Bare Metal
EC2 - Instance Types
DR MC GIFT PX
- D for Density
- R for RAM
- M - main choice for general purpose apps
- C for Compute
- G for Graphics
- I for IOPS
- F for FPGA
- T cheap general purpose (think T2 micro)
- P - Graphics (think Pics)
- X - Extreme memory
EC2 - Instance Types

EC2 - Instance Types
EC2 - Launch new instance
- Termination protection is turned off by default, you must turn it on (flag in Instance Details: Enable termination protection)
- On an EBS-backed instance, the default action for the root EBS volume is to be deleted when the instance is terminated (flag in Storage: Delete on Termination)
- EBS root volume of your DEFAULT AMI’s cannot be encrypted. You can use a third party tool to encrypt the root volume or this can be done when creating AMI’s in the AWS console or using the API
- Additional EBS volume can be encrypted

EC2 - Launch new instance
- Termination protection is turned off by default, you must turn it on (flag: Enable termination protection)
- On an EBS-backed instance, the default action for the root EBS volume is to be deleted when the instance is terminated
- EBS root volume of your DEFAULT AMI’s cannot be encrypted. You can use a third party tool to encrypt the root volume or this can be done when creating AMI’s in the AWS console or using the API
- Additional EBS volume can be encrypted
Security Groups
- Security Groups are virtual firewall
- All Inbound Traffic is blocked by default
- All Outbound Traffic is allowed by default
- Changes to Security Groups take effect immediately
- You can have any number of EC2 instances within a security group
- You can have multiple security groups attached to EC2 instances
- Security Groups are STATEFUL
- If you create an inbound traffic rule allowing traffic in, that traffic is automatically allowed back out again
- You cannot block specific IP addresses using Security Groups, instead use Network Access Control Lists
- You can specify allow rules, but not deny rules
Security Groups
- Security Groups are virtual firewall
- All Inbound Traffic is blocked by default
- All Outbout Traffic is allowed by default
- Changes to Security Groups take effect immediately
- You can have any number of EC2 instances within a security group
- You can have multiple security groups attached to EC2 instances
- Security Groups are STATEFUL
- If you create an inbound traffic rule allowing traffic in, that traffic is automatically allowed back out again
- You cannot block specific IP addresses using Security Groups, instead use Network Access Control Lists
- You can specify allow rules, but not deny rules
EBS Consists of:
- General Purpose SSD - GP2 - (Up to 10,000 IOPS)
- Provisioned IOPS SSD - IO1 - (More than 10,000 IOPS)
- HDD, Throughput Optimized - ST1 - frequently accessed workloads
- HDD, Cold - SC1 - less frequently accessed data
- HDD, Magnetic - Standard - cheap, infrequently accessed storage
You cannot mount 1 EBS volume to multiple EC2 instances, instead use EFS.

EBS Consists of:
- General Purpose SSD - GP2 - (Up to 10,000 IOPS)
- Provisioned IOPS SSD - IO1 - (More than 10,000 IOPS)
- HDD, Throughput Optimized - ST1 - frequently accessed workloads
- HDD, Cold - SC1 - less frequently accessed data
- HDD, Magnetic - Standard - cheap, infrequently accessed storage
You cannot mount 1 EBS volume to multiple EC2 instances, instead use EFS.
EC2 - EBS
-
General Purpose SSD (GP2)
- General purpose, balances both price and performance
- Ratio of 3 IOPS per GB with up to 10,000 IOPS and the ability to burst up to 3,000 IOPS for extended periods of time for volumes under 1 GB
-
Provisionned IOPS SSD (IO1)
- Designed for I/O intensive applications such as large relational or NoSQL databases
- Use if you need more than 10,000 IOPS
- Can provision up to 20,000 IOPS per volume
EC2 - EBS
- General Purpose SSD (GP2)
- General purpose, balances both price and performance
- Ratio of 3 IOPS per GB with up to 10,000 IOPS and the ability to burst up to 3,000 IOPS for extended periods of time for volumes under 1 GB
- Provisionned IOPS SSD (IO1)
- Designed for I/O intensive applications such as large relational or NoSQL databases
- Use if you need more than 10,000 IOPS
- Can provision up to 20,000 IOPS per volume
EC2 - EBS
-
Throughput Optimized HDD (ST1)
- Big Data
- Data Warehouse
- Log processing
- Cannot be a boot volume
-
Cold HDD (SC1)
- Lowest cost storage for infrequently accessed workloads
- File server
- Cannot be a boot volume
-
Magnetic (Standard)
- Lowest cost per GB of all EBS volume types that is bootable. Magnetic volumes are ideal for workloads where data is accessed infrequently, and applications where the lowest storage cost is important
EC2 - EBS
- Throughput Optimized HDD (ST1)
- Big Data
- Data Warehouse
- Log processing
- Cannot be a boot volume
- Cold HDD (SC1)
- Lowest cost storage for infrequently accessed workloads
- File server
- Cannot be a boot volume
- Magnetic (Standard)
- Lowest cost per GB of all EBS volume types that is bootable. Magnetic volumes are ideal for workloads where data is accessed infrequently, and applications where the lowest storage cost is important
Volumes and Snapshots
- Volumes exist on EBS
- Volumes = Virtual Hard Disk
- Snapshots of a Volume exists on S3
- Snapshots are point in time copies of Volumes
- Snapshots are incremental, this means that only blocks that have changed since your last snapshot are moved to S3
- You can create AMI’s from both Volumes and Snapshots
- You can change EBS volume sizes on the fly, including changing the size and storage type
- To create a snapshot for Amazon EBS volumes that serve as root devices, you should stop the instance before taking the snapshot (for consistency reason)
- However you can take a snapshot while the instance is running.
Volumes and Snapshots
- Volumes exist on EBS
- Volumes = Virtual Hard Disk
- Snapshots of a Volume exists on S3
- Snapshots are point in time copies of Volumes
- Snapshots are incremental, this means that only blocks that have changed since your last snapshot are moved to S3
EBS Volumes in Region
Amazon EBS volumes are created in a specific AZ and can then be attached to any instances in that same AZ
- To move an EC2 volume from one AZ to another, take a snapshot of it, create an AMI from the snapshot and use the AMI to launch the EC2 instance in a new AZ
- To move an EC2 volume from one regio to another, take a snapshot of it, create an AMI from the snapshot and then copy the AMI from one region to the other. Then use the copied AMI to launch the new EC2 instance in the new region.
EBS Volumes in Region
Amazon EBS volumes are created in a specific AZ and can then be attached to any instances in that same AZ
- To make a volume available outside of the AZ, you can create a snapshot and restore that snapshot to a new volume anywhere in that region
- You can copy snapshots to other regions and then restore them to new volumes there
AMI
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provides pre-configured operation systems such as Linux and Windows.
AMI’s are regional. You can only launch an AMI from the region in which it is stored. However, you can copy AMI’s to other regions using the console, command line or the Amazon EC2 API.
You can choose an AMI from:
- Basic Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provided by AWS
- AWS Marketplace
- Community AMIs
- Create your own AMI
- VM Import/Export
AMI
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provides pre-configured operation systems such as Linux and Windows.
AMI’s are regional. You can only launch an AMI from the region in which it is stored. However, you can copy AMI’s to other regions using the console, command line or the Amazon EC2 API.
You can choose an AMI from:
- Basic Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provided by AWS
- AWS Marketplace
- Community AMIs
- Create your own AMI
- VM Import/Export
You can select your AMI based on:
- Region (see Regions and Availability Zones)
- Operating System
- Architecture (32-bit or 64-bit)
- Launch Permissions
- Storage for the Root Device (Root Device Volume)
- EBS
- Instance Store (EPHEMERAL STORAGE)

Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provides pre-configured operation systems such as
Linux and Windows.
You can select your AMI based on:
- Region (see Regions and Availability Zones)
- Operating System
- Architecture (32-bit or 64-bit)
- Launch Permissions
- Storage for the Root Device (Root Device Volume)
- EBS
- Instance Store (EPHEMERAL STORAGE)
AMI’s are regional. You can only launch an AMI from the region in which it is stored. However, you can copy AMI’s to other regions using the console, command line or the Amazon EC2 API.
EBS vs Instance Store
All AMIs are categorized as either backed by Amazon EBS or backed by instance store
EBS Volumes: Network attached, persistent storage. The root device for an instance launched from the AMI is an Amazon EBS volume created from an Amazon EBS snapshot
Instance Store Volumes: Locally attached instance storage. The root device for an instance launched from the AMI is an instance store volume created from a template stored in Amazon S3

EBS vs Instance Store
All AMIs are categorized as either backed by Amazon EBS or backed by instance store
For EBS Volumes: The root device for an instance launched from the AMI is an Amazon EBS volume created from an Amazon EBS snapshot
For Instance Store Volumes: The root device for an instance launched from the AMI is an instance store volume created from a template stored in Amazon S3
EBS vs Instance Store
- Instance Store Volumes are sometimes called Ephemeral Storage
- Instance Store Volumes cannot be stopped. If the underlying host fails, you will loose your data
- EBS backed instances can be stopped. You will not loose the data on this instance if it is stopped
- You can reboot both, you will not loose your data
- By default, both ROOT volumes will be deleted on termination, however with EBS volumes, you can tell AWS to keep the root device volume (uncheck “Delete on Termination” flag)
EBS vs Instance Store
- Instance Store Volumes are sometimes called Ephemeral Storage
- Instance Store Volumes cannot be stopped. If the underlying host fails, you will loose your data
- EBS backed instances can be stopped. You will not loose the data on this instance if it is stopped
- You can reboot both, you will not loose your data
- By default, both ROOT volumes will be deleted on termination, however with EBS volumes, you can tell AWS to keep the root device volume (uncheck “Delete on Termination” flag)
EBS vs Instance Store
In general, Instance Store volumes are ideal for temporary storage of information that is continually changing, such as buffers, caches, scratch data and other temporary content, or for data that is replicated across a fleet of instances. Unlike EBS volumes, Instance Store cannot be detached or attached to another instance.
EBS vs Instance Store
In general, Instance Store volumes are ideal for temporary storage of information that is continually changing, such as buffers, caches, scratch data and other temporary content, or for data that is replicated across a fleet of instances. Unlike EBS volumes, Instance Store cannot be detached or attached to another instance.
ENI vs. ENA vs. EFA [SAA-C02]
- ENI: For basic networking. Perhaps you need a separate management network to your production network or a separate logging network and you need to do this at low cost. In this scenario use multiple ENIs for each network.
- Enhanced Network: For when you need speeds between 10Gbps and 100Gbps. Anywhere you need reliable high throughput
- Elastic Fabric Adaptor: For when you need to accelerate High Performance Computing (HPC) and machine learning applications or if you need to do an OS by-pass. If you see a scenario question mentioning HPC or ML and asking what network adaptor you want, choose EFA
Encrypted Root Device Volumes - Snapshots
- Snapshots of encrypted volumes are encrypted automatically
- Volumes restored from encrypted snapshots are encrypted automatically
- You can share snapshots, but only if they are unencrypted (the encryption key is tied to your AWS account)
- These snapshots can be shared with other AWS accounts or made public
- You can now encrypt root device volumes upon creation of the EC2 instance.
Snapshots
- Snapshots of encrypted volumes are encrypted automatically
- Volumes restored from encrypted snapshots are encrypted automatically
- You can share snapshots, but only if they are unencrypted (the encryption key is tied to your AWS account)
- These snapshots can be shared with other AWS accounts or made public
- To create a snapshot for Amazon EBS volumes that serve as root devices, you should stop the instance before taking the snapshot
Spot Instances and Spot Fleets [SAA-C02]
- Spot Instances save up to 90% of the cost of On-Demand Instances
- Useful for any type of computing where you dont need persistent storage
- You can block Spot Instances from terminating by using Spot block
- A Spot Fleet is a collection of Spot Instances and, optionally, On-Demand Instances
EC2 - Hibernate [SAA-C02]
- EC2 Hibernate preserves the in-memory RAM on persistent storage (EBS)
- Much faster to boot up because you do not need to reload the operating system
- Instance RAM must be less than 150Gb
- Instance families include C3, C5, C5, M3, M4, M5, R3, R4 and R5
- Available for Windows, Amazon Linux 2 AMI and Ubuntu
- Instances can’t be hibernated for more than 60 days
- Available for On-Demand instances instances and Reserved Instances
CloudWatch
- CloudWatch is used for monitoring performance
- CloudWatch can monitor most of AWS as well as your applications that run on AWS
- CloudWatch with EC2 can monitor events:
- Standard Monitoring = every 5 mins
- Detailed Monitoring = every 1 min
- You can create CloudWatch Alarms which trigger notifications
CloudWatch VS CloudTrail
- CloudWatch is for performance monitoring (CPU, Network, Disk, Status Check)
- CloudTrail monitors API calls in the AWS platform.
CloudWatch
- Standard Monitoring = 5 mins
- Detailed Monitoring = 1 min
- CloudWatch is for performance monitoring (CPU, Network, Disk, Status)
- CloudTrail is for auditing
What can I do with CloudWatch
- Dashboards: Creates awesome dashboards to see what is happening with your AWS environment
- Alarms: Allows you to set Alarms that notify you when particular threshold are hit
- Events: CloudWatch Events helps you to respond to state changes in your AWS ressources
- Logs: CloudWatch Logs helps you to aggregate, monitor and store logs
What can I do with CloudWatch
- Dashboards: Creates awesome dashboards to see what is happening with your AWS environment
- Alarms: Allows you to set Alarms that notify you when particular threshold are hit
- Events: CloudWatch Events helps you to respond to state changes in your AWS ressources
- Logs: CloudWatch Logs helps you to aggregate, monitor and store logs
IAM Roles
- Roles are more secure than storing your access key and secret access key on individual EC2 instances
- Roles are easier to manage
- Roles can be assigned to an EC2 instance after it is created, but currently only using the command line
- Roles are universal, you can use them in any Region
IAM Roles
- Roles are more secure than storing your access key and secret access key on individual EC2 instances
- Roles are easier to manage
- Roles can be assigned to an EC2 instance after it is created, but currently only using the command line
- Roles are universal, you can use them in any Region
EC2 Instance Meta-data
- Used to get information about an instance (such as public IP)
- Command: curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data
- Command: curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-data
EC2 Instance Meta-data
- Used to get information about an instance (such as public IP)
- Not user meta data
- Command: curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data
EFS
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) is a file storage service for Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances. Amazon EFS is easy to use and provides a simple interface that allows you to create and configure file systems quickly and easily. With Amazon EFS, storage capacity is elastic, growing and shrinking automatically as you add and remove files, so your applications have the storage they need, when they need it.
EFS
Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) is a file storage service for Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances. Amazon EFS is easy to use and provides a simple interface that allows you to create and configure file systems quickly and easily. With Amazon EFS, storage capacity is elastic, growing and shrinking automatically as you add and remove files, so your applications have the storage they need, when they need it.