4 Radioactivity and Particles Flashcards
Name the three types of radioactive particles?
alpha, beta, gamma

Describe an alpha particle
It is a helium nucleus

Describe a beta particle
It is a high speed electron

Describe gamma radiation
EM wave
travels at the speed of light
No charge or mass

Name the subatomic particles in an atom
proton
neutron
electron
What are the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron?
proton = 1
neutron = 1
electron = 0
Define the atomic number
number of protons in an atom
Define the mass number
Number of protons + neutrons in an atom
What is another name for the mass number?
nucleon number
What are the relative charges of the proton, neutron and electron?
proton = +1
neutron = 0
electron = -1
Where are the electrons found in an atom?
In shells in the space around the nucleus
Where are the protons and neutrons found in the atom?
in the nucleus
atoms are neutral, so what is true about the number of protons and electrons?
number of protons = number of electrons
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element with same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
Two common isotopes of carbon are C-12 and C-14
(Carbon has an atomic number of 6)
Name one similarity and two differences about these isotopes?
They both have 6 protons
C-14 has 8 neutrons but C-12 only has 6 neutrons.
C-14 is an unstable isotope of carbon and C-12 is a stable isotope
What is another name for an unstable isotope?
radioisotope or radioactive isotope
Why does an unstable isotope break down?
An ustable isotope has too many or too few neutrons in the nucleus which makes it emit alpha, beta, neutron or gamma radiation
Name four types of radiation
alpha
beta
neutrons
gamma
Radioactive isotopes decay spontaneously.
What does this mean?
It means that you can’t say when any one of them is going to decay and you can’t do anything to at all to make a decay happen. It is a random process.
Which type of radiation occurs without changing the radioisotope into a new element?
gamma
Name the three types of radiation which will change a radioisotope into a new element.
alpha
beta
neutrons
There is low level background radiation all around us all the time. It comes from….
- Rocks, soil, buildings and food (from Earth)
- cosmic rays from space
- living things
- radiation due to human acitvity - nuclear waste, nuclear fall-out
Nucelar radiation causes ionisation. What is ionisation?
When radiation bashes into atoms, knocking electrons from them.
These atoms are turned into ions which are charged
How can we detect ionising radiation?
Geiger-Muller tube - GM tube OR photographic film
Radiation is less penetrating if it is….
more highly charged
more massive
slower moving
Radiation is more penetrating if it is….
less charged
less massive
faster moving
Radiation is more ionising if it is….
more highly charged
more massive
slower moving
Radiation is less ionising if it is….
less charged
less massive
faster moving
Radiation is more penetrating if it is _________ ionising
less ionising
Radiation is less penetrating if it is ____________ ionising
more ionising
I am a radioactive particle.
I am big, heavy and slow-moving.
What am I?
An alpha particle
I am a radioactive particle
I am small, light and fast moving
What am I?
I am a beta particle
I am a type of radiation
I have no mass or charge and I travel at the speed of light.
What am I?
gamma radiation
Place alpha, beta and gamma in order of penetration from least to highly.
alpha < beta < gamma
Why are alpha particles strongly ionising?
They are highly charged (+2), massive and move slowly
Which radiation can be deflected by a magnetic field?
only alpha and beta as they are both charged
Gamma is not charged- therefore not deflected in a magnetic field
What happens to the atomic number and mass number of a radioactive isotope when they release an alpha particle?
atomic number goes down by 2
mass number goes down by 4
Different radiations can penetrate by different amounts
You can identify the type of radiation by its penetrating power.
Alpha particles are blocked by…
paper, skin or a few cm of air
Different radiations can penetrate by different amounts
You can identify the type of radiation by its penetrating power.
Beta particles are blocked by…
thin metal (5mm of aluminium) or 30 cm of air
Different radiations can penetrate by different amounts
You can identify the type of radiation by its penetrating power.
Gamma particles are blocked by…
thick lead or very thick concrete
Gamma emission always happens after beta or alpha decay. Explain why
You never just get gamma emission
Gamma waves are emitted from a nucleus after it has decayed and is still in an ‘excited state’
Gamma rays are weakly ionising because they tend to pass through rather than collide with atoms. But eventually they hit something and do damage.
Why do gamma rays behave this way?
They have no charge, no mass and move at the speed of light.
Why are alpha particled deflected by a magnetic field?
They are charged (+2)
A geiger-Muller tube gives a count rate. What is count rate?
The number of radioactive particles reaching the counter per second
Why is the count rate different from the overall activity of a radioactive sample?
The count rate is the number of particles reaching the GM tube per second NOT the total number of radioactive particles the sample emits per second.
Radioactive sources can be dangerous if you don’t use them properly.
Describe three safety procedures
- keep radioactive sources in a lead lined box when not in use
- Pick up radioactive sources using long-handled tongs
- Do not point radioactive sources at anyone- keep a safe distance from them.
A teacher carried out an investigation to work out which radiation was emitted from a radioactive rock found near their school.
What equipment will they need?
- GM tube and counter
- paper
- 5 mm of aluminium
- thick lead
- ruler
- stopwatch
A teacher carried out an investigation to work out which radiation was emitted from a radioactive rock found near their school.
They need to find the background count first. Explain how this is done.
- Remove any sources and return them to their lead cases.
- Measure the background count for 2 minutes
- Repeat this three times
- Calculate the mean background count
- Count rate = mean count/ 120 seconds
A teacher carried out an investigation to work out which radiation was emitted from a radioactive rock found near their school.
They found the back ground count. The first few steps of the method are written below. How should they use the materials (paper, 5mm of Al) to determine which radiation is emitted?
- Place the GM tube 1 cm from the rock sample with no material present
- Measure the count for 30 seconds
- Repeat this three times
- Calculate the mean count
- Calculate the count rate - count rate = mean count/30s
- Subtract the background count to find the corrected count rate.
- Repeat steps 2-6 with paper between the rock and GM tube. If the count rate remains the same - no alpha is emitted.
- Repeat steps 2-6 with 5mm of aluminium between the rock and GM tube. If the count rate remains the same- no beta is emitted
- If there is still a count rate (it has not dropped to zero) after step 8 then gamma is emitted
What is true about a balanced nuclear equation?
Overall charge (proton number) and mass (mass number) have the be the same on both sides of the equation.

Write the balanced equation for the beta decay of carbon-14
The atomic number of carbon is 6

What is the mass number and proton number of an alpha particle?

What is the mass number and proton number of a beta particle?

What is the mass number and atomic number of gamma radiation?

Write the balance nuclear equation for the alpha decay of Radium-226
The atomic number of radium is 88

Write the balanced nuclear equation for gamma emission from technecium-99
The atomic number of Tc is 43

Energy is released in a fusion reaction because…
A- there is a gain in mass by the nuclei involved in the reaction
B- there is a loss of mass from the nuclei involved in the reaction
C- protons are turned into neutrons during the reaction
B
there is a loss of mass from the nuclei involved in the reaction

In a nuclear reactor, a uranium-235 nucleus can split when…
A ..it is absorbs gamma radiation
B…it collides with an electron
C… it collides with a fast moving neutron
D…it collides with a slow moving neutron
D.. it collides with a slow moving neutron.
The moderator (often water or graphite) is used to slow the fast moving neutrons so that the reaction can continue.
True or False?
When a radioactive nucleus emits a betal particle, its atomic number increases
True
A beta particle is a electron, in the nucleus a neutron transforms into a proton and electron (which is emitted)
n –> p+ + e-

True or False
Radioactive waste from a nuclear power station is often diffciult to dispose of safely because it has a long half-life
True
It takes around 70 year to decommision a nuclear power station. Nuclear waste must first drop to a safe level before transporting it.

The count rate of a radioactive sample falls from 130Bq to 65Bq in 15 minutes. What is its half life?
130Bq –> halves to 65Bq in one half life. This took 15 minutes to happen….
Therefore the half life is 15 minutes
Nuclear fission reactions release high-energy neutrons. The role of the moderator in a nuclear reactor is to…
A. limit the rate of fission by absorbing excess neutrons
B. slow the neutrons down so they can be absorbed by uranium nuclei
C. transfer energy from the neutrons to the water in the heat exchanger.
B. slow the neutrons down so they can be absorbed by uranium nuclei

What happens in nuclear fusion?
A. One heavy nucleus emits a beta particle
B. One heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei
C. Two light nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus
C. Two light nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus

What is the role of the shielding around a nuclear reactor?
What material is typically used?
To absorb the ionising radiation released during fission. This is typically think layers of concrete.
Lead works well but is expensive!
An object has been contaminated if….
A. it has been exposed to a radioactive source
B. unwanted radioactive atoms have got on to it or into it
C. it has become radioactive
B. unwanted radioactive atoms have got on to it or into it
An object has been irradiated if….
A. it has been exposed to a radioactive source
B. unwanted radioactive atoms have got on to it or into it
C. it has become radioactive
A…it has been exposed to a radiaoctive source
What are the fission products of an uranium-235 nucleus?
Two radioactive daugther nuclei and a small number of neutrons
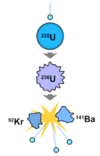
Nuclear fusion does not happen at low temperatures and pressures, due to electrostatic repulsion of…
A. electrons
B. protons
C. neutrons
B. protons

What happens to the mass number and proton number after a nucleus undergoes neutron emission?
(Hint: the nucleus loses a neutron!)

Medical tracers come from irradiating Mo-98 with neutrons. This is called neutron radiation or neutron capture.
Decribe what forms when Mo-98 is irradiated with neutrons.
Mo-98 forms Mo-99 since it gains a neutron!
Mo-99 is radioactive and decays to form Tc-99 which is used as a medical tracer

Medical tracers are radioactive sources with are injected into, swallowed by or inhaled by a patient.
As the source moves around the body, the radiographer uses a detector and computer to monitor its progress on a display.
What sort of emitter should these radioactive tracer be?
gamma is best but beta works in some cases.
gamma is least ionising and most penetrating and can be detected outside the body.
alpha is a huge NO NO as it is least penetrating and will be completely absorbed by the body and cause huge damage to organs.

Medical tracers are radioactive sources with are injected into, swallowed by or inhaled by a patient.
As the source moves around the body, the radiographer uses a detector and computer to monitor its progress on a display.
What are radioactive tracers mainly used for?
To check whether the organs in the body are working as they should.


