3.27 STROM Hematologic Malignancies II: B cells Flashcards
Tingible Bodies
Macrophages that are located in the lymph node that take up apoptosed B cells in the germinal center reaction
-Tend to take up hematoxyin

B Cell Markers
- TdT: Expressed during early B cell development
- CD10: Early dev and when B cell is in Germinal center
- CD19, CD20: B cell marker throughout (can target with Rituximab)
CD20 Immunohistostaining
Stains B-cells, in germinal centers and in the mantle zones

CD10 Immunohistostain
Some B cells, mostly ones in the germinal center

CD5 or 3 Immunohistostain
T-cell Stain, mostly in the paracortex

Translocations and Oncogenesis
Common motif is for an prooncogene to translocate next to an Ig promoter to form an oncogene
-Common Ig Promoters: IgH (14q32)**, Ig lambda (22q11) and Ig kappa (2p12)
Common Oncogene Associations in B cells
Cyclin-D and Myc: over expressed in malignancies of naive B cells (worse)
- Bcl-2 and Bcl-6: B cells derived from germinal centers
- C-Maf, Cyclin D3 and Pax-5: B memory cells/myelomas
Typical Organ Distribution of CLL
-Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
See mostly in the PB and some in the BM and lymph nodes
- If blood is primary site use: leukemia
- If not use lymphoma
- If there is more lymph node involvement it could be called a SLL (small lymphocytic LYMPHOMA)
CLL Facts/Presentation
- Presentation: lymphocytosis in older males (high familial incidence)
- Malignancy of Memory B-cells, see more PB (CLL) involvment and see small lymphocytes with little cytoplasm and “SMUDGE CELLS”
- Cells have already been through a germinal center rxn/class switching and express IgG
- Pseudofollicular: looks like germinal center (reactive) in germinal center, but is actually a proliferative center, Ki67 should be over expressed in these

CLL: Genetics and Markers
Genetics: 80%: del13q14.3>trisomay 12>del11q (MLL gene), del17p (p53)
Immunophenotype: Light chain restricted (kappa or lambda) CD20-weak, CD5+ and CD23+
Key clinical predictors: immunopheno; ZAP-70+ (bad), CD38+ (bad), markers of somatic hypermutation state (means more or les differ)
Genetics: 17p deletion (p53/bad) and 13q deletion (good)
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
- Mantle cells: reserve of naive cells that encirlcle the germinal center
- Often misdiagnosed as CLL (less common than CLL)
- Differ in morphology of lymph node do not have proliferative centers, have a starry sky from macros w/ cll remnents
- all have t(11;14) (IgH;Cyclin D1) is ALWAYS present (FISH)
- More aggressive than CLL
Immunopheno markers: CD5+ (t cell marker), CD20 strong, CD23-
- Also have light chain restriction
- can also stain with Ki-67
-

Follicular Lymphoma
Presents mainly in the Lymph nodes, also found in BM and PB, finding outside of normal distribution usually means an increase in aggressiveness
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
Found Mainly in GI tract and Lymph nodes, also found some in PB
Genetics: t(2;8), t(8;14) or t(8;22) rearrangement of c-MYC
Immunology: Surface IgM+, CD10, 19, 20, 22, 79a all pos and Ki67 (85%)
-Occurs more often in children
Plasma Cell Neoplasms, Types
Monoclonal gammaopathy of uncertain significant (MGUS), mild form, usally asymptomatic can progress to myeloma
-Myeloma: more severe form associated with multiple lytic bone lesions
Involved sites: BM>>>PB
- See Rouleaux (row of coins) on peripheral smear from protein production
- Almost always presents in elderly (aquired mutations)

Diagnosis of Plasma Cell Neoplasms
Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP): can show abundence of Igs (not light chain only)
-Immunofixation electrophoresis (IFE): can determine if monoclonal and will show light chain restrictive
Plasma Cell Neo Morphology
- See a lot of cytoplasm and an eccentric nucleus, usually have clumpy chromatin and prominent golgi apparatus
- Will look like bone is being eaten away in places (osteoclasts)

General Plasma Cell Neoplasms
- Immunophenotype: CD38++++, CD138++++, CD19-, CD20-; light chain restricted
- Genetics: Translocation of IgH (chromo 14) in about 2/3 of cases, Trisomes of ODD # chromo are common
- MGUS: 1%/yr progress to mult myeloma
- Mult Myeloma: median survival 3-4 years
Predictors of worse outcome: t(4;14)-FGFR3, t(14;16)-C-MAF, t(14;20)-MAFB, del17p (p53 region) and Serum beta 2 microglobulin (all these are usually not found but when they are it is a poor prognosis
Follicular Lymphoma
- Presentation: lymphadenopathy in older individuals, can involve BM and PB
- Results from failure of germinal B-cells to apoptose (b/c of Bcl-2 over expression-anti-apoptotic)
- t(14;18)-Bcl-2 w/ IgH promoter
- Immunopheno: CD19+, CD10+ (germ cen), Bcl-2 (90%), BCL-6 (85%)
–BCL-2 staining will not be seen in a reactive center reaction
- Will like a germinal center but will lack: polarity (Iarge cells at one end and smaller cells at the other end) and tingible body macrosphages (sign of rapid turn over, no cells are apoptosing)
- Clinical Course: (1)30% will progress to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (2) Quite variable, depends on stage, grade, cytogenetics
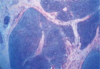
–Grade 1 will have mostly centrocytes (small dark cells) and Grade 3 will have mostly Centroblasts (larger cells)
PICTURE: Darker staining center is abnormal and the lighter stained center is normal

Grade 1 Follicular Lymphoma
-Most centrocytes, smaller than centroblasts

GRADE 3 FOLLICULAR LYMPHOMA
MOSTLY CENTROBLASTS (LARGER)

DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA
- “garabage” category of B-cell lymphomas
- Clinical presentation: Rapidly growing adenopathy, ELDERLY, 40% present with extranodal disease (GI, BM, other)
- IMMUNOPHENO: CD19+, CD20+, CD10+ (30-60%)
- Genetics: t(v, 3q27)(v, BCL-6) ~30%, t(14;18) (BCL-2)~20-30% and others may occur
- Clinical course: depends on stage, generally have a more acute course
- KEY PREDICTORS: BM involvement and BM appearnace (concordant vs discordant), can see follicles w/o germinal centers, big cells with mitotic figures, generally

Hodkin Lymphoma Pathophysiology
- Cannot be killed (NFkB or EBV or other anti-apoptotic mutation), similar to Follicular lymphoma, B-cells which went into germinal centers and did not die.
- Classical: do have Ig rearrangement, but do not express Ig w/n cell or on their surface (cripple Ig promoter/transcription factor mutation) (strom-it has a “shaved head”)
- Nodular: express surface Igs and other B-cell markers

Hodgkin Lymphoma (clasical)
Clinical Presentation
-Sub-categories: (1) Classical Hodgkin
-Clinical Presentation: males 30-50, localized or diffuse adenopathy, often w/ involvement of cervical, mediastinal or abdominal lymph nodes and/or spleen

Classical Hodgkins: Morphology
-Morphology: Reed/Sternberg cells (large lymphoid w/ mono-/bi-nucleated appearance, huge eosinophilic nucleoli and overall horseshoe shape likely) and Diverse background cells: small lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, histocytes
–Lymph node architecture: wholly or partially effected; can be criss-crossed by fibrous bands
-will not see germinal centers