2.03 - Basis Of The ECG Flashcards
What is the standard recording speed of an ECG?
25mm/s
In seconds, how long is one small square and one large square
One small square = 0.04seconds = 40ms
One large square (5 small squares) = 0.2seconds = 200ms
Describe the calibration pulse
A pulse of 1mV (2 large vertical squares) on each channel
Draw a typical ECG tracing and label the deflections
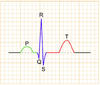
State what each deflection in a standard ECG tracing represents
P wave: Atrial excitation
Q: early ventricular excitation
R: ventricular excitation
S: late ventricular exciation
T wave: ventricular repolarisation
U wave: late repolarisation (attached to the T wave, can be positive or negative)
List the major intervals on a typical ECG tracing, how to measure them, their normal values and what they represent
RR Interval: Between two beats –> determins heart rate [60-100bpm]
P-R interval: From start of P to start of Q/R [0.12-.22s]
QRS: From Q/R to end of S [0.08-0.11s]
ST Interval: From end of S to end of T [0.27-0.33]
QT Interval: From start of Q/R to end of T [0.35-0.42]
What are the steps involved in interpreting an ECG recording?
- Patient details - Name, Sex & Age
- Date the ECG was performed
- Quality of recording - Calibration pulses, muscle activity, leads correctly placed, patient movement, poor contact
- Rate - Beats per minute
- Rhythm - regular vs irregular, is it sinus rhythm?
- Cardiac axis - Normal is -30 to 90 degrees
- Intervals & Segments: RR, PR, QRS, QT, ST
Which areas are the first to repolarise?
The areas that depolarised last
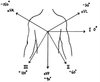
Draw the ‘orientation’ for each of the limb leads
Describe the location of the chest leads
V1: 4th intercostal space, right sternal edge
V2: 4th intercostal space, left sternal edge
V3: Halfway between V2 and V4
V4: 5th intercostal space, midclavicular line
V5: Anterior axillary line, same horizontal plane as V4
V6: Mid axillary line, same horizontal plave as V4


