20190109-20191116 Flashcards
A 47-yr-old man from Brazil comes to the physician because of edema and dyspnea. He is otherwise healthy. His temperature is 100F, pulse is 96/min, and BP is 120/75 mmHg. Physical exam reveals bilateral crackles. Echo reveals decreased end diastolic volume and increased compliance. Endocardial biopsy shows fibrosis of the endocardium. The myocardium has focal necrosis and inflammatory infiltrate. Congo-red stain is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
a. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
b. Cardiac amyloidosis
c. Endomyocardial fibrosis with hypereosinophilia
d. Viral endocarditis
A 47-yr-old man from Brazil comes to the physician because of edema and dyspnea. He is otherwise healthy. His temperature is 100F, pulse is 96/min, and BP is 120/75 mmHg. Physical exam reveals bilateral crackles. Echo reveals decreased end diastolic volume and increased compliance. Endocardial biopsy shows fibrosis of the endocardium. The myocardium has focal necrosis and inflammatory infiltrate. Congo-red stain is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
a. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy
b. Cardiac amyloidosis
c. Endomyocardial fibrosis with hypereosinophilia
d. Viral endocarditis
Explanation: Chagas disease (T. Cruzi) Parasite so hypereosinophilia.
Learning objectives:
149a Describe the impact of myocarditis on the development of cardiac failure. Be familiar with the different organisms that can cause infective pericarditis and myocarditis.
A 51-yr-old woman is admitted to the hospital for an elective cardiac catheterization because of a 9-month history of worsening fatigue and shortness of breath. The results of cardiac catheterization are shown:
Pulmonary artery pressure: 45/25 mmHg
Pulmonary wedge pressure: 30 mmHg
Left ventricular pressure: 120/5 mmHg
Aortic pressure: 120/80 mmHg
What is the most likely diagnosis?
a. Aortic regurgitation
b. Aortic stenosis
c. Mitral regurgitation
d. Mitral stenosis
e. Myocardial infarction
A 51-yr-old woman is admitted to the hospital for an elective cardiac catheterization because of a 9-month history of worsening fatigue and shortness of breath. The results of cardiac catheterization are shown:
Pulmonary artery pressure: 45/25 mmHg
Pulmonary wedge pressure: 30 mmHg
Left ventricular pressure: 120/5 mmHg
Aortic pressure: 120/80 mmHg
What is the most likely diagnosis?
a. Aortic regurgitation
b. Aortic stenosis
c. Mitral regurgitation
d. Mitral stenosis
e. Myocardial infarction
Explanation: Elevated pulmonary capillary wedge pressure and elevated pulmonary artery pressure. Normal LVEDP that is unequal to the pulmonary wedge pressure. A pressure gradient between 5-30 mmHg is indicative of mitral stenosis.
Learning objective:
137a List normal systolic and diastolic hemodynamic parameters in the following cardiovascular structures: right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary artery, left atrium, left ventricle, and aorta
145a Explain normal hemodynamics and the abnormal hemodynamics that are created by mitral stenosis and aortic stenosis, which translate into the physical findings and abnormalities in chest X-ray and echocardiography.
146a Explain the abnormal hemodynamics created by regurgitation of the aortic and mitral valves, which translate into the physical findings and abnormalities in chest X-ray and echocardiography.
Which of following is true regarding sex difference in heart disease?
A. Coronary artery disease is usually more severe at the time of manifestation due to increased comorbidities.
B. Women are more prone to acute thrombi due to plaque rupture.
C. Fibromuscular dysplasia is more common in males and associated with coronary artery dissection.
D. Repeat pregnancy does not increase risk of development of cardiomyopathy.
E. Male are more prone to formation of thrombus due to inability of atria to maintain rhythmic contraction.
Which of following is true regarding sex difference in heart disease?
A. Coronary artery disease is usually more severe at the time of manifestation due to increased comorbidities.
B. Women are more prone to acute thrombi due to plaque rupture.
C. Fibromuscular dysplasia is more common in males and associated with coronary artery dissection.
D. Repeat pregnancy does not increase risk of development of cardiomyopathy.
E. Male are more prone to formation of thrombus due to inability of atria to maintain rhythmic contraction.
Explanation:
A. Women develop disease at a later age, which allows for development of other comorbidities such as diabetes.
B. Erosion is more common in female vs plaque rupture is more common in male.
C. Females are more prone to fibromuscular dysplasia, which can be a risk factor for artery dissection. This should be considered in young patient (a typical one would be young pregnant woman having heart attack).
D. The repeated pregnancy can result in worsening of the subclinical changes in heart muscle that occur during first pregnancy.
E. In A-fib, women are more prone to thromboembolic event.
Learning objecitve:
143a Describe physiologic sex differences in cardiovascular disease.
143a Describe sex differences in risk factors for coronary artery disease
143a Explain gender-specific cardiovascular changes from pregnancy to menopause.
What murmur is associated with the pressure abnormality below?
A. Harsh holosystolic murmur at left sternal border without radiation
B. ‘opening snap’ followed by decrescendo low-pitched rumble (diastole) near apex
C. Pansystolic murmur with radiation to the axilla
D. Crescendo-decrescendo murmur at 2ndinterspace (systole) radiating to carotids
E. Decresendo mumur immediately after S2 at 2nd-4thinterspace with radiation to apex

What murmur is associated with the pressure abnormality below?
A. Harsh holosystolic murmur at left sternal border without radiation
B. ‘opening snap’ followed by decrescendo low-pitched rumble (diastole) near apex
C. Pansystolic murmur with radiation to the axilla
D. Crescendo-decrescendo murmur at 2ndinterspace (systole) radiating to carotids
E. Decresendo mumur immediately after S2 at 2nd-4thinterspace with radiation to apex
Explanation: Mitral valve regurgitation. Higher than normal atrial filling during a normally low pressure part of the atrial curve, something must be contributing blood to the atria other than passive filling. Underlying etiologies for other murmurs:
A. Ventricular septal defect.
B. Mitral stenosis
D. Aortic stenosis.
E. Aortic regurgitation.
Learning objectives:
145a Explain normal hemodynamics and the abnormal hemodynamics that are created by mitral stenosis and aortic stenosis, which translate into the physical findings and abnormalities in chest X-ray and echocardiography.
146a Explain the abnormal hemodynamics created by regurgitation of the aortic and mitral valves, which translate into the physical findings and abnormalities in chest X-ray and echocardiography.
A 30 year-old patient presents with shortness of breath and reports “feeling tired all the time”. He notes that as a child he remembered having a fever, sore throat, and pain in his knee that eventually went away. On physical exam, a right ventricular impulse is felt on palpation, and a diastolic decrescendo murmur with an opening snap was heard on auscultation. An irregularly irregular rhythm is heard. What do you expect to see on echocardiography?
A) Immobility of the tricuspid valve, right atrial enlargement
B) Immobility of the mitral valve, left atrial enlargement, no enlargement of left ventricle
C) Immobility of the aortic valve, left ventricular hypertrophy
D) Left atrial enlargement, left ventricular dilatation
What do you expect to see on echocardiography?
A) Immobility of the tricuspid valve, right atrial enlargement
B) Immobility of the mitral valve, left atrial enlargement, no enlargement of left ventricle
C) Immobility of the aortic valve, left ventricular hypertrophy
D) Left atrial enlargement, left ventricular dilatation
The correct answer is B. This patient has mitral stenosis. Common symptoms of mitral stenosis are fatigue from reduced cardiac output and dyspnea from pulmonary congestion. The patient has a history of rheumatic fever, which is the most common cause of mitral stenosis. In acute rheumatic fever, the most common symptoms are fever, chills, and migratory arthritis 2-3 weeks after the throat infection. Rheumatic fever is diagnosed by the Jones Criteria. Acute rheumatic fever leads to carditis due to autoimmune cross-reactivity that can lead to valve damage. Symptomatic mitral stenosis does not usually present until around 20 years after the episode of acute rheumatic fever. Other causes include calcification of the mitral annulus, infective endocarditis resulting in large vegetations, and rare congenital stenosis. On physical exam, an increased right ventricular impulse is heard because of increased right ventricular pressure. On auscultation, a diastolic opening snap after S2 is characteristic from the tensing of the chordae tendineae and stenotic leaflets as the mitral valve opens. A decrescendo diastolic murmur follows due to turbulent flow across the mitral valve. Mitral stenosis leads to increased left atrial pressure which causes left atrial dilatation that can result in atrial fibrillation. An irregularly irregular rhythm is characteristic of atrial fibrillation. Electrocardiography of patients with mitral stenosis shows immobility of the mitral valve, left atrial enlargement, and no enlargement of the left ventricle, since mitral stenosis leads to restricted flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. Right ventricular dilatation can also be seen due to pulmonary hypertension. A is incorrect because this is the characteristic echocardiogram for tricuspid stenosis. C is incorrect because this is the characteristic echocardiogram for aortic stenosis. While rheumatic fever can also cause aortic stenosis, the physical exam findings do not match (no systolic thrill or midsystolic murmur etc.) D is incorrect because this is the characteristic echocardiogram for aortic regurgitation. While rheumatic fever can cause concurrent aortic regurgitation, the physical exam findings do not match (no midsystolic outflow murmur, no increased left ventricular impulse, etc.)
Learning Issue Covered: Obstructive valvular heart disease: Explain normal hemodynamics and the abnormal hemodynamics that are created by mitral stenosis and aortic stenosis, which translate into the physical findings and abnormalities in chest X-ray and echocardiography. (MKS1b,1d)
SM 145a:Valvular Heart Disease Obstructive
A 58 year old woman presents with shortness of breath and chest pain after she exercises. She also “feels faint” around 5 minutes after she starts running and has to stop and rest. She notes that she has never had these symptoms before a few months ago. On physical exam a midsystolic crescendo-decrescendo murmur that radiates to the carotids is heard, and weak and delayed upstrokes of the carotid artery is observed. A split S2 is heard during expiration, but not during inspiration, and a S4 is appreciated. An echocardiogram shows a thickened and immobile aortic valve and left ventricular hypertrophy. The aortic valve area was measured to be 0.5 cm2. What is the best next step for this patient?
A) Percutaneous balloon valvulopasty
B) Start diuretics
C) Follow-up echocardiogram in 6 months
D) Valve replacement surgery or transcatheter aortic valve implantation
What is the best next step for this patient?
A) Percutaneous balloon valvulopasty
B) Start diuretics
C) Follow-up echocardiogram in 6 months
D) Valve replacement surgery or transcatheter aortic valve implantation
The correct answer is D). The patient has symptomatic severe aortic stenosis and so meets the indications for valve replacement surgery (symptomatic and aortic valve area less than 0.6 cm2). She is presenting with dypnea, angina, and syncope upon exertion, the common symptoms of aortic stenosis. There is no current medical treatment that slows the progression of aortic stenosis and patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis have low survival rates with no surgical treatment. If the patient is at high risk for cardiac surgery, transcatheter aortic valve replacement is the best treatment option and was found to be noninferior to surgical aortic valve replacement with similar survival rates. On physical exam, aortic stenosis presents with a midsystolic ejection murmur due to the systolic pressure gradient, and parvus et tardus (weakened and delayed carotid upstrokes) due to obstructed left ventricular outflow. An S4 can be heard because of atrial contraction into a stiff left ventricle. Delayed closure of the aortic valve can lead to paradoxical splitting of the S2 where splitting is heard with expiration. The patient’s echocardiogram is also indicative of aortic stenosis and is used to determine the severity of aortic stenosis and left ventricular systolic function. A is incorrect. Percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty is the indicated treatment option for patients with mild mitral stenosis. It is not a successful treatment option for patients with calcific aortic stenosis, since patients often develop restenosis. B is incorrect. There is no effective medical treatment currently recommended for severe aortic stenosis. Diuretics can be used to reduce pulmonary venous congestion if needed but is not the best treatment option here. C in incorrect. If the patient has asymptomatic aortic stenosis with no left ventricular systolic dysfunction and an aortic valve area >0.6 cm2, then watchful waiting is indicated. For patients with severe aortic stenosis (valve area <1 cm2) but with no symptoms, follow-up echocardiography is recommended every 6-12 months.
Learning Issue Covered: Obstructive valvular heart disease: Explain normal hemodynamics and the abnormal hemodynamics that are created by mitral stenosis and aortic stenosis, which translate into the physical findings and abnormalities in chest X-ray and echocardiography.(MKS1b,1d) Describe indications for surgery, and the rational for surgical and catheter-based treatments of obstructive valvular heart disease. (MKS1e)
SM 145a:Valvular Heart Disease Obstructive
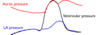
A 53 year old man is here for his annual physical exam. On physical exam, a displaced left ventricular impulse was observed and a decrescendo diastolic blowing murmur is heard. A S3 was appreciated. Capillary pulsations could be seen at the lip and “water-hammer” pulses with brisk upstrokes and rapid fall-offs were appreciated. Which hemodynamic profile do you expect to see with this patient? (See attached image)

The correct answer is A. The patient’s physical exam findings are most consistent with chronic aortic regurgitation. The volume overload and increased pressure load leads to left ventricular hypertrophy and dilatation which manifests as a displaced left ventricular impulse. A decrescendo diastolic blowing murmur is due to regurgitant flow during diastole. The wide pulse pressure (difference between systolic pressure and diastolic pressure) causes findings such as the capillary pulsations (Quincke sign) and “water-hammer” pulses (Corrigan pulse). This is because the dilatation of the left ventricle allows for the accommodation of a larger volume, leading to a drop in diastolic pressure while the high stroke volume leads to high systolic arterial pressure.
This can be seen in the hemodynamic profile in A where the aortic pressure falls quickly (blue arrow) while the left ventricular pressure rises during diastole.
B is incorrect because this is the hemodynamic profile for aortic stenosis. A systolic pressure gradient between the left ventricle and aorta can be seen shaded in blue due to the increased left ventricular pressure.
C is incorrect because this is the hemodynamic profile for mitral regurgitation, where a large systolic v wave is seen in the pressure tracing for the left atrium.
D is incorrect because this is the hemodynamic profile for mitral stenosis, where the left atrial pressure is increased and there is a diastolic pressure gradient between the left atrium and left ventricle (shaded in blue).
Images from Pathophysiology of Heart Disease: Lilly 6th edition.
Learning issue covered: Valvular Heart Disease: Regurgitation 1. Explain the abnormal hemodynamics created by regurgitation of the aortic and mitral valves, which translate into the physical findings and abnormalities in chest X-ray and echocardiography. (MKS1b,d)
SM 146a: Valvular Heart Disease: Regurgitation
A previously healthy 21-year-old man presents with chest pain and shortness of breath. He describes it as sharp, radiating to the back, and worse with inspiration. Leaning forward while sitting helps alleviate the pain. The shortness of breath does not increase with exertion. His temperature is 99.7 degrees F. He is currently taking no medications and has no significant medical history or surgical history. On physical exam, a friction rub is heard. ECG reveals diffuse ST segment elevation and PR segment depression. What is the most likely cause of his condition?
A) Tuberculosis
B) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
C) Coxsackievirus group B
D) Coxsackievirus group A
E) Acute myocardial infarction
F) Staphylococcus aureus
What is the most likely cause of his condition?
A) Tuberculosis
B) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
C) Coxsackievirus group B
D) Coxsackievirus group A
E) Acute myocardial infarction
F) Staphylococcus aureus
The correct answer is C) Coxsackievirus group B. The patient has acute pericarditis. The most frequent symptoms of acute pericarditis are chest pain and fever. The pain is described as sharp, pleuritic (worse with inspiration and coughing), and positional (alleviated by sitting and leaning forward) and usually radiates to the back and is in the retrosternal area. Dyspnea is not exertional and usually is caused by an inability to breathe deeply from the pleuritic pain.
On physical exam, a pericardial friction rub can be heard, which is caused by the rubbing of the inflamed pericardial layers against each other. The ECG is also typical for acute pericarditis, where there is diffuse ST segment elevation in most of the ECG leads because of inflammation of the myocardium. PR segment depression is also seen due to atrial epicardial inflammation leading to abnormal atrial repolarization.
In patients who are young and previously healthy, the cause of acute pericarditis is usually idiopathic or viral. The most common viral causes of acute pericarditis are echovirus or Coxsackievirus group B. Other viral causes include influenza, hepatitis B, and varicella.
A is incorrect. Tuberculosis is an important cause of pericarditis in immunosuppressed patients when the bacteria spread from mediastinal lymph nodes into the pericardium, spread from another site within the lungs, or through the bloodstream. The patient is not immunosuppressed and most likely does not have HIV infection.
B is incorrect. Immune-mediated diseases like SLE or connective tissue disease can cause acute pericarditis but does not fit this patient’s clinical presentation.
D is incorrect. Coxsackie group A does not cause acute pericarditis but is instead associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease and aseptic meningitis.
E is incorrect. Acute pericarditis can occur a few days after an MI or a few weeks to several months after an acute MI (Dressler syndrome). The patient does not have a history of MI. The clinical presentation and ECG of this patient also do not match with that of an acute MI (the dyspnea is non-exertional and there is PR depression and diffuse ST segment elevation instead of in only a few leads).
F is incorrect. Bacterial pericarditis is rare in healthy patients; it is more commonly seen in immunocompromised patients such as patients with AIDS, severe burns, or malignancies. Bacterial infections are usually caused by perforating chest trauma, contamination during chest surgery, infective endocarditis, extension from pneumonia, or spread from the bloodstream from a distant location.
Learning issue covered: Describe the impact of myocarditis on the development of cardiac failure. Be familiar with the different organisms that can cause infective pericarditis and myocarditis. (MKS1b)
SM149a: Valvular and Myocardial Pathology
A 54-year old woman presents with increased fatigue and shortness of breath with exercise over the past year. On physical exam, her temperature is 36.8 degrees F and a blood pressure of 118/ 76 mmHg. Crackles were heard upon auscultation of her lungs and she has an elevated jugular venous pressure. The abdomen was distended with a fluid wave. Cardiomegaly and pulmonary edema was seen on chest x-ray. Her echocardiogram measures an ejection fraction of 35%. Last month, she had a cerebral infarction. What is the most likely cause of her condition?
- Chronic alcohol use
- Mutations in myosin and actin
- Amyloidosis
- Chronic acetaminophen use
What is the most likely cause of her condition?
- Chronic alcohol use
- Mutations in myosin and actin
- Amyloidosis
- Chronic acetaminophen use
The correct answer is A. The patient has dilated cardiomyopathy. She has symptoms of right sided and left sided heart failure (fatigue, dyspnea). She also exhibited signs of heart failure including crackles from pulmonary edema, and elevated JVP and ascites from increased venous pressure. Cardiomegaly can be seen from dilatation of the heart (eccentric hypertrophy, where the sarcomeres are added in series). She also presented with embolic events. Some of the causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include chronic alcohol abuse, Coxsackie B virus myocarditis, wet Beriberi, chronic cocaine use, Chagas disease, Doxorubicin toxicity, and peripartum cardiomyopathy.
B is incorrect. Genetic mutations in actin and myosin is the most common cause of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy which presents with angina and sudden syncope.
C is incorrect. Amyloidosis is a cause of restrictive cardiomyopathy. While restrictive cardiomyopathy can also lead to heart failure, it usually leads to right sided heart failure with diastolic dysfunction and a preserved ejection fraction (>50%).
D is incorrect. Chronic acetaminophen use can lead to hepatic necrosis and nephropathy but not dilated cardiomyopathy.
SM149a: Valvular and Myocardial Pathology
A 22-year-old man is evaluated in the ED for rapid heart rate and lightheadedness. HE reports episodes of a “racing heart” a few times each year since his early teens. He escribes today’s episode as different: It started as one of his regular episodes but then become erratic. In addition, the lightheadedness has never happened before. He is otherwise healthy and takes no medications.
On physical exam, the patient is diaphoretic. BP is 72mm/palp. His lungs are clear, and cardiac examination demonstrates a rapid irregular rhythm with no murmurs. ECG is shown:
Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy for this patient:
A. D-C cardioversion
B. IV procainamide
C. IV verapamil
D. overdrive atrial pacing

A 22-year-old man is evaluated in the ED for rapid heart rate and lightheadedness. HE reports episodes of a “racing heart” a few times each year since his early teens. He escribes today’s episode as different: It started as one of his regular episodes but then become erratic. In addition, the lightheadedness has never happened before. He is otherwise healthy and takes no medications.
On physical exam, the patient is diaphoretic. BP is 72mm/palp. His lungs are clear, and cardiac examination demonstrates a rapid irregular rhythm with no murmurs. ECG is shown:
Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy for this patient:
A. D-C cardioversion
B. IV procainamide
C. IV verapamil
D. overdrive atrial pacing
Explanation: The patient is having A fib with an accessary pathway. Note the variable QRS complex width and irregularity. In case of structural abnormality, NEVER use drugs that target AV node. Prodcainamide is an option if the patient is hemmodynamically stable. However, the blood pressure suggest that the patient have issue maintaining cardiac output, so D-C cardioversion is preferred.
Learning objective:
144a Describe the major clinical uses of each of the drugs covered within this lecture
141a Describe the mechanisms and basic clinical features and management of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and flutter.

A 63-year-old man with a history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation is brought into the emergency room and found to have a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Initially, family member reported no history of any cardiac disease. Therefore, you started the patient on ibutilide. While you are interviewing family member to figure out if anything that is missed, a code alarm went off. You rush to the bed side and saw the following ECG:
Which of the following could explain the patient’s episode?
A. Presence of an accessory conductive pathway
B. Mutation in potassium channel
C. Patent foramen ovale
D. Pulmonary hypertension
E. Vegetation on mitral valve

A 63-year-old man with a history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation is brought into the emergency room and found to have a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Initially, family member reported no history of any cardiac disease. Therefore, you started the patient on ibutilide. While you are interviewing family member to figure out if anything that is missed, a code alarm went off. You rush to the bed side and saw the following ECG:
Which of the following could explain the patient’s episode?
A. Presence of an accessory conductive pathway
B. Mutation in potassium channel
C. Patent foramen ovale
D. Pulmonary hypertension
E. Vegetation on mitral valve
Explanation: The patient is experience Torsade de pointe, and long QT syndrome is a potential underlying cause.
Learning objective:
141a Compare and contrast Ventricular tachycardia as a life-threatening condition with benign forms
144a Describe the major side effects of each of the drugs covered within this lecture

A 63-year-old man with a history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation is brought into the emergency room and found to have a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Initially, family member reported no history of any cardiac disease. Therefore, you started the patient on ibutilide. While you are interviewing family member to figure out if anything that is missed, a code alarm went off. You rush to the bed side and saw the following ECG:
Which of the following is not considered a proper therapy for this patient?
A. Magnesium
B. Isoproterenol
C. DC Cardioversion
D. Overdrive pacing
E. Lidocaine

A 63-year-old man with a history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation is brought into the emergency room and found to have a ventricular tachyarrhythmia. Initially, family member reported no history of any cardiac disease. Therefore, you started the patient on ibutilide. While you are interviewing family member to figure out if anything that is missed, a code alarm went off. You rush to the bed side and saw the following ECG:
Which of the following is not considered a proper therapy for this patient?
A. Magnesium
B. Isoproterenol
C. DC Cardioversion
D. Overdrive pacing
E. Lidocaine
Explanation: SHOCK if hemodynamically unstable. Goal: shortening QT to outpace the irregular rhythm. The only drug here that does not shorten the QT is lidocaine.
Learning objective:
144a Describe which drugs and classes of drugs are useful for the arrhythmias discussed in this lecture
141a Compare and contrast Ventricular tachycardia as a life-threatening condition with benign forms.

A 62-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of chest tightness. An electrocardiogram reveals ST segment elevation in the infero-lateral leads. He is treated for an acute myocardial infarction. His hospitalization is complicated by ectopy and several runs of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia. In an effort to reduce the risk of further arrhythmia in the post-myocardial infarction period, he is started on a Class 1 antiarrhythmic medication with very low affinity for its target channel. Which of the following images best represents the effect of the likely medication on the patient’s action potential?

A 62-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of chest tightness. An electrocardiogram reveals ST segment elevation in the infero-lateral leads. He is treated for an acute myocardial infarction. His hospitalization is complicated by ectopy and several runs of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia. In an effort to reduce the risk of further arrhythmia in the post-myocardial infarction period, he is started on a Class 1 antiarrhythmic medication with very low affinity for its target channel. Which of the following images best represents the effect of the likely medication on the patient’s action potential?
Answer B
Explanation: The patient is receiving class Ib antiarrhythmic agent. The effect of class I antiarrthymic agent on the rate of depolarization and action potential duration are shown below:
Rate of depolarization (affinity of sodium channel) IC > IA > IB
Action potential duration IA > IC > IB (decreases)
Learning objective:
144a Recapitulate the Vaughan-Williams Classification Scheme of Antiarrhythmic Drugs

A 65-year-old female with a history of HTN, type 2 diabetes, and asthma presents to the emergency department with severe nausea, sweating, and shortness of breath. ECG showed STEMI. She immediately receives treatment for her condition and is subsequently admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit (CICU). In the CICU, the patient has episodes of recurrent sustained ventricular tachycardia. The hospital is in short supply of amiodarone, so the attending physician starts lidocaine IV to prevent the development of an arrhythmia. Which of the following toxicities is associated with this medication?
A. CNS Effects
B. Cinchonism
C. Torsade de pointes
D. Exacerbation of asthma
E. Flushing
A 65-year-old female with a history of HTN, type 2 diabetes, and asthma presents to the emergency department with severe nausea, sweating, and shortness of breath. ECG showed STEMI. She immediately receives treatment for her condition and is subsequently admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit (CICU). In the CICU, the patient has episodes of recurrent sustained ventricular tachycardia. The hospital is in short supply of amiodarone, so the attending physician starts lidocaine IV to prevent the development of an arrhythmia. Which of the following toxicities is associated with this medication?
A. CNS Effects
B. Cinchonism
C. Torsade de pointes
D. Exacerbation of asthma
E. Flushing
Explanation:
A. Lidocaine is associated with CNS effects.
B. Cinchonism is usually a toxicity for quinidine
C. Torsade de pointes is a concern for class Ia and III antiarrhymic agents, except for amiodarone.
D. Class II antiarrhymic agent can exacerbate athma
E. Flushing is associated with CCB that is in dihydropyridine class.
Learning objective:
144a Describe the major side effects of each of the drugs covered within this lecture
A 58 year old Hispanic woman presents with fatigue and shortness of breath after 15 minutes of walking that has developed over the past year. She sleeps with two pillows at night and reports that she “sometimes wakes up at night out of breath.” She has a history of uncontrolled hypertension. On physical exam there is 3+ pitting edema bilaterally, her heart rate is 110 bpm with a respiratory rate of 22. An elevated JVP is observed. On echocardiography the left ventricular ejection fraction is measured to be 37%. Which of the following is the best first-line treatment option?
A) Implantable cardioverter defibrillator
B) Digoxin and an ARB
C) An ACE-inhibitor, a beta-blocker, and a diuretic
D) Ivabradine
E) Hydralazine and nitrates
The correct answer is C. This patient has heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), since her ejection fraction is < 40%, most likely caused by chronic uncontrolled hypertension. Common symptoms of HFrEF seen in this patient are dyspnea on exertion caused by pulmonary edema and decreased cardiac output, and orthopnea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea because of increased venous return when lying down. Common signs of heart failure seen in this patient include an elevated JVP caused by increased right atrial pressure and peripheral edema from fluid transudation.
The first-line treatment for HFrEF is an ACE-Inhibitor or ARB and a beta blocker with a diuretic added as needed. Since the patient has fluid overload evidenced by elevated JVP and peripheral edema, a diuretic can be added.
A is incorrect. An implantable cardioverter defibrillator should be considered if the left ventricular ejection fraction is less than or equal to 35%.
B is incorrect. Digoxin and an ARB would not be considered first-line treatment. Digoxin can be considered in patients with atrial fibrillation or as an add-on if there are persisting signs and symptoms of heart failure on follow-up.
D is incorrect. Ivabradine targets the If current in the sinoatrial node to reduce the heart rate. It is a treatment option if the patient has a HR greater than 70 bpm in sinus rhythm, and is already taking the highest dose of a beta blocker. It is thus not a first-line treatment and a beta-blocker should be given first.
E is incorrect. Hydralazine and nitrates should be considered if signs and symptoms persist in African-American patients, where it has shown to improve both symptoms and mortality.
Learning Issue covered:
147a Heart Failure Treatment
SM 26: Define the clinical syndrome of heart failure, relate this syndrome in its various manifestations to underlying hemodynamic changes, and describe the differences between: left-sided and right-sided heart failure; high-output and low-output heart failure; heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). [MKS-1b]
SM 27: Explain pharmacologic therapy of HFrEF. [MKS-1e]


