2019 Final Exam Flashcards
(26 cards)
Question 1. Explain what is meant by location transparency. List three other different types of distribution transparency.
Question 1.
Location Transparency is hiding the location of the resource.
3 others could be access transparency, failure transparency and concurrency transparency.
Question 2. What does openness mean for Distributed Systems? How do you define a portable distributed systems?
Question 2. Openness for a distributed system means that it has:
Portability - the extent to which different systems with the same interface can support the same applications without modification
Question 3.
Suppose a process in a distributed systems runs on one node and accesses data from another node. After some time, for load balancing purposes, this process relocates to a different node. What kind of transparencies should be provided for this process in a distributed system? Explain your answer.
Question 3.
Types of transparency
- Location transparency
- Migration transparency
- Relocation transparency
Question 4.
Do messaging systems such as IBM Websphere MQ provide transient synchronous communication?
IBM Websphere MQ provides persistent communication because consuming applications can use the middleware to temporarily store messages in queues. In addition, the receiver doesn’t have to be alive when the message is sent and the sender doesn’t have to be alive when the message is received.
It can be synchronous/asyncronous according to its documentation.
Question 5. Describe and Indentify the communication below.
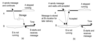
Question 4.
a) Persistent Asynchronous Communication
b) Persistent Synchronous
Persistent = Persistence means that the network is capable of storing messages for an arbitrary period of time until the next receiver is ready.
Transient = : Message is stored only so long as the next receiver is ready.
Asynchronous: It continues immediately after submitting the message.
Synchronous: Blocks the process until the message is received or the sender gets a response from the server
Question 6. What are the main issues to consider when parameter passing in RPC?
Pass by reference is an issue. Sender/Receiver can have different architectures, OSs and data representations.
Question 7. Explain how key=17 can be resolved from node 1.
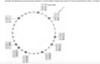
i) Node 1 forwards it on to node 9
ii) Node 9 forwards it on to node 14
iii) Node 14 forwards it on to node 18
v) Node 18 passes its address to node 1
Give reasons why thread synchronization is important to support a functional multi-thread process.
Thread synchronisation is important because threads share the same address space. Thread synchronisation helps avoid resource conflicts such as dead-locks.
Describe how redundancy can be used to mask failures in a distributed system.
Redundancy such as time redundancy, information redundancy and physical redundancy. One case could be to perform an action and if need be, to perform the action again.
Consider Byzantine Failures. To achieve agreement in a distributed system that tolerates k faulty processes, what is the required replication of the resources? Explain.
To achieve agreement the system must achieve a two-thirds majority of correct processes i.e. 2k+1 processes and hence requires a total of 3k+1 processes to achieve agreement.

FIFO multicast. The messages m3 and m4, as well as m1 and m2 are received by P2 and P3 in the same order as they were sent.
Not FIFO atomic because it is not totally-ordered as P2 and P3 receive messages in a different order
Question 14. What are the benefits of logical clocks over physical clocks?
The notion of time is difficult to manage in a DS. Usually time-ordering is less important than operation-ordering, so logical clocks are useful for ensuring the proper sequence. Logical clocks don’t decay and skew over time like physical, crystal clocks.
What is the role of the fusion layer in processing sensed context information?
The Fusion Layer aggregates the location information gathered by the abstraction layer for a particular entity to provide a single, coherent location of the entity. Any location conflicts resolved at this layer.
Describe different types of adaption that can be applied at the application layer.
- Internal adaptation. For example, using a GPS device and a network based location, as they would be members of the same type of context (i.e. location) . Switches to one when it’s better to do so.
- External adaptation: Adapt when an external resource is unavailable.

- Chuck starts out by sending Alice’s identity, along with a challenge.
- Bob returns his challenge and the response in a single message.
- Chuck sends Alice’s identity and Bob’s challenge in a single message, in a new session.
- Bob responds with the secret key and a new challenge.
- At that point, Chuck has the secret key needed for the first session and sends it to Bob.
Provide an example of a security policy. Explain how this security policy can be enforced by an organisation.
Security policies detail what the entities of a DS are allowed to do.
For example, as a user I need to have a password that meets certain criteria. Enforce this, by ensuring passwords meet this criteria.
Justify why it is wrong to implement a nonce as a timestamp.
While timestamps are generally uniqe, they follow a specific format and this predictatibility is not a good for security.
A consistency model uses a small number of locks. Each lock protects updates to a different variable.
What kind of consistency model is this?
This is an entry consistency model where locks are used to access critical sections. No other process can access the resource until the resource is released from a lock.
What kind of consistency model is provided for replicated databases if all operation requests are delivered by a totally ordered multicast?
TODO

Demo on the picture.
Strict Consistency means that every read is what the previous write is.

The reads are in the same order after the writes for each process.
Compare and contrast the iterative and recursive approach to resolving DNS names.
Iterative approach:
- Client contacts the name resolver
- The name resolver contacts the root name server which resolves as much of the name as it can and then goes back to the name resolver referring it to another name server who knows more
- This process repeats until the name is fully resolved
Recursive approach:
- Client contacts name resolver
- Name resolver contacts the root name server which resolves as much as it can and then passes the query on to the next name server who knows more. Intermediate results are not sent to the name server.
- The process repeats until the name is fully resolved and the name servers pass the fully resolved name back up the chain of name servers
- The root name server passes the fully resolved name to name resolver
Assume a DS with 4 machines. Their internal clocks are supposed to tick 1000 times per msec. One machine perfectly performs that while the second one only ticks 995 times per msec, the third one does 1002 ticks per msec and the fourth one does 1004 ticks per msec. If we have UTC updates come every 20 seconds, what is the maximum clock skew that will occur?
The maximum clock skew is calculated my taking the biggest difference between the ticks per msec.
In this case, 995 and 1004. This is 9 ticks per msec
Multiple it by 1000 to make it /ticks.
Then multiple it by 20 seconds.
9000 * 20 = 180 000 is the maximum clock skew that will occur.
A consistency model uses a small number of locks. Each lock protects updates to a different variable. i. What kind of consistency model is this? Explain.
This is an entry consistency model where critical sections are used to acquire locks on resources. No other process can access the resource until the resource is released from a lock.
Pros: Ensures serial access to resources
Cons: Possible failed process, deadlock


