2 - Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism Flashcards
What are the major nitrogen containing compounds?
- Amino acids
- Proteins
- Purines and pyrimidines (DNA/RNA)
- Small amounts in others (e.g. haem, creatine phosphate, neurotransmitters, hormones)
What is creatinine and how is it used clinically?
A breakdown product of creatine and creatine phosphate. Usually produced at a constant rate and filtered into the urine.
Used as a clinical marker to estimate muscle mass (measure creatinine excretion over 24 hrs). Also used as an indicator of renal function.
- How is nitrogen brought into the body?
- Where is nitrogen stored within the body?
- Where is nitrogen excreted from the body?
- Nitrogen intake comes from dietary protein
- Nitrogen is stored in body protein, the amino acid pool and other nitrogen-containing compounds
- Nitrogen is excreted through waste products in faeces and urine and through loss of skin, hair and nails

Normal nitrogen balance is when N intake = N output. What causes positive or negative N balance?
- Positive - Intake > Output - increase in body protein. Normal state in growth, pregnancy or when recovering from malnutrition
- Negative - Intake < Output - loss of body protein. Never normal - commonly trauma, infection or malnutrition
Describe the process of protein breakdown in the body.
- Dietary protein is digested into free amino acids
- The amino group is converted to urea and excreted in the urine
- The carbon skeleton is broken down into glucose and ketone bodies
Give one example of:
- A glucogenic amino acid
- A ketogenic amino acid
- An amino acid that’s both glucogenic and ketogenic
- Glucogenic - Alanine
- Ketogenic - Lysine
- Glucogenic and ketogenic - Tryptophan

Decribe the hormonal control of protein synthesis and degradation.
- Insulin and growth hormone increase protein synthesis and decrease protein degradation
- Glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol) decrease protein synthesis and increase protein degradation

What is the effect on protein reserves of Cushing’s syndrome?
Excess cortisol causes excessive protein breakdown. This weakens the skin structure leading to striae (stretch marks).
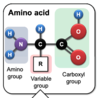
What are the three groups of an amino acid?
Amino group
Carboxyl group
R group
Give an example of an essential amino acid.
Isoleucine

In children and pregnant women there are three further essential amino acids. What are they and why are they necessary?
Arginine, tyrosine and cysteine
Required due to the high rate of protein synthesis
When non-essential amino acids are synthesised by the body where do the following come from?
- carbon atoms
- amino groups
- Carbon atoms - intermediates of glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, krebs cycle
- Amino groups - provided by other amino acids by transamination or from ammonia
Give some examples of some non-protein nitrogen-containing compounds.
- Catecholamines
- Glutathione
- Serotonin
- Histamine
- GABA
- Purines
- Haem
What two pathways remove nitrogen from amino acids?
Transamination
Deamination
What are the two key aminotransferases involved in transamination and how do they differ?
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Converts alanine to glutamate (and alpha-ketoglutarate to keto acid)
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
Converts glutamate to aspartate (and oxaloacetate to keto acid)