13 - Urinary Incontinence Flashcards
When somebody loses weight from vomiting where is this weight lost from?
ECF so loss of fluid not body mass
When does urinary incontinence occur?
- When bladder pressure is greater than urethral sphincter pressure.
- Can be due to high detrusor pressure or low urethral sphincter pressure

What are the different tissues that achieve continence?
- Smooth muscle of urethra
- Peristriated muscle
- Elasticity of connective tissure
- Ligaments of pelvic floor
What are some neurological causes of urinary incontinence?
Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia can cause issues with voiding

What are some lower urinary tract symptoms?

What are the different types of incontinence?
- Function UI also

What is functional urinary incontinence?

How is an overactive bladder linked to urinary incontinence?

What is the prevalence of UI with age?
- Increases with age, especially amongst women
- Peak increase around the time of menopause

Which type of urinary incontinence is the most common?
Stress then mixed

What are the risk factors of urinary incontinence?
- Red is just female
- Prostate cancer
- Hysterectomy
- Blockage
- Chronic cough

What should you do when someone presents to you with UI?
- History
- Examination
- Refer for investigations

What are some investigations you can do into a patient with urinary incontinence?

What type of incontinence may occur when a male has his prostate removed?

What is a pressure flow study?
- Measuring bladder pressure and detrusor pressure
- Detrusor = bladder pressure - abdominal pressure
- Can see if you have detrusor underactivity and measure obstruction to voiding
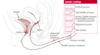
What can be some temporary causes of UI?
- Stone in bladder
- Tumour
- Intravesicular inflammation e.g UTI
What is generic management of all types of UI?
- Depends on which symptoms and how much it bothers the patient. Personalise treatment to patient

How can you deal with a patient that has failed to respond to conservative or medical management of UI?
- Surgical
- Indwelling catheter
- Sheath device
- Incontinence pads

How can we manage a patient with stress UI?
- Pelvic floor muscle training: 8 contractions, 3 times a day for at least three months
- Duloxetine: NA and serotonin uptake inhibitor. Increased activity of striated sphincter in filling
- Surgery
What are some surgical options to treat stress UI in females?
- Permanent: open retropubic suspension, classical autologous sling, low tension vaginal tapes
- Temporary (if more pregnancies wanted): intramural bulking agents that are injections of silicone and collagen to allow urethra to resist increased abdominl pressure

What are some surgical options to treat stress UI in males?
- Artifical urinary sphincter
- Male sling procedure

How can we manage a patient with urgency urinary incontinence?
- Bladder training: schedule of voiding for 6 weeks, void ever hour and do not void inbetween for example and increase by 15-20 mins until 2-3 hours
- Anticholinergics
- B3 adrenoreceptor agonist
- Intravesical injection of botulin toxin (inhibits release of Ach) (3rd line)
- Surgical (last resort)

What are some drugs used to treat UUI?
- Anticholinergics (M2/M3): oxybutynin. Side effects like dry mouth and constipation
- B3 agonist: mirabegron increases bladder’s capacity to store urine
- Botulinum toxin: type A, lasts 3-6 months.
What are some surgical options for UUI?

What is enuresis?
Involuntary wetting during sleep at least twice a week in a child aged over 5 with no CNS defects

What are some questions you need to ask in a history with a child presenting with enuresis?

How can you manage a patient that presents with enuresis?
- Primary without daytime symptoms: reassurance, alarms, positive reward system, desmopressin
- Primary with daytime symptoms: may be anatomical so refer to secondary care
- Secondary: treat underlying condition, e.g UTI, constipation, family problems, psychological problems

Fill in the following table to distinguish the difference between the different types of urinary incontinence?


What are the two types of urodynamic study?
- Voiding pressure flow study for voiding
- Cystometrogram for filling and storage

What are the different parameters that can be measure on a voiding pressure flow study and what is the shape of this graph if voiding is normal?
- Can tell you if there is an obstruction as detrusor pressure and urinary flow rate can give you outlet resistance
- Should be bell curve with rapid onset and slow decline in flow

What can a cystometrogram give you an idea of and what should it look like?
- Bladder contractility
- Pressure should maintain the same or increase very slowly during filling
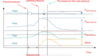
What are the three different types of urinary retention?

What are some host defences against UTIs?

What are the symptoms of a UTI?

What are some factors of a patient’s history that would make you suspect a complicated UTI?

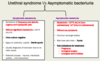
How can you tell the difference between urethral syndrome and asymptomatic bacteriuria?