13 - Pancreas Flashcards
What is the shape of the pancreas and where is it found?
- Behind the stomach
- Head and tail
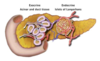
Where is the pancreas derived from?
Foregut
Where are hormones stored in the pancreas?
- Islets of Langerhans
- Stored intracellularly in vesicles
When are the hormones of the pancreas released, what tissues do they act on, what metabolism do they affect and how?

What is the structure of insulin?
- Two polypeptide chains (A and B)
- Chains linked by two disulphide bonds
- Third intra-chain disulphide bond in A chain

How is insulin synthesised?-
1. Preproinsulin (single chain 109aa)
2. Proinsulin (86 aa) when signal sequence cleaved in ER
3. Proinsulin folds to allow disulphide bonds to form
- Proinsulin goes from ER to golgi then into vesicles
5. Proteolysis in vesicles removes connecting peptide (C-peptide 31aa with 4 basic aa)
- Single chain has been broken into two from proteolysis and they are held by disulphide bonds
- Vesicles secrete C-peptide and insulin in equimolar amounts
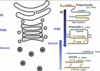
How are the cells arranged in the islets of Langerhans?
- Alpha peripherally
- Beta centrally

What is the normal blood plasma glucose and what is the renal threshold?
- 3-3.6 mmol/L
- 7-8 mmol/L after meal
- Renal threshold is 10mmol/L
How are insulin and glucagon transported around the blood?
- Water soluble so dissolved in plasma, no transport proteins
- Free hormone
- Short half life
How can you measure endogenous insulin secretion?
Measure plasma C-peptide levels
How is insulin stored in the beta cells?
Crystalline zinc-insulin complex
What are the target cells of insulin?
- Liver
- Skeletal muscle
- Adipose tissue
What receptors do the insulin and glucagon hormones use?
Insulin = tyrosine kinase
Glucagon = GPCR (Gs)
What are the actions of insulin?
- Affects Carbohydrate, Lipid and AA metabolism
- Affecting cell growth and division in long term as it can stimulate DNA and protein synthesis

How is insulin secretion controlled?
- Metabolite levels (e.g high blood glucose)
- GI tract hormones (gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin)
- Neurotransmitters (A/NA/Ach)
(A/NA inhibit secretion whilst others stimulate)

How does insulin increase glucose uptake in target cells?
- Insertion of GLUT4 into membrane

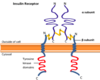
What is the structure of the insulin receptor?
- Dimer
- Two identical subunits connected by disulfide bond
- Alpha chain exteriorly, Beta chain span cell membrane
What is the structure of glucagon?
- Single chain 29 aa hormone
- NO DISULPHIDE BONDS
- Flexible 3D structure that takes active conformation when binding to its receptor on surface of target cells

How is glucagon synthesised?
- Alpha cells in pancreas
- Preproglucagon in cells then post translational modification
- Margination and exocytosis
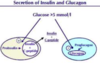
What effects does glucagon have?

When is glucagon used clinically?
In emergency can inject when person with diabetes is hypoglycemic and cannot take sugar orally
How does glucagon act on its receptor to stimulate changes?
- Gs GPCR
- PKA phosphorylates and activates important enzymes in target cells
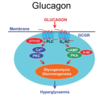
How is the secretion of glucagon controlled?
- Decreased blood glucose stimulates release
- Inhibition of release by insulin and increased blood glucose
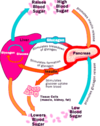
What is diabetes mellitus characterised by?
- Chronic hyperglycaemia
- Elevate glucose in urine

What is type 1 diabetes?
- Absolute insulin deficiency by autoimmune destruction of B-cells
- Mainly in the young
- Rapidly fatal if not treated



