11: Newborn Assessment Findings Flashcards
This is the name for the abnormal fusion of the digits (fingers or toes).

Syndactyly
Nonunion of the two rectus muscles from the umbilicus to the xiphoid causing a mild herniation in the midline.

Diastasis Recti
This is the term for widely spaced eyes as depicted below. The diagnosis should be made on the measurement of the inner canthal distance.

Hypertelorism
Foot problem associated with genetic syndromes, particularly trisomies.

Rocker Bottom Feet
These vascular lesions are normally seen on the occipital area, eyelids, and glabella. They disappear spontaneously within the first year of life.

Macular Hemangioma (Stork Bite)
The frenulum on the underside of the tongue prevents complete tongue protrusion.

Ankyloglossia (Tongue Tie)
Numerous small areas of red skin with a yellowish/red papule at the center.

Erythema Toxicum
This skull deformity is the result of a hemorrhage, usually from a traumatic or forceps delivery. It does NOT cross suture lines.

Cephalohematoma
Approximately 40% of full-term infants have these multiple yellow or pearly-white papules. They are benign and usually diappear within a few weeks.

Milia
Dark blue or purple macular areas resembling bruises, usually located over the lumbosacral area.

Mongolian Spots
These small white inclusion cysts generally cluster around the juncture of the hard and soft palates. This is a normal finding that generally resolves with sucking.

Epstein Pearls
Present in approximately one in 3,500 live births.

Natal Teeth
Transient condition of unknown cause. Characterized by pustules, vesicles, and hyperpigmented macules.

Pustular Melanosis
Adduction of the forefoot, correctable with active ROM. Most common congenital foot deformity.

Metatarsus Adductis
Deep red or purple in color, usually present at birth, blanch only minimally with pressure, do not disappear with time.

Port Wine Stain (Nevus Flammeus)
These “salt and pepper” spots of the iris are often seen with Down syndrome.

Brushfield Spots
This fold over the medial aspect of the eye may be familial but occurs in less than 1% of the population. It is also seen as a common feature of Down syndrome and other syndromes.

Epicanthal Folds
The arm is in the position of tight adduction and internal rotation of the shoulder with arm extension and pronation at the elbow.

Erb-Duchenne Palsy
Erb’s Palsy
Brachial Plexus Injury
A diffuse edematous swelling of the soft tissues of the scalp, which may extend over suture lines.

Caput Succedaneum
Rupture of small conjunctival capillaries, which can occur normally but is most common following a traumatic delivery.

Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
A lacy red pattern noted on the skin seen in the infant with cold stress, hypovolemia, or sepsis.

Cutis Mamorata
A single transverse palmar crease. Highly associated with congenital abnormalities.

Simian Crease
Yellow color of the skin as a result of increased bilirubin levels, which are usually visible at bilirubin levels greater than 5 mg/dL

Jaundice
This congenital structural depression of the sternum is usually of no clinical concern.

Pectus Excavatum
This congenital defect occurs in one in 3000 males where the placement of the urethral meatus is anywhere between the tip of the glans and the perineum.

Hypospadius
The feet are turned downward and inward, and the sole is directed medially.

Club Feet (Talipes Equinovarus)
Raised, pigmented areas found vertical and medial to the true nipple.
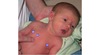
Supernumerary Nipple
Usually appears within a few days of birth as a raised pink or red macule that is sharply demarcated.

Strawberry Hemangioma
Results from incomplete fusion of the palate.

Cleft Palate
The reflex occurs by placing the infant in the supine position and turning the head to one side. The upper extremity on the side that the head is turned toward should extend, and the upper extremity on the opposite side should flex.

Tonic Neck (Fencing)


