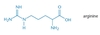
1.1 Amino Acids Found in Proteins Flashcards
Biochem Chapter 1 represents 20% of all biochem questions on the MCAT. Know this stuff!!
What are the 7 nonpolar, nonaromatic Amino Acids?

What are the 3 aromatic Amino Acids?

What are the 5 Amino Acids with polar side chains?

What are the 2 Amino Acids with negatively charged (acidic) chains?
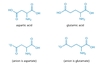
What are the 3 Amino Acids with positively charged (basic) side chains?

What are the 3-letter abreviations and 1-letter abbreviations for all 20 amino acids?


The alpha carbon, is the carbon adjacent to?
The carboxyl carbon
The 20 alpha-amino acids encoded by the human genetic code are knows as?
Proteinogentic amino acids


All chiral amino acids in eukaryotes are L-amino acids, so the amino group is drawn on the left in a Fischer projection. In the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system, this translates to an (S) absolute confirguration for almost all chirla amino acids. The exception is what, and why?

Cysteine
Which while still being an L-amino acid has an (R) absolute confiruation becase the -CH2SH group has priority over the -COOH group


Which amino acids have amide side chains and why is this important?
Asparagine and Glutamine
Unlike the amino group common to all amino acids, the amide nitrogens do NOT gain or lose protons with changes in pH; they do NOT become charged.

Cystein has an -SH group in its side change, which is know as a?
What about this group makes it prone to oxidation?

Thiol
Because sulfur is larger and less electronegative than oxygen, the S-H bond is weaker than the O-H bond.

Unlike asparagine and glutamine, aspartate and glutamate have corboxylate (-COO-) groups in their side chains, rather than?
amides

Histidine has an aromatic ring with two nitrogen atoms. Thsi ring is called an?
Histidine is one of the positively charged side chains but given its ring stucture, how can histidine acquire a positive charge?

imidazole
The pKa of it’s side chain is about 6, which is relatively close to physiologic pH (7.4) so, at physiologic pH, one nitrogen atom is protonated and teh other isn’t, Under more acidic conditions, the second nitrogen atom can become protonated, giving the side change a positive charge.
The surface of a protein tends to be rich in amino acids with _______ side chains.
Strongly hydrophobic amino acids tend to be found in the __________ of proteins.
charged
interior
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Glycine
Gly
G
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Glycine
Gly
G
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Alanine
Ala
A
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Alanine
Ala
A
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Valine
Val
V
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Valine
Val
V
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Leucine
Leu
L
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Leucine
Leu
L
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?
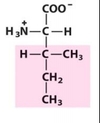
Isoleucine
Ile
I
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Isoleucine
Ile
I
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Methionine
Met
M
Name this amino acid. What is it’s 3-letter abbreviation and it’s 1-letter abbreviation?

Phenylalanine
Phe
F
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Methionine
Met
M
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Proline
Pro
P
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Proline
Pro
P
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Tryptophan
Trp
W
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Tryptophan
Trp
W
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Phenylalanine
Phe
F
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Tyrosine
Tyr
Y
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Tyrosine
Tyr
Y
Name this amino acid. What is its 3-letter abbreviation and its 1-letter abbreviation?

Serine
Ser
S