11/17- Pediatric Urology Flashcards
What are causes of acute scrotum?

- Testicular torsion
- Torsion of the appendix testes
- Epididymo-orchitis, epididymitis
- Trauma
- Incarcerated hernia
- Scrotal wall process: HSP, Fournier’s
What are the 2 types of testicular torsion?
When does each typically occur?
1. Extravaginal- perinatal (almost exclusively)
2. Intravaginal- perinatal and older (most common in 8-30 yo)
What is extravaginal torsion? Treatment?
Torsion of entire cord proximal to tunica vaginalis attachment
- Tx: Salvage of torsed testis unlikely; surgery to protect contralateral testis is controversial

What is intravaginal torsion?
Torsion distal to tunica vaginalis attachment
- Bell-Clapper or horizontal lie predisposes to torsion
- (Recall: most common in 8-30 yo, rare in older, but not uncommon in younger)

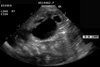
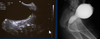
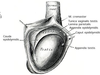
What is shown here?

Bell Clapper Deformity
- Risk factor predisposing someone to torsion (intravaginal)
What is the presentation of testicular torsion?
- Acute, severe pain
- Scrotal swelling
- N/V
What are physical exam findings of testicular torsion?
- Erythema, edema, loss of cremasteric reflex, high riding testis
- Caveat: Not all older children/adults have a cremasteric reflex
- Absence does not mean torsión
- Hard, non-tender testis in infant: antenatal/neonatal torsion
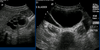
How is testicular torsion diagnosed?
Ultrasound (see lack of blood flow) is definitive but not mandatory if:
- high index of suspicion
- obtaining study will delay care

How are pts with suspected testicular torsion managed?
Manual reduction with narcotics
- ONLY IF SURGERY NOT AVAILABLE
- “Open the Book”
- Both inward and outward rotation occurs
Prompt surgical exploration
- Detorsion of testis with orchiopexy or orchiectomy
- Orchiopexy for contralateral testis
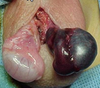
What are salvage rates by time?
- 0-6 hrs: 85-90%
- 6-12 hrs: 50%
- >24 hrs: 5% or less
What are the embryological sources of the appendix testes? Appendix epididymis?
- Appendix testes: Mullerian system
- Appendix epididymis: Mesonehpros
What is the presentation of torsion of the appendix testes/epididymis?
- Slow, gradual onset over days
- Less nausea and vomiting
- Pain related to inflammation caused by necrotic structure
What are physical exam findings of torsion of the appendix testes/epididymis?
“Blue Dot” Sign
- Necrotic appendage seen through thin scrotal skin
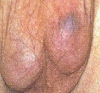
What is treatment for torsion of the appendix testes/epididymis?
If diagnosis certain, then treat with comfort care:
- Anti-inflammatories
- Analgesics
- Scrotal support
What are infectious processes that contribute to epididymo-orchitis, epididymitis, and orchitis? Non-infectious?
Infectious:
- Children: UTI
- “Young man’s”: STD
- “Old guy’s”: UTI
- TB and mumps are rare
Non-infectious
- Medications (amiodarone)
- Urine reflux into ejaculatory ducts
- Trauma
Describe the presentation of epididymo-orchitis, epididymitis, and orchitis?
- Gradual, progressive onset of pain
- Irritative, voiding symptoms
What are physical exam findings for epididymo-orchitis, epididymitis, and orchitis?
Tenderness posterior and lateral to the testis (the usual location of the epididymis)
Describe diagnosis of epididymo-orchitis, epididymitis, and orchitis
- Urinalysis and culture if indicated
- Imaging with scrotal ultrasound
- Enlarged, hypervascular epididymis
- Normal or increased testicular blood flow
What is the treatment for epididymo-orchitis, epididymitis, and orchitis?
If infectious cause:
- Antibiotics, scrotal elevation, analgesics, rest
- Evaluate for possible urinary anomaly
If non-infectious process:
- Anti-inflammatories
- Analgesics
- Scrotal elevation
- Rest
Which gender has highest risk/rate of UTI in 1st year of life?
Males
What is one main determining risk factor for male UTIs?
Circumcision status
- Uncircumcised UTI risk is 3-12x circumcised
- Routine neonatal circumcision for medical benefit is not supported by the AAP
What are congenital GU causes of UTIs in males?
- Nonfunctioning renal segments
- Obstructive defects in the GU tract
- Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
- Neurogenic bladder
- Poor emptying
- Clean intermittent catheterization (CIC)
What are acquired GU causes of UTIs in males?
- Kidney stones
- Voiding dysfunction
What are pathologic consequences of UTI?
- Cystitis
- Acute and Focal Pyelonephritis
- Pyonephrosis
- Perinephric or Renal Abscess
- Renal Scarring
- Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis (XGP)
What are symptoms of UTIs?
Infants/young children: vague symptoms
- Fever*, irritability, poor feeding, vomiting, diarrhea
Older children
- May describe localizing symptoms: dysuria, suprapubic pain, incontinence, voiding dysfunction
- May have generalized symptoms: fever, vomiting
What are physical exam findings with UTI?
- Flank or abdominal tenderness
- Perineum
- Labial adhesions
- Ectopic ureteroceles
- Scrotal changes: epididymitis
- Phimosis
- Sacral dimple, skin lesion, hair
- Neurogenic bladder
What are diagnostic tests for UTIs?
- Urinalysis
- Urine culture (gold standard); may take 24-48 hrs for result
(According to AAP guidelines, whether/not to pursue workup on infants [2-24 mo] with fever depends on likelihood of UTI)