10. Management of Pain - Opioids Flashcards
What are 6 examples of Opioid analgesic?
Opioid analgesics - Examples
- Morphine
- Codeine
- Oxycodone
- Fentanyl
- Tramadol
- Methadone
Opioid analgesics exert their effects by acting on which receptors?
4 types?
What kind of receptors are they?
What are they stimulated by?
Opioid Receptors
Opioid analgesics exert their effects by acting as agonists on opioid receptors
- These receptors are
- mu (μ),
- kappa (κ),
- delta (δ) opioid
- opioid receptor like-1 (ORL1)
- Opioid receptors are stimulated by endogenous peptides called endorphins, and all are G protein-coupled receptors
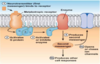
Where do Opioids (Narcotic) Analgesics exert activity?
How?
Opioids (Narcotic) Analgesics
- Opioid (narcotic) analgesics exert activity in a number of sites within the brain and spinal cord
- They exert their analgesic effects primarily by stimulating mu (μ) receptors (some kappa (κ) and delta (δ) stimulation also)
- Mu (μ) receptor stimulation increases the opening of K+ channels causing hyperpolarisation and an inhibition of the opening of voltage-gated Ca ++ channels and reduced transmitter release
- This decreases neuronal excitability and cellular function
What kind of pain is Opioids (Narcotic) Analgesics effective against?
Opioids (Narcotic) Analgesics
- Opioid (narcotic) analgesics are effective against a wide variety of pain states
- They relieve most types of pain but are more effective against dull, constant pain rather than sharp, intermittent pain
- It is important to note that neuropathic pain generally responds poorly to opioid (narcotic) analgesics
- Opioid (narcotic) analgesics may also change a patient’s perception of their pain
- A patient may remain aware of their pain but they become far less agitated and distressed by it
- Tolerance may develop with the repeated use of opioid (narcotic) analgesics resulting in the need to increase the dose to maintain adequate pain relief
Apart from producing analgesia, what are 7 other effects exerted by opioid (narcotic) analgesics?
Opioids (Narcotic) Analgesics - Effects
Apart from producing analgesia, opioid (narcotic) analgesics also exert the following effects:
- Sedation, mental clouding and mood changes including euphoria and dysphoria → mu (μ) receptors
- Respiratory depression due to a reduction in the responsiveness of the respiratory centre to carbon dioxide → mu (μ) receptors
- Nausea and emesis → direct stimulation of the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ)
- reduces with ongoing therapy
- Decreased gastrointestinal motility and constipation
- Pupillary constriction (pinpoint pupils)
- Suppression of the cough reflex → inhibiting the cough centre in the medulla
- Physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms following continued use/abuse
How do Opioids cause decreased gastrointestinal motility and constipation?
Opioids (Narcotic) Analgesics
Decreased gastrointestinal motility and constipation
- There are many opioid receptors in the gastrointestinal tract (mu (μ) receptors mainly)
- Cause an increase in the tone of gastrointestinal smooth muscle, but reduced peristalsis
- Management plan to treat constipation with longer term use
- Use of codeine, loperamide and diphenoxylate to treat diarrhoea
How do Opioids cause pupillary constriction (pinpoint pupils)?
Opioids - Pupillary constriction (pinpoint pupils)
- Due to stimulation of the oculomotor nucleus which causes increased tone of the parasympathetic nerve fibres innervating the pupillae constrictor muscles of the pupil
- mu (μ) and kappa (κ) receptors
Of the effects of opioids, which can you develop tolerance to and which can’t you?
Opioids - Tolerance
- Tolerance develops to
- analgesia
- respiratory depression
- nausea and vomiting
- cough suppression
- sedation, mental clouding and euphoria
- Tolerance does not develop to
- pupillary constriction (pinpoint pupils)
- decreased gastrointestinal motility and constipation
What is Codeine?
Which receptors does it act on?
What is it converted into and by which enzyme?
Codeine
- Codeine is a weak agonist at mu (μ) receptors
- Codeine is converted to morphine in the body by the cytochrome P450 enzyme 2D6
- It is thought that the analgesic effect of codeine is due primarily to its conversion to morphine
- The cytochrome P450 enzyme 2D6 is subject to genetic variation
- About 7 to10% of the European white population are poor metabolisers of codeine and possibly receive no analgesic effect from codeine
- Can’t convert it to morphine
What is Tramadol?
Which receptors does it act on?
What is it converted into and by which enzyme?
What can tramadol induce?
What is it used to treat?
Tramadol
- Is a weak agonist at mu (μ) receptors
- It is metabolised by the cytochrome P450 enzyme 2D6 to an active metabolite, O- desmethyltramadol, which is a more potent agonist at mu (μ) receptors
- Tramadol also inhibits the reuptake of noradrenaline and serotonin at nerve terminals (contribution to analgesic effect?)
- It may induce the Serotonin Syndrome
- It is used to treat moderate to severe pain
What is Buprenorphine?
What is the benefit of Buprenorphine over other opioids?
Buprenorphine
- Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist which acts at mu-opioid receptors - analgesic ceiling effect
- It binds to and dissociates from the mu-receptor slowly - longer duration of analgesia
- Slow dissociation from the mu-opioid receptors reduces opioid withdrawal symptoms and craving for opioids - use in opioid maintenance treatment programs
- It also has antagonistic activity at kappa (κ) receptors
What is Naloxone?
Which receptors does it act on?
What is it used for?
Why may it need to be given on multiple occasions?
Naloxone
- Naloxone is a completive antagonist of opioid (narcotic) analgesics at mu (μ) > kappa (κ) > delta (δ) receptors
- In the absence of opioid (narcotic) analgesics it exhibits essentially no pharmacologic activity
- Used to treat opioid (narcotic) analgesic overdose
- It has a short half life (1-2 hours) and the duration of action of some opioids may exceed that of naloxone (may need to be given on multiple occasions in the treatment of overdose)
- May be given IV, IM, SC or as a nasal spray
- It is an S3 medicine available from pharmacies
Give an example of an opioid which is a:
- Full agonist?
- Partial agonist?
- Competitive antagonist?
Full Agonist, Partial Agonist and Competitive Antagonist
- Methadone has affinity and maximum efficacy or intrinsic activity (full agonist)
- used for opioid maintenance therapy in opioid dependence and for chronic pain management.
- Buprenorphine has affinity and reduced efficacy or intrinsic activity (partial agonist)
- Naloxone has affinity but no efficacy or intrinsic activity (competitive antagonist)
- used to prevent opioid overdose
What are Analgesic Adjuvants?
When are they used?
2 examples?
Analgesic Adjuvants = medications which are not primarily designed to be analgesics but can exert analgesic activity in neuropathic pain
- Neuropathic and nociplastic pain are very often refractory to simple analgesics - NSAIDS, paracetamol
- Neuropathic and nociplastic pain are less responsive to opioids than nociceptive pain (sometimes not responsive), so higher doses are generally required - adverse effects, dependence etc
- Examples include
- Tricyclic and other antidepressants
- Antiepileptic drugs
How can tricyclic antidepressants be used as Analgesic Adjuvants?
Analgesic Adjuvants - Tricyclic antidepressants
- Tricyclic antidepressants (eg. amitriptyline) are used in the treatment of neuropathic pain
- They relieve pain independently of their antidepressant effect
- Their exact mechanism of action is not known but may involve inhibition of noradrenaline and serotonin reuptake, and an increase in gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) activity
- The doses used to treat neuropathic pain are less than those used to treat depression
- The SNRIs duloxetine and venlafaxine may also be effective
How can Antiepileptic drugs be used as Analgesic Adjuvants?
Adverse effects?
Analgesic Adjuvants - Antiepileptic drugs
- Antiepileptic drugs - eg. gabapentin and pregabalin are used to treat neuropathic pain
- Their exact mechanism of action is not known but may involve an increase in gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) activity, and an action on voltage-gated calcium channels in the spinal cord and brain which reduces the release of several neurotransmitters including glutamate, noradrenaline and substance P
- Adverse effects include dizziness, somnolence, weight gain and suicidal thoughts and behaviour


