1. Skull Vault and cervical spine Flashcards
skull vault a.k.a
calvaria
roof of cranial cavity
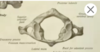
norma verticalis
view of skull from above

norma frontalis
view of skull from front
norma lateralis
view of skull from side
normal occipitaris
view of skull from behind
frontal eminence
left and right sides (yellow)
most prominent part of upper forehead
similar curvature to rest of bone - more likely male

frontal bone in young child

young child (2-3 years) is in 2 halves which fuse together by school age
8% have 2 halves for life
metopic suture in between
parietal bones
over the parietal lobes of brain (yellow)
right and left

parietal eminence
sides of skull (orange)
curvature similar to rest of skull - more likely male
more markedly curved - more likely female

sutures
fibrous joints join bone of skull together
unossidied parts of membrane
assisting parts of membrane
serrated interlocking pattern
coronal suture
from side to side
separates frontal bone from 2 parietal bones

sagittal suture
front to back - like sagittal plane
midline of coronal suture to occiptal bone

anterior fontanelle
child of 18-24 months has a diamond shaped opening called anterior fontanelle
closes completely at 2 years
metopic suture (between 2 halves of frontal bone) meets coronal and sagittal sutures
soft point

ossification of skull
Bones of skull form a membrane in embryo
- Intramembranous ossification
Membrane forms from mesenchyme
- Mesenchymal differentiate into osteoblasts and lay down the bone
No cartilage precursor in vault of skul
parietal foramen
Carries vein from veins in skull to veins inside head
Venous communication between inside and outside of cranial cavity

lambdoid suture
joins sagittal suture
Upside down V
Like Greek letter Lambda

sutural/Wormian bones
islands of bones seen in sutures

sutures use in fetal life
Grow as new bone being laid on outside and resorbed at inside
- Can occur at sutures
Thin bones at time of birth, sutures allow little movement of skull so baby’s head can pass through birth canal
occipital bone
at rear of skull
Lambdoid suture separates parietal and occipital
Part in vault of skull
- Squamous part of occipital bone
Part in base of skull
- Basilar part
below occipital protuberence

external occipital protuberence
most posterior part of skull
muscles of neck attach below that

frontal bone
Forehead and roof
Gabela – midline front above bridge of nose
Coronal suture separates from parietal bones

temporal bone
Passage of time – hear goes grey at this area first
Squamous part
- Flat piece on side of vault of skull
Zygomatic process
- Comes forward – meets zygomatic bone at suture
- Zygomaticotemporal suture
Mastoid part
- Rear on outside
Mastoid process - behind ear
- Helps differentiate sex – males larger than females in general
- Forms at age of 2
External acoustic metauts with bone on outside tempanic plate
- Styloid process - Long bone process done to mandible
Petrymastoid parts
- Dense bone inside skull

sphenoid bones
butterfly shaped
greater and lesser wings
lies on floor of cranial cavity across midline
extends to side of skull and contributes to normal lateralis - greater wing
pterion
sutures join in H shape
Means wing, like Mercury God
Thin area of skull – can be easily broken
- Middle meningeal artery run in grove below this
Extradural haemorrhage risk