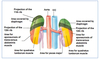
1 - Anatomy of the Urinary System Flashcards
What is the location of the kidneys in the body? (use anatomical landmarks)
- Upper pole: T11/12 for L and T12 for R
- Lower pole: L2/3 for L and L3/4
- Hilum: L1
- Top of the kidey is at the 12th rib on the right
- Retroperitoneal
- Ureter travels at tips of transverse process and kinks at the ischial spine

What is the size of the kidneys and at what size should we be investigating pathology of the kidneys?
- 6 to 7 cm by 9 to 14 cm (males larger)
- Less than 8cm length need to be referred, maybe CKD
- If difference in sizes of each kidney by >2cm

Label this CT scan of the abdomen.
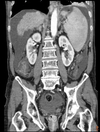
Ignore protate label on the right, it is the label at the bottom that is correct

What is the renal angle?
- Area you can ballot for the kidneys
- Patient will feel tenderness here is kidney is inflammed, e.g perinephric abscess

What are the renal fascial layers and what is their importance?
- Gerota’s fascia or renal fascia
- Collagen bundles in the fascia keep the renal fat and kidneys in place as no ligaments hold the fascia
- Perirenal fat continuous with fat in hilum and pararenal is with lumbar region

What is the anatomy and function of the ureter?
- Smooth muscle propelling urine to bladder
- 25-30 cm retroperitoneal
- Ureter splits into 3 after pelviuteric junction

Where is the most common area of utereric injuries?
- Near pelvic brim
- Near where uterine vessels are, e.g in hysterectomy they may be accidentally ligated

In the pelvis what is the ureter crossed by?
Man: Ductus deferens in front, seminal vesicles behind
Woman: Uterine Artery and Ovary in front and passes into base of broad ligament
Water under the bridge

Where does the ureter enter the pelvic cavity?
Area anterior to the bifurcation of the common iliac artery
Why does urine reflux from the bladder into the ureters not occur?
- Intramural segment of the ureter runs obliquely and posterolaterally through the muscle of the bladder wall and coalesces with the destrusor muscle
- Ureter enters low down on the base of the bladder
- 1.5-2.5cm
- No sphincter at VUJ, bladder muscle stretches and contracts to stop urine passing back up

What is the epithelial lining of the utereric wall like?
Lumen covered in urothelium that is found in the bladder, ureter and pelvis of the kidney (transitional cells)

What are some anatomical variations in the positioning of the ureters?
- Duplex ureter with both entering bladder (asymptomatic)
- Duplex ureter with one not entering bladder (constant dribbling of urine will need sorting)
- Retrocaval around the IVC (rare)

What is a trigone?
- Triangular area formed by the two ureteral orifices and the internal urethral orifice. Sensitive to stretch and when stretched, need to urinate
- Smooth, no rugae

What are the two pouches found around the uterus?

Label this diagram of the female urinary system.
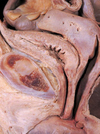

What is the urachus?
- Fibrous remnant of the allantois, canal that drain bladder of fetus through the umbilical cord.
- Median umbilical ligament on anterior abdominal wall

What does it mean if a cadaver has a thin detrusor muscle?
They had urinary retention so their bladder was stretched

Label this diagram of the male cadaveric urinary system


What are the male urethral divisions?
- Prostatic
- Membranous
- Penile/Spongy
IUS has sympathetic innervation that when signalled contracts to stop bladder being full of semen. No big role in women

What are the female urethral divisions?

Label this diagram of the kidney collecting system.
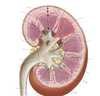
- Once in collecting ducts already urine
- Glomeruli only in cortex
- Stripes in renal pyramid due to collecting ducts

What is the function of the nephrons in basic terms?

What are the two different types of nephrons - compare and contrast them.
- Cortical
- Juxtamedullary
Differences mainly in their LOH, with corticals shorter

In macroscopic terms, what is the blood supply to the kidneys and how would you locate it on a cadaver?
- Right and Left renal arteries from the AA
- Find superior mesenteric artery and renal just below
- Can have some accessory renal arteries
- When renal artery enters hilum splits into anterior and posterior branches