0729- anatomy of kidney- CG Flashcards
Name 3 functions of kidney (renal physician)
- Regulate body fluid, electrolyte balance and acid-base balance.
• Remove metabolic wastes and toxins (urea, urobilinogen)
(RFT: EUC [urea creatine, CMP- calcium, mg, phosphate)
• Endocrine functions
erythropoietin, renin).
Outline the plumbing system of urinary system (urologist)
Ureters transport urine from kidney to bladder.
Bladder stores urine.
Urethra discharges urine from body.
Label
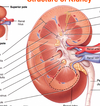
NB- renal sinus is the whole area occupied by calyx, blood vessels in renal pelvis
It’s actually empty space
Renal pyrmid in medulla, topped by a renal cortex. Junction is where stuff flows

Name and label the renal segments
Anterior view
Superior (apical)
Anterosuperior
Anteroinferior
Inferior
Posterior view
Posterior
Inferior and superior bend onto posterior side
Kidney: segment –> lobe!
Lung and liver: lobe –> segments!
Outline the inflow and outflow of blood supply to kidney. Which is most clinically relevant?

How perfused are kidneys? Where is most of the blood in kidneys located?
Rich blood supply- 25% of total CO
90% blood in cortex, 10% in medulla
Altruistic organ- handle large amounts of blood but use little
Describe the kidney’s relationship to structures around it
Retroperitoneal space- T12 and 12th rib to sacrum/iliac crest) (between peritoneum and posterior abdo wall- psoas major and quadratus lumborum). left kidney- T11-L2, right- T12-L3)
Other retroperitoneal organs- SAD PUCKER
3 layers (from inside)
Fibrous capsule (renal capsule)
Adipose capsule (perirenal fat)- affix it to wall
Renal fascia (dense connective tissue)
Describe the ureters
Vertically down tips of transverse processes, sacro-iliac joint, and tip of ischial spines
3 constrictions- kidney stones more likely to lodge there
- Junction of renal pelvis with ureter (ureteropelvic junction)
- Crossing iliac blood vessels at pelvic brim
- ureters enter bladder (oblique course, functions like a valve)
Compare relation of ureters in male and females
In females-
Ureter lies below uterine artery (water under the bridge)- be aware when doing hysterectomies(need to ligate uterine a)
Also females have uterus anterior to bladder, males have vas deferens and seminal vesicles
Describe the bladder
Sections
- Apex!
- Base (posterior surface)!
- Superior surface (covered with peritoneum)!
- Inferolateral surfaces (X2)!
- Neck!
Position depend on filling (completely in pelvis when empty), extraperitoneal,
intra-abdominal, above pubis in children
(in males, can aspirate when full- pass needle right above pubic symphysis)
Describe features inside the bladder
NB ureteral openings have ‘valve’ to prevent backflow into ureters

Compare male and female urethra/bladders
Both has 2 sphincters- internal and external
Female- short, wide urethra, close to vaginal opening (UTIs more common)
Male- long, thin (esp prostate urethra), 2 curves- 1 in front of pubic symphysis- drooping dick..1 permanent- near bulb of penis, going up past bulbourethral glands)
in elderly males- may have trouble passing urine because of enlarged prostate
4 parts- prostatic, membranous, bulbar, penile


