04 Waves Basics and EM Spectrum - 3rd Form Flashcards
What is the use of UV radiation?
produced by tanning bed lights to tan skin
used to detect conterfeit money
Give three properties (features) common to all EM waves
They all…
travel at the speed of light
all transverse waves
all travel through a vacuum
all transfer energy and information without transferring matter
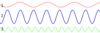
Which wave has the largest wavelength?

wave 1
largest distance between adjacent crests
List the EM spectrum in order of decreasing frequency
Gamma
X-ray
UV
Visible
IR
Microwave
Radio
How is wavespeed, wavelength and frequency related?
wavespeed = wavelength x frequency

Label the compressions, rarefactions and wavelength on the longitudinal wave below


What is 204 nm in m?
204 x 10-9 m
How can you make a longitudinal wave with a slinky?
move your hand in a forwards and backwards movement
How would you measure the frequency of waves passing a jetty?

Time how long it take for 10 waves to pass the end of the jetty
frequency = 10 waves / time for 10 waves to pass
Fred noticed that 10 waves passed a point in 5 seconds. What is the frequency of the wave?
frequency = 10 waves/ 5 s
= 2 Hz
What is 700 micrometres in metres?
700 x 10-6 m
Fred noticed that 10 waves passed a point in 5 seconds. What is the period of the wave?
Time period = 5 seconds / 10 waves
= 0.5 seconds for one wave to pass
Which wave has the largest amplitude?

wave 2
It has the largest displacement from the equilibrium
What is the unit for time period?
seconds or s
What is the unit for amplitude?
metres (m) or decibels(dB)
Define wavefront
A line joining points on a wave at the same point in their wave cycle

Why are UV waves dangerous?
They can damage the retina and damage eye sight
They can cause damage to surface cells and may cause skin cancer
What is the use of microwaves?
produced by microwaves to cook food
produced by mobile phones to communicate
Produced by satellites to send signals to satellite dishes
What is a transverse wave?
Where the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of energy travel
How do the waves of red light differ from waves of violet light
ROY G BIV
Red light-larger wavelength and lower frequency- it has less energy
Blue light- smaller wavlength and higher frequency- it has more energy
What are the uses of infrared radiation (IR)
emitted by ovens to cook food
emitted by radiators to heat houses
emitted by tv controllers to control t.v.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency of a wave?

As wavelength increases, frequency decreases
They are inversely proportional
What is the use of X-rays?
Used to detect breaks in bones
used to detect crystal structure in salts
List the EM spectrum in order of increasing frequency
Radio
Microwave
IR
Visible
UV
X-ray
Gamma