01 Intelligent agents Flashcards
(12 cards)
Intelligent agent
An agent is anything that can be viewed as perceiving its environment through sensors and acting upon that environment through actuators
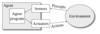
Rational agent
A rational agent is an agent that for every situation selects the action the maximizes its expected performance based on its perception and built-in knowledge.
Definition depends on:
– Performance measure (success criterion)
– Agent’s percept sequence to date
– Actions that the agent can perform
– Agent’s knowledge of the environment
This means that an agent can be rational under some asumptions, but may not be it under other asumptions.
The task of AI
The task of AI is to build problem solving computer programs as rational agents
Properties of environments
Fully observable vs. partially observable
Does the sensors detect all aspects relevant for selecting action?
Single agent vs. multi agent
Does the environment include other agents?
Deterministic vs. stochastic
Is the next state determined by current state and action?
Episodic vs. sequential
In episodic environments, the choice of action in each episode depends only on the action itself
Static vs. dynamic
Does the environment change?
Semidynamic: The environment itself does not change with the passage of time, but the agent’s performance score does
Discrete vs. continuous
Is the number of distinct percepts and actions limited?
Known vs. unknown
Are the outcomes and/or probabilities of all actions known to the agent?
Task environment characterization
PEAS
Performance measure
Environment
Actuators
Sensors
Types of agents
- *Table lookup agents** are only useful for tiny problems
- *Simple reflex agents** respond immediately to percepts
- *Model-based reflex agents** remember the state
- *Goal-based agents** act to achieve goals
- *Utility-based agents** maximize utility
- *Learning agents** improve their performance over time
Agents need environment models of increasing complexity
Table-driven agent
The table driven agent program is invoked for each new percept and returns an action each time using a table that contains the appropriate actions for every possible percept sequence.
Simple reflex agent
Simple reflex agents act only on the basis of the current percept, ignoring the rest of the percept history. The agent function is based on the condition-action rule: if condition then action.
This agent function only succeeds when the environment is fully observable. Some reflex agents can also contain information on their current state which allows them to disregard conditions whose actuators are already triggered.
Infinite loops are often unavoidable for simple reflex agents operating in partially observable environments. Note: If the agent can randomize its actions, it may be possible to escape from infinite loops.

Model-based reflex agent
A model-based agent can handle a partially observable environment. Its current state is stored inside the agent maintaining some kind of structure which describes the part of the world which cannot be seen. This knowledge about “how the world works” is called a model of the world, hence the name “model-based agent”.
A model-based reflex agent should maintain some sort of internal model that depends on the percept history and thereby reflects at least some of the unobserved aspects of the current state. It then chooses an action in the same way as the reflex agent. The reasoning may involve searching and planning.

Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents further expand on the capabilities of the model-based agents, by using “goal” information. Goal information describes situations that are desirable. This allows the agent a way to choose among multiple possibilities, selecting the one which reaches a goal state. Search and planning are the subfields of artificial intelligence devoted to finding action sequences that achieve the agent’s goals.
In some instances the goal-based agent appears to be less efficient; it is more flexible because the knowledge that supports its decisions is represented explicitly and can be modified.
Utility-based agents
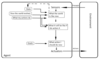
Goal-based agents only distinguish between goal states and non-goal states. It is possible to define a measure of how desirable a particular state is. This measure can be obtained through the use of a utility function which maps a state to a measure of the utility of the state. A more general performance measure should allow a comparison of different world states according to exactly how happy they would make the agent. The term utility, can be used to describe how “happy” the agent is.
A rational utility-based agent chooses the action that maximizes the expected utility of the action outcomes- that is, the agent expects to derive, on average, given the probabilities and utilities of each outcome. A utility-based agent has to model and keep track of its environment, tasks that have involved a great deal of research on perception, representation, reasoning, and learning.
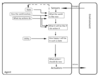
Learning agent
Learning has an advantage that it allows the agents to initially operate in unknown environments and to become more competent than its initial knowledge alone might allow. The most important distinction is between the “learning element”, which is responsible for making improvements, and the “performance element”, which is responsible for selecting external actions.
The learning element uses feedback from the “critic” on how the agent is doing and determines how the performance element should be modified to do better in the future. The performance element is what we have previously considered to be the entire agent: it takes in percepts and decides on actions.
The last component of the learning agent is the “problem generator”. It is responsible for suggesting actions that will lead to new and informative experiences.