Myofilaments Flashcards
anatomy of sk mm
-multi nucleated - below plasma membrane is the sarcolemma which is where the oval nuclei can be seen - dark nuclei lay adj to myofibrils - alternating light (I) bands and dark (A) bands that give the striped appearance

sacromere
myofibrils are chains of these contractile units
aligned end to end like coke cans
are between the two z lines

myofilaments
actin (thin filament) + myosin (thick filament, protein)
- contains ATPase which wil lsplit ATP to generate power for mm contraction
- thick filmaent is the length of the dark A band
- myosin contains the heads of the cross bridges

actin
thin filaments
contractile protein
aids in preventing contractions (the heads of myosin)
anchored to the Z disc
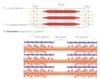
contraction process
when it occurs:
- actin filaments slide toward each other into the center of the sarcomere
- the H zone or bare zone disappear bc the actin and mysoin are completely overlapped
sacroplasmic reticulum
surrounds each myofibril (like a sleeve of loosely crocheted sweater material around your arm)
F: store and release Ca when the mm fiber is stimulated to contract

Sliding Filament Theory
MM contraction (filaments are actin and myosin, myson has the ehads like an oar in boat)
- electrical signal is sent, heads will attach to the binding sites of thin actin filaments
- creates sliding mechanism
- ATP supplies the energy, allowing pulling mechanism of thin filaments toward the center of the sacromere
- goes on simultaneously in sarcomeres through out the cell adn mm cell shortens
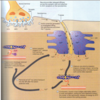
role of Ca in mm contraction
- attachment of myosin heads to actin require Ca
- AP stimualtes the SR to release Ca (where it is stored) into cytoplasm
- Ca trigger the binding of myosin to actin, initiates sliding
- AP ends, Ca absorbed into SR storage, mm relaxes and goes back to original length
happens in few thousands of a second
length of zones in contractions
A zones get closer together, but they do not change in length
light H zone in centre dissapears, Z discs are closer to thick filaments, I bands dissapered

myosin heads binding
heads cocked like hammer to gun or mouse trap
ATP allows for cock to recock (like crew team)
myofilaments do NOT shorten, just glide past each other
Troponin tropomyosin aid in “unnecessary contraction:” they cover the actin and are untwisted for contraction
T tubules and troponin/tropomyosin
transverse tubules that are extensions of the cell membrane that penetrate into the centre of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells
F: conduct impulses from surface of the cell (sarcolemma) down into the SR
creates opening for AP to travel in cell to SR
- Ca ions bring to troponin, troponin changes shape, removing blocking action of tropmyosin, actin active sites exposed
z line
formed btw adj sacromeres, where thin actin filaments attach

