Muscle Activity Flashcards
irritibility vs contractility
I - ability to receive and respond to stimulud
C - ability to shorten by force when an adequete stimulus is received
what is needed for mm to contract
nerve stimulus and action potential
- sk mm stimulated by nerve impulse to contract
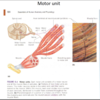
- one motor neuron (aka nerve cell) may stimulate fre or hundred mm cells, the one neuron and all the mm cells stimulated are called a motor unit
motor unit
consists of neuron and all the muscle fibers it activates
axon terminal, and synaptic cleft
nn fiber/axon extends from neuron to mm and branches into number of axon terminals
- each terminal forms junctions with sarcolemma of different mm cell and create a NMJ
- connection points - synaptic cleft
- never touch

Steps of NMJ
- nerve impulse reaches axon teminal, NT released (acetylcholine or ACh)
- diffuses accross synaptic cleft, attaches to receptors (membrane proteins) that are part of sarcolemma
- sarcolemma becomes more permeable ot Na+, it rushes into mm cell, while 2 K+ rush out (more Na enters than K+ leaves)
- cells inside have excess of +ions, results in change in electrical surrenct and action potential is generated
- Once AP started, cant be stopped. travels over entire surface of sarcolemma,
- contraction of mm
AcH
acetylcholine NT sent in AP
after AP, Ach is broken down to acetic acid and choline by enzyme acetylcholinesterase
- only one nerve impulse will make only one contraction
- this way the mm will not continue ot contract over and over in the absence of nerve impulse
- the mm cell relaxes until next stimulation

action potential visualization

“all or none”
contraction of sk mm
mm cell will contract to its fullest when stimulated adequetly, no partial contractions
are skeletal mm organs?
yes
thousand of mm cells that recat to a stimuli with a graded response
graded response
being able to vary the response of a mm contraction, allows for proper control of mm system
occurs in 2 ways:
- changing frequency of stimulation
- changing the strength of the stimulus (or by changing the # of cells being stimulated)
this allows us to pick up a pen vs picking up a 30 lbs weight
is impoulse does not slow down and continues to be delivered to mm…
mm will not relax completely, impulses builds until contraction of mm gets stronger and smoother
- this mm is now considered complete tetanus/tetanic contraction
- until this point is reached, mm is said to be incomplete tetanus
tetanus of lockjaw
caused by bacterium and causes mm to go into controllable spasm
can cause respiratory arrest
tetanos = convulsive, tension

