MSK Flashcards
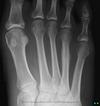
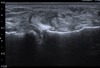
Rice bodies
TB and RA
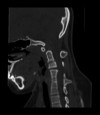
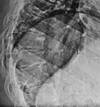
Diagnosis?
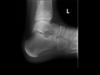
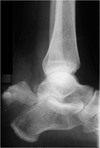
Sever’s
- calcaneal apophysis
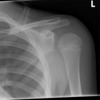
Diagnosis?

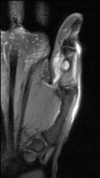
Bizarre parosteal osteochondromatous proliferation (BPOP)
- also known as Nora lesions
- benign osteochondral lesions which have the appearance similar to an osteochondroma
- typically seen in hands and feet
- continuous with underlying cortext without continuation of the medulla
Concern for septic joint. Sign and indication?

Pneumoarthrogram sign
- Presence of air in the joint excludes a joint effusion and is a normal finding
- No septic joint
T score vs Z score for DEXA
T score = Density relative to young adults
> - 1.0 normal, -1.0 to -2.5 osteopenia, < -2.5 osteoporosis
- False positive - absent normal structures such as laminectomy
- False negative - too much osteophytces, dermal calcifications, metal
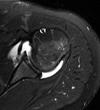
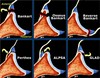
Name 4 types of impingments of the shoulder
- External Primary: abnormal coracoacromial arch
- External Secondary: multidirectional instability “increased glenohumeral volume” with injection
- Internal Posterior Superior: Throwers, posterior superior labrum torn
- Internal Anterior Superior: associated with subscapular damage
Diagnosis?

Os trigonum syndrome
Diagnosis?

Partial Ulnar Collateral Ligament Tear
- Throbwers, anterior bundle of ulnar collateral ligament torn (medial and poster bundles can also be involved)
- T sign
Diagnosis?

Monteggia Fracture
Best radiotracer for osteomyelitis in the spine?
Gallium > WBC scan (In-111)
Diagnosis?

Cortical Desmoid
- misnomer, not a true desmoid
- typically ages 10-15
- repetitive stress injury
- typically seen posterior medial femur at site of medial gastroc attachment or distal adductors
Grading of stress fracture on MRI
Grade 0: Normal
Grade 1: Subtle periosteal edema
Grade 2: Periosteal edema with marrow edema on T2
Grade 3: More edema with changes on T2 and T1
Grade 4: True stress fracture with visible fracture line on MRI or radiograph
Sign and diagnosis?

Double PCL
- Medial meniscus bucket handle tear
- Proves ACL is intact
Pincer type FAI keywords and associations
- Coxa profunda
- Acetabular protusion
- Prominent ischial spine
Asscoiated with os acetabuli, labral tears and early arthritis
Sign and associations?

Looser zones
- wide lucent bands that transverse bone at right anles to the cortex
- Classic locations are femoral neck and pubic rami and have surrounding sclerosis
- Think of osteomalacia and rickets, less common OI
- They are a type of insufficiency fracture
Diagnosis?

Medial epicondylitis
- less common than lateral
- seen in golfers
- common flexor tendon and ulnar nerve may enlarge from chronic injury
Name these 3 wrist factures

- Colles’ fracture - Dorsal angulation
- Smith fracture - Volar angulation
- Barton fracture - involving radial rum, volar is more common
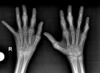
Diagnosis?

Thyroid acropachy (drumstick fingers)
Sign and association?

Arcuate sign
- avulsion of proximal fibula (insertion of arcuate ligament complex)
- 90% are associated with cruciate ligament injury PCL > ACL
Diagnosis?
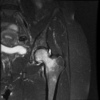
Transient osteoporosis of the hip
- Ddx for MRI - AVN (has serpigenous dark lines and involves more the subchondral femoral head)
- Bones is lucent on X-ray which looks very different than AVN (sclerotic)
- Regional migratory osteoporosis is similar however affects different joints
DDx Vertebra Plana
MELT
Mets/myeloma
EG
Lymphoma
Trauma/Tb
Diagnosis?

Trevor Disease
- multiple osteochondromas develop at the epiphysis resulting in joint deformity
- most common in ankle and knee
- these point toward the joint
- aka dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica (DEH)
Diagnosis?

Nail-patella syndrome
- AKA Fong disease and bunch of other names
- Absent/hypoplastic nails from birth, flexion conractures, recurrent knee disloctions, hypoplastic patellas
- Posterior iliac horns (Fong prongs) is pathognomic
- In elbow can see dysplastic radial head, hypoplastic capitellum and lateral epicondyle and prominent medial epicondyle

Has the appearance of a chondroblastoma, but is in adult
Think clear cell chondrosarcoma
Seen near the medial elbow

Epitrochlear Lymphadenopathy
- Classic look for cat-scratch disease
Diagnosis?

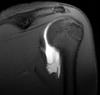
Periosteal Osteosarcoma
- Tends to occur in diaphyseal region (rather than metaphyseal)
- Ages 15-25
- Usually no marrow extension
Diagnosis? Potential complication?

Navicular Stress Fracture - seen in runners who run on hard surfaces
- high risk for AVN
Sign and associations

Looser Zones
- Cortical infractions or Milkman lines
- Wide transverse lucencies traversing part way through a bone, usually at right angles to the involved cortex
- Associated with osteomalacia and rickets
- Represent pseudofractures, have sclerotic irregular margins and are often symmetrical
- Commonly located in pubic rami, medial proximal femure, lateral scapula, posterior proximal ulna, ribs
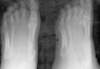
Findings of hyperparathyroidism
- subperiosteal bone resorption of the radial aspect of the 2nd and 3rd fingers
- rugger-jersey spine
- brown tumors
- terminal tuft erosions
Name that ossicle

Cyamella
- located within the popliteus tendon
Bone tumor with fluid-fluid levels DDX
Telangiectatic osteosarcoma, ABC, GCT
Diagnosis?

Dorsal Intercalated Segmental Instability (DISI)
- widening of the SL angle with dorsiflexion of the lunate
DDx?

Osteofibrous dysplasia
- unable to differentiate from adamantinoma, however if anterior bowing present favor OFD
Diagnosis?
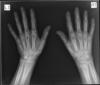
Reflex Sympathatic Dystrophy
- a.k.a. Complex reginal pain syndrome and Sudeck atrophy
- Severe osteopenia - looks like unilateral RA, with preserved joint spaces
- Hand and shoulder are most common sites
- usually history of trauma or infection
- 3 phase hot bone scane with intra-articular uptake of tracer due to increased vascularity of synovium

Diagnosis?
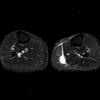
Plantaris Rupture
- associated with ACL tears
- only 10% of population has this tendon
- fluid between gastrocnemius and soleus
Skull findings in Paget’s
- Osteolysis circumscripta - large area of osteolysis in the frontal and occiptal bones (lytic phase)
- Cotton wool appearance (mixed phase)
- Thickened sclerotic look affecting inner and outer table (FD favors outer table)
- Tam O’Shanter Sign
- Spine - picture frame sign (extra-credit)
Diagnosis?

Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
- Primary form is more rare and causes acro-oestolysis
- Secondary form (90%) often due to lung maligancy and causes phaleangeal tuft sclerosis
- Radiographs - long bone metaphyseal and diaphyseal smooth periosteal reaction
- Tc99m MDP - tram track appearance
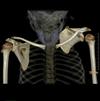
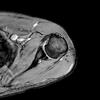
Findings in adhesive capsulitis
- Decreased glenohumeral volume with injection
- thickened inferior and posterior capsule
- enhancement of the rotator cuff interval
- loss of fat in the rotator cuff interval
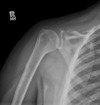
Diagnosis and association?

Meniscal ossicle
- ossification of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus
- associated with radial root tears
Types of OI
4 types, in order of most to least common
- least severe and has gracile thin tubular bones and ostepenia
- most severe and typically lethal at the time of or shortely after birth
- most severe that survives into childhood and adulthood
- similar to type 1 except more likely to have basilar skull impression
Sign and association?

Deep Intercondylar Notch Sign
- associated with ACL tears
High risk Stress fractures (7)
- femoral neck (tensile side)
- transverse patellar fracture
- anterior tibial fracture
- 5th metatarsal
- talus
- tarsal navicular
- sesamoid great toe
Diagnosis?

Extensor Carpi Ulnaris Subsheath Injury
Diagnosis?
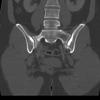
Osteitis condesans ilii
- benign sclerosis of the ilium adjacent to the SI joint, typically bialteral and triangular in shape
- usually asymptomatic but uncommonly may case lower back pain, often seen in multiparous women
Components of conjoint tendon?
- Biceps femoris tendon
- LCL
Diagnosis?

Little leaguer elbow
- Stress fracture, avulsion or delayed closure of the medial epicondylar apophysis
- usually associated with UCL injury
- valgus overload
Diagnosis?

Scaphoid-Lunate Advanced Collapse (SLAC)
- injury or degeneration (via CPPD) to the S-L ligament
Dupuytren contracture
palmar fibromatosis: progressive condition that causes shortening and thickening of the fibrous tissue of the palmar fascia. Presents as a firm nodularity on the palmar surface of the hand with coalescing cords of soft tissue on the webs and digits.
Compared to a Volkmann ischemic contracture which refers to complex and variable flexion deformity involving distal limbs (typically the wrist and fingers) resulting from fibrosis and contracture of flexor muscles. (results from untreated compartment syndrome)
Intertrochanteric lesions
Lipoma, SBC, FD
Also can think of LMFT

Diagnosis?

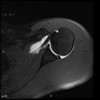
Buford complex
- variant in about 1% of population which consists of absent anterior/superior labrum (1-3 o’clock), alogn with a thickend MGHL
Classic association with patellar tendon tear (alta)?
SLE
Can also be seen with elderly, trauma, athletics or RA
Diagnosis?

Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Radiographs show non-specific features such as joint effusion and bone erosions
- CT and ultrasound can also demonstrate the hypertrophic synovium as a slightly hyperdense/echogenic soft tissue mass.
- MRI is the best approach showing the mass-like synovial proliferation with lobulated margins, with low signal intensity and “blooming” artefact on gradient echo due to hemosiderin deposition.

Diagnosis?

Paget’s of skull
Tam O’Shanter Sign
Diagnosis and association?

Ulnar impaction syndrome
- associated with positive ulnar variance
- distal unla smashes into the lunate, degenerating it and tears up the TFCC
Name Attachments
- Iliac Crest
- ASIS
- AIIC
- Greater trochanter
- Lesser trochanter
- Ischial tuberosity
- Symphysis
- Iliac Crest: Abdominal muscles
- ASIS: Sartorius and TFL
- AIIC: Rectus Femoris
- Greater trochanter: Gluteal muscles
- Lesser trochanter: Iliopsoas
- Ischial tuberosity: Hamstrings
- Symphysis: Adductor group
Diagnosis? Association?
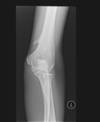
Supracondylar spur (Avian spur)
- can cause compression of median nerve if the Liagment of Struthers smashes it
Diagnosis?

Perthes Disease (LCP)
- white kid age 4-8
Diagnosis?

Volar Intercalated Segmental Instability (VISI)
- volar-flexion of the lunate & scaphoid
- injury to lunotriquetral ligament (ulnar side)
Diagnosis?

Galeazzi Fracture
- Radial shaft fracture with dislocation of the ulna at the DRUJ
Name of this hereditary disorder

Fibrodysplasia ossificans progresiva
- mature ossification within soft tissues, typically starts with sternocleidomastoid followed by shoulder girdle, upper arms, spine and pelvis
- Age of onset is about 5 years of age
- Autosomal dominant
Borders of Quadrilateral Space
- Teres minor
- Teres major
- Medial head of Triceps
- Humerus
- Compression of axillary nerves results in atrophy of teres minor
Diagnosis?

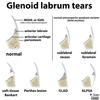
SLAP
- suprior margin and track anterior to posterior, invovles the labrum at the insertion of the long head of the biceps
- When involves biceps anchor (type 4) needs surgical management (biceps tenodesis)
- Not associated with instability

Most likely dx

Glomus tumor
- Hypervascular, T2 bright (compared to GCT tendon which is T2 dark)
Diagnosis and associations?

Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Assocation with dialysis, pregnancy, DM, and HYPOthyroidism
- Look for bowing of the flexor retinaculum
Name this sign and what it indicates

Reverse Hamburger Sign
Seen with facet dislocation which can be unilateral or bilateral
Diagnosis?

NF-1
- unilateral, anterior lateral tibial bowing
- may have a psuedofibulararthrosis
- Can be seen in ulna as well

Diagnosis?

Calcaneal stress fracture
- most fractured tarsal bone
- usually intra-articular (75%)
- perpendicular to the trabecular lines
Sign and ddx

Shiny corner sign
- seen in ankylosing spondylitis
- also can see bamboo spine, dagger sign and hatchet sign of humerus (erosion superolateral margin)
Sign and DDx?

Thickened Heel Pad
- Usually <21; if > 2.3 cm in male or 2.15 cm in female then highly suggestive of acromegaly
- DDx MADCOP
- Myxedema, acromegaly, phenytoin therapy (drug), callus, obesity, peripheral edema