MORPHOLOGY Flashcards
EMBRIOLOGY
Respiratory (laryngotracheal) Diverticulum
- week 4
- from ventral wall of the foregut (endoderm)
- lower respiratory tract formation (trachea, bronchi and lungs)
- endoderm → respiratory epithelium
- mesoderm → muscles + cartilages + connective tissues

EMBRIOLOGY
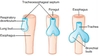
Development of Respiratory Diverticulum
- Respiratory Diverticulum enlarges → lung bud (distal portion)
- Bifurcation → lung bud + 2 bronchial buds
- Tracheoesophageal Septum
- Divisions → bronchial tree formation (month 6)
- main bronchi
- secondary bronchi
- terciary bronchi (bronchopulmonar)
EMBRIOLOGY
What is the critical time for lung formation?
25 - 28 week
- pneumocytes (types I and II) are formed
- surfactante production is possible
- premature fetus at this time can survive (intensive care)
EMBRIOLOGY
Clinical Correlate: Tracheoesophageal Fistula
- malformation of the tracheoesophageal septum
- 90% → esophagus + distal third of the trachea
- esophageal atresia + polyhydramnions
- symptoms
- regurgitation of milk
- cyanosis after feeding
- abdominal distention after crying
- pneumonitis (reflux into lungs)

EMBRIOLOGY
Clinical Correlate: Pulmonary Hypoplasia
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
(herniation of abdominal contents into thorax)
or
Potter’s Sequence
(bilateral renal agenesia → no urine → oligohydramnio → increase of fetal thorax pressure)

ANATOMY
Upper Respiratory Tract

ANATOMY
Trachea
- hollow tube
- 10 cm length
- 2 cm diameter
- bifurcation at the carina
- C-shaped hyalin cartilage rings
- 16 - 20 rings
- anterior wall
- rings are interconnected by smooth muscle

ANATOMY
Bronchi
Bronchial Tree
- Primary Bronchi (enter the lung)
- Secondary Bronchi (lobar)
- 2 left lung
- 3 right lung
- Tertiary Bronchi (segmental)
- 10 segmental bronchii each lung

ANATOMY
Lung: surfaces and regions
Costal
(convex + smooth + related to chest wall)
Mediastinal
(concave + related to mediastinum and heart)
Diaphragmatic
(base + concave)
Apex
(4 cm above first rib + crossed by subclavian vessels)

ANATOMY
Right lung is superior than the left lung
True or False?
TRUE
liver presence in the right
ANATOMY
Cardiac impression in the left lung is more pronuced than the right lung
True or False?
TRUE
ANATOMY
Lung: lobes and fissures
- RIGHT LUNG
- superior lobe
- horizontal fissure
- middle lobe
- oblique fissure
- inferior lobe
- superior lobe
- LEFT LUNG
- superior lobe
- oblique fissure
- inferior lobe
- lingula (corresponds middle lobe)
- superior lobe

ANATOMY
Lung Projections: fissures
- Oblique Fissure
- 5th intercostal space → 6th costal cartilage
- both lungs
- midclavicular line
- Horizontal Fissure
- only right lung
- 5th intercostal space → 4th costal cartilage
ANATOMY
Lung Projections: lobes
superior → above 4th rib (anteriorly)
middle → below 4th rib (anteriorly)
inferior → below 6th rib (posteriorly)
ANATOMY
Lung: segments

PLEURAL CAVITY
Pleura
- mesodermal-derived membrane (serous)
- double-layered membrane
- friction-reducing movements
- parietal layer
- visceral layer
- pleural cavity → potencial space

PLEURAL CAVITY
Parietal Pleura
Costal Parietal Pleura
(lateral → ribs + intercostal space)
Diaphragmatic Parietal Pleura
(inferior)
Mediastinal Parietal Pleura
(medial → reflects to become visceral pleura at hilum)
Cervical Parietal Pleura
PLEURAL CAVITY
Visceral Pleura
Tightly invest the surface of the lungs
fissures + lobes
PLEURAL CAVITY
Pleural Innervation
- Parietal Pleura
- somatic sensory innervation
- intercostal nerve → costal + diaphragmatic pleura
- phrenic nerve → diaphragmatic + mediastinal pleura
- Visceral Pleura
- visceral sensory innervation
- autonomic nerves
PLEURAL CAVITY
Pleural Cavity and Pneumothorax
- Cavity
- potencial space
- closed space + small amount of serous fluid
- negative pressure
- Pneumothorax
- introduction of air into the pleural cavity → lost negative pressure → lung collapse
- open pneumothorax x tension pneumothorax













