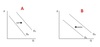Microeconomics Test 1 Flashcards
Ceteris Paribus
All Else Equal
Correlation means _____________________________
two variables change at the same time
Define Positive correlation
when both variables move in same direction
Define Negative correlation
one increase and other decreases
Spurious correlation is defined as
A->B, B->A, A&B together Trying to relate un-relatable variables
What is Post Hoc Fallacy
Post hoc Ergo Prompter which equals “after this therefore because of this” A -> B. A is always first
Define Fallacy of Composition
What is true for the individual is not true for the group.
What are the four criteria for evaluating economic policy
- Efficiency. (Microeconomics)
- A. Produce
- B. What people want
- C. At lowest possible cost
- D. Using all of societies resources
- Equity - Is it fair
- Growth - is the economy producing more from year to year. (Macroeconomics)
- Stability - Avoiding large increase or large decreases in inflation(Macroeconomics)
Define Scarecity
Wants and needs are limitless; resources are not
Define production
Production is the process that transforms resources into final goods and services or you can say inputs into outputs.
Name the three economic questions that we deal with in microeconomics
- What to produce - > what people want
- How to produce. - > lowest possible cost
- For whom to produce -> for those with the resources and means to buy it
Define Absolute advantage
Absolute advantage
The country or individual who can product the most (in total units) of a good has the absolute advantage.
Define Comparative advantage:
Comparative advantage:
The individual or country that can produce a good at the lowest
oppurtunicy cost is said to have the comparative advantage.
What is the formula for Oppurtunity Cost
Opportunity Cost = what you give up / what you get
According to David Ricardo’s theory of Comparative Advantage …
countries should specialize in production of goods in which they have comparative advantage and should trade in other
Define Terms of trade
Trade ratio of goods between the two trading partners
What is the Production Possibilities Frontier
Production Possibilities Frontier
Graph that shows all combinations of goods that can be produced using all of society’s resources.
True or False
PPF is concave to the origin
True
PPF is concave to the origin
Define the Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs
The Law of Increasing Opportunity Costs states that as society produces more of a good it must give up increasingly more other goods to produce it.
What are the criteria for effiecient production
For it to be efficient it must meet all three criteria,
- Producing what people want
- At the lowest cost
- Using all the available resources
True or False
There are Pure Communist and Free Market economies in the world
False
There are no Pure Communist systems or Free Market economies.
Define Firm
Firm. =. Person. Or a group. Of. People that produces goods or services, by transforming input into outputs.