iClicker Questions Flashcards

A

B

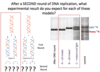
A – fragment 5 is the largest fragment; smaller fragments migrate faster through the gel and will therefore be further to the bottom

C – DNA polymerase synthesizes 5’ to 3’!

B – EcoRI cuts leaving a sticky end, whereas PCR leaves (mostly) blunt ends
C is also ok
D is defensible if you don’t know that E.coRI creates sticky ends

C – to transcribe insulin – vectors for protein expression need a promoter for RNA polymerase binding

B – this is a tricky question… in eukaryotes the AUG is embedded in the Kozak sequence and mRNA is recognized by the 5’cap but if we want to express a human protein in bacteria, we have to embed the AUG in the prokaryotic ribosome binding site (shine dalgarno sequence)

Both A and D are correct
All patients have about the same amount of GapDH – that is an internal control to make sure you put about the same amount of material into the reaction (each cell expresses GapDH)
Lower Ct means earlier begin of exponential phase in qPCR and therefore higher amounts of starting material / template – so higher virus load

E - 4 because the probe will also anneal to both of the normal chromosomes 9 and 22

B, C, and D
B has more cells with normal chromosomes, C only Philadelphia chr cells and D has more philad chr cells than normal cells

B – it doesn’t recognize the 5’cap and the EK mRNA doesn’t have the shine dalgarno sequence

Correct answer: A – it is most similar to the consensus sequence
B had the highest level of translation within the few mutants analyzed
C had high levels of translation but less than B (in the mutation analysis)
D would also work as G in pos -3 is also found more than by chance (36% vs 25% by chance) – however, A is twice as often in this position
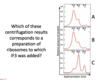
Correct answer: C
IF3 prevents the 30S and 50S subunits to aggregate to the 70S

Correct answer: A
(c and d are nucleic acids, not polypeptides!!)

Correct answer: A
Keep in mind – in other processes, ATP can also be used to drive conformational change! This is not universally true

Correct answer: D
All steps of the pathway would occur. RF1/2 don’t need GTP hydrolysis of RF3 to transfer the polypeptide chain to an h2O – only needs RF3 to be released from ribosome

Correct answer C - Histone – nuclear proteins are synthesized in the nucleus before they are transported into the nucleus by importin
Antibody and hormones are secreted, surface receptors are in the plasma membrane. All of those proteins are synthesized in the ER

B – A is a purine, T is a pyrimidine – that is a transversion

D

B

B

A

D

D

C

C