Histology of Muscle Flashcards
What type of muscle fibres are striated?
Skeletal and cardiac
Where is the epimysium, perimysium and fasciculi found in a muscle fibre?
in muscle

What does skeletal muscle look like? and what is the impact of fasciculi?
The size of the fasciculi reflects the function of the particular muscle- eg muscles for highly controlled movements will have small fasciculi and a greater proportion of perimysial tissue
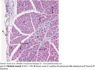
describe this picture

The individual pink-stained (fasciculi) muscle cells (fibres) are cut in transverse section, the spaces between them being occupied by small amounts of barely visible endomysial supporting tissue. The endomysium, which consists mainly of reticulin fibres and a small amount of collagen conveys numerous small blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves throughout the muscle.
Surrounding individual fasciculi F is the perimysium P composed of collagen and through which larger vessels and nerves run.
The epimysium E is a collagenous sheath that binds the fascicles into a single muscle. The endomysium En is barely visible as the delicate support tissue surrounding each muscle fibre.
Describe this image

Alternating broad light I bands (isotropic in polarised light) and dark (anisotropic) A bands. Fine dark lines called Z bands (Zwischenscheiben) can be seen bisecting the lines.
small amount of sarcoplasm containing rows of mitochondria Mt in a similar orientation.
Z bands are the most electron-dense and divide each myofibril into numerous contractile units, called sarcomeres, arranged end to end.

