Histology of Epithelia Flashcards
4 tissue types in the body?
- epithelia 2. connective tissues 3.Muscle 4. Nerve
What is epithelium?
continuos sheet of cells which adhere closely to one another with little intercellular substance
what do the cover?
Both internal and external surfaces
What is the basement membrane?
A term given to basal lamina with reticular fibres ( in supporting tissue)
do epithelial tissues have capillaries or blood vessels?
No
Why are epithelial cells structurally and functionally polarised?
due to substances entering or leaving the body having to cross the epithelium
What are the two main functions of epithelium?
Protection and control of transfer ( what passes it)
what does specialised to transfer mean?
secretion, absorption or both. Normally SIMPLE one cell thick
Where are specialized to transfer epithelial cells found?
lining blood vessels eg alimentary tract, lungs, body cavities
what are specialized to protect epithelial cells?
Normally compound ( more than one cell thick)
examples of specialised to protect epithelia are?
lining mouth, oesophagus, outer layer of the skin
do epithelial cells line glands? like?
yes, salivary and endocrine
what does simple epithelia look like?
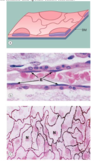
What does simple columnar look like? and where is it found?
absorptive surfaces e.g. smal intestines, secretory surfaces like stomach
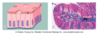
What does simple cuboidal epithelia look like? and what does it line?
small ducts and tubules that may have excretory, secretory or absorptive functions; examples are the collecting tubules of the kidney and the small excretory ducts of the salivary glands and pancreas.