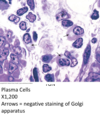
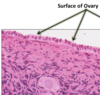
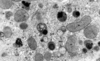
Histo Flashcards

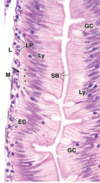
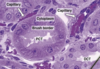
Kidney - Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)

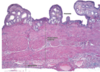
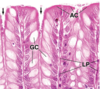
Vagina


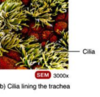
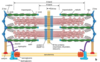
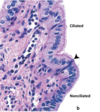
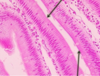
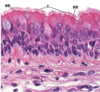
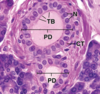
Trachea


Gallbladder

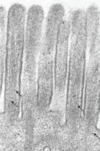
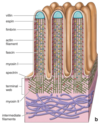
Microvilli


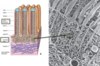
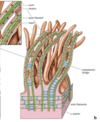
Cilia

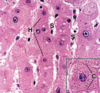
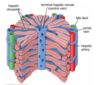
Liver

Clathrin-Coated Pits
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis

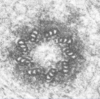
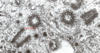
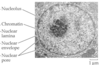
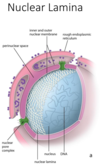
Arrows point to Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC)
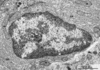
Chromatin in Nucleus


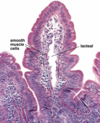
H&E stain of smooth muscle


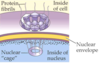
Nuclear Pores



cell movement

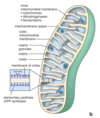
Mitochondria in Heart Muscle
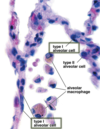


Trachea
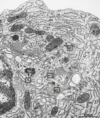
Scanning EM

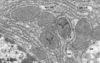
Mitochondria in Liver
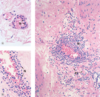
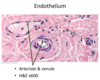
Neutrophil Migration:
a. white blood cells in blood vessel
b. after diapedesis
c. after chemotaxis


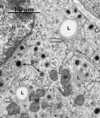
Lipid on EM

rER

Nucleus

Male Reproductive Tract

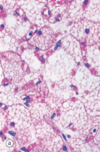
Lipid stained with H&E

Lysosome

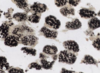
Lipid stained with Osmium Tetroxide (OT)

Phagocytosis
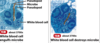
Urinary Bladder


Lamin A mutation; Hutchinson Gilford Progeria (aging)



Glycocalyx

rER


Trachea
Transmission EM
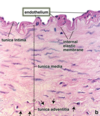



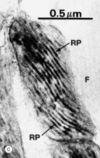
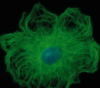
Actin

microvilli & stereocilia
fast growing + end, slow - end

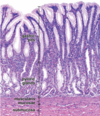
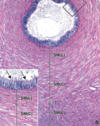
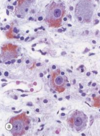
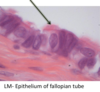
Uterine Tube
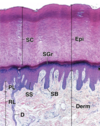
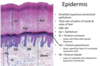

Pinocytosis