Fish Flashcards
What are the three funcitons of aquarium filtration?
* Mechanical filtration- removal of solid particles by entrapment
* Biological filtration- oxidation of ammonia (NH3) to nitrite (NO2) and then to nitrate (NO3) by bacteria which colonize the filter
* Chemical filtration- removal of substances by absorption into filter material such as activated charcoal zeolite ionizing resins, peat moss
What is the purpose of the biological filtration in an aquarium? What bacteria play a role? What is also released?
Conversion of ammonia (NH3) to nitrite (NO2) and then to nitrate (NO3).
* Hydrogen ions are released and therefore the water becomes more acidic– aquariums tend to “shift acid” with time

What is the conditionin period in an aquarium? How can you shorten it?
Biofilters take several weeks to establish… NH3 levels rise until Nitrosomas spp. begin to reduce NH3. As NH3 levels decrease, NO2 levels increase until Nitrobacter establish. As Nitrobacter spp. begin to convert NO2 to NO3.
Conditioning period is the period in which enough nitrifying bacteria are developing.. where ammonia and nitrite become 0.
* Can be shortened by inoculating with live gravel
** then test for ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate to find the end of the period
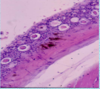
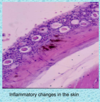
What are the signs of ammonia toxicity in fish?
* Depression, anorexia, dull colours, inflammation, excess mucous, cloudy eyes, blindness, secondary bacterial disease and death.
How do you reduce ammonia toxicity?
* Water changes daily, monitor daily, reduce pH to < 7, conditioned gravel, stop feeding, reduce temperature, ammonia absorbers (zeolites, carbons, ion exchange resins)
Signs of nitrite toxicity in fish
* Methaemoglobin interferes with oxygen transport
* If nitrite high gills and blood are brown
* Rapid breathing, gulping, anorexia, depression
* Death
How do you reduce nitrite levels?
* Water changes daily
* Stop feeding
* Add 0.3% salt NaCl (3 heaped teaspoons to 10 liters)
* Chloride is the antidote
* Decrease temperature
* Conditioned gravel
What happens if you allow nitrate levels to rise above 50 ppm?
* Changes water to microbial broth
* Opportunistic infections
* Immunosuppression
* High organic loads
What do high organic levels in an aquarium do?
* Reduce growth rates and suppress the immune system. Many fish diseases are associated with high organic levels
(Organics refers to nitrates, phosphates, sulphates, bacteria, debris, protozoa, fungi)
Causes of ammonia and nitrite problems in an establish tank
* Increase in fish size or fish numbers (overloading of biological filter)
* Medications (antibiotics)
* Acid shift (below 6.5 nitrifying bacteria slow down, below 6.2 shut down totally– therefore ammonia will come through)
* Nitrifying bacteria being removed by cleaning or replacing filter beds
* Cleaning or replacing filter beds
* Debris and detritus can clog the filter bed producing anaerobic conditions– conversion of nitrate to nitrite occurring when the biological filter become anaerobic
* Cessation of water flow through filter damagins the nitrifying bacteria
What differs between marine aquariums and regular?
Marine aquariums do not cope with nitrate as well
What is general hardness in relation to water? What is soft? medium? Hard?
* Measure of calcium and magnesium, the harder the water the more stable the pH
* Increases with conditioning salts and neutralizing blocks
* Shell grit, crushed coral
* Decreases with dilution, ion exchange resins, peat moss, remove shell grit and crushed coral
* Soft: 50-100 ppm (Tetra, Discus)– ** the softer the water the more challenging the maintenance, lower pH generally
* Medium: 100-200 ppm (Livebearers)
* Hard: 200-500 ppm (Africans)
Long Term healthy aquariums
* Regular maintenance: frequent and efficient water changes, gravel cleaning, filter cleaning
What is the general approach to an aquarium problem?

Problems with post mortem in fish
* Fish undergo rapid autolysis after death (only useful on euthanised or fresh dead fish)
* Micro + histopath most helpful
* External parasites do not stay on dead fish for long
How do you prevent acid shift in an aquarium?
* Partial water changes, add alkalizing agents, increase hardness with conditioning salts or by adding shell grit or crushed coral, reducing debris, detritus and decay by gravel cleaning and filter bed cleaning
Why are mechanical water pumps used in aquariums?
* To aid in aeration– refers to bubbles in the aquarium producing movement of water. This allows an increased rate of oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide elimination at the water surface.
How long should you fast fish before anaesthesia?
24 hours
What are you looking for in a fish for the appropriate level of surgical anaesthesia?
* No reaction to any stimuli. Slow opercula rate.
What anaesthesia is recommended for fish?
* Alfaxan (safter than clove oil as you give too much you can easily kill them)
How can you prolong surgery in a fish?
Gill irrigation with alfaxan water
Fish anaesthetic set up

Major differences in the aquatic environment
* Oxygen availability
* Exposure to waste products and nitrogen cycle
* Temperature and effects on animals
* Exposure to salinity and pH
If water quality is poor, what else is impacted with fish?
Feed Conversion Ratio
Poikilotherms vs. homeotherms.. Tuna?
Organism whose internal temperature varies considerably, from a variation in the ambient environmental temperature. Whereas a homeotherm maintains thermal homeostasis.
** Tuna can heat themselves like homeotherms therefore are able to live all over the world in a variety of environments… heat exchanger as the muscle warms up there is a rete where the heat contained in the outgoing blood transferred to the incoming blood. If they are heating up too much, the blood can bypass and head straight to the gill.
** e.g. burnt tuna: huge build up of lactic acid can cause cooking/acidic of the muscles internally essentially– looks green as a break down product of myoglobin
Determinism of diseases
Pressure: farming activities, unrelated water activities, land based activities, climate change
* Biotic and abiotic parameters: temperature, salinity, etc…. and plants, animals, microorganisms
What can stress aquatic animals?

The first question to ask in any examination of a fish disease? Other considerations?
Are these fish stressed and why?
* knowledge of the production system so you can give better advice
* History, site visit, examination of the fish as a group, individual exam, sampling of fish, sampling of water, laboratory, advice +/- treatment
What is important in a fish history?
* duration, system, fish (how many, rate), species, clinical signs, feeding, water quality, handling/ grading, any treatments e.g. vaccinations
Fish health problem as a group
* Eating, schooling, colour, alert, gill movements, moralities, circling, growth rate, food conversion rate, feed storage, smolt (young salmon) quality
What would happen if a tuna stopped swimming?
It would die because it does not have a buccal pump mechanism to pump water over their gills– it must swim to do so
When would you treat the Southern Blue Fish Tuna and with what for Schistosomes? How do you medicate the fish because you can’t stomach tube them all?
* 4 weeks into new environment so that they can begin to develop resistance to the schistosomes but kill them off before some of them proliferate
* Praziquantel
* SBFT eat sardines (but Prazi is not palitable for fish)– using special machine with praziquantel and lots of needles injected it into sardines
Approach to an aquarium problem

Post mortem diagnosis of disease in fish considerations

How do you euthanize fish?