Dermatopathology Flashcards
Oculocutaneous albinism, retained visual acuity, immunodeficiency, early dementia
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
- Presence of giant lysosome-related organelles (melanosomes, platelet-dense granules, neutrophil granules)
Disorders with complete absence of melanocytes (3)
- Vitiligo
- Piebaldism
- Waardenburg syndrome
Decreased visual acuity
Lung and GI problems
Absence of dense bodies within platelets
AlbinismHermansky Pudlak syndrome
Hermansky Pudlak syndrome
Absence of stage III/IV melanosomes
Photophobia WITH decreased visual acuity
NO dementia
Albinism
Oculocutaneous albinism
Melanocytes with an INCREASED number of normal-sized melanosomes
Silvery-grey hair
Type 1 has neurologic impairment
Type 2 requires HSCT
Griscelli syndrome
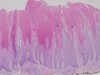
Newborn with clustered vesicles in an arcuate and polycyclic array
What type of EB is this?
EB simplex, Dowling-Meara (EBS-DM) subtype
- Split seen within basal keratinocytes
- Clumping of tonofilaments within keratinocytes’ cytoplasm
What type of EB shows absence of anchoring fibrils due to collagen VII defect?
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB)
What type of EB shows perinuclear stellate inclusions?
Autosomal dominant EB
Reduced number of hemidesmosoms is seen in what type of EB?
Junctional EB
Ziehl-Neelson stain is used to identify what type of bacteria?
Acid-fast bacteria (i.e., mycobacteria)
PCT may have identical histopathologic features to what EB? What type of collagen is targeted in that form of EB?
What findings on DIF can help differentiate the two conditions?
What are the various porphyrin abnormalities in PCT? (3)
(Non-inflammatory) EB acquisita (autoantibodies against type VII collagen)
- DIF for PCT shows perivascular IgG > IgM and complement in the upper dermis
- DIF for EBA shows linear BMZ deposition
- In PCT, there is elevated urine, stool, and serum uroporphyrin.

What type of EB is this?
On electron microscopy, what cytological structures would be absent in the specimen?
What gene mutation is present?
Recessive dystrophic EB (RDEB)
Absence of anchoring fibrils
- Compound heterozygous mutation within the COL7A1 gene, leading to a truncated collagen VII protein that in most cases is nonfunctional

Absence of anchoring filaments, hemidesmosomes, and sub-basal dense plates is seen in what type of EB?
Herlitz subtype of junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB)
- Anchoring fibrils are still present in JEB probably accounting for less severe scarring compared with RDEB
Multiple sclerotic fibromas (storiform arrangement of thickened collagen bundles with interspersed spindled cells) are associated with what disease?
What cancers are associated? (2)

Cowden disease
- Autosomal dominant mutation of PTEN gene
- Oral papillomas, trichilemmomas, acral keratosis, sclerotic fibromas
- Benign and malignant breast and thyroid tumors
- GI polyps, skeletal abnormalities
What syndrome is associated with acrochordons, multiple fibrofolliculomas, and trichodiscomas?
What is the genetic mutation?
What cancer is associated? What lung finding may occur?
Birt-Hogg-Dube (BHD) syndrome
Mutation in BHD gene
Associated with renal cell carcinoma and pneumothorax
Gardner syndrome is caused by what genetic mutation?
What are the three skin findings of this syndrome?
APC gene
Epidermoid cysts, osteomas, desmoid tumors
Associated with colorectal adenocarcinoma
What CD is “langerin”?
What is this a marker of?
CD207
Marker of Birbeck granules
What is the best tissue sample for transmission electron microscopy when evaluating for an inherited blistering disease?
A clinically induced blister at the time of biopsy.
Pretibial myxedema histology
Increased mucin within the upper dermis that separates collagen bundles.
The overlying epidermis may demonstrate acanthosis, papillomatosis, and hyperkeratosis.

Muir-Torre syndrome is associated with mutations in which mismatch repair genes? (4)
25% of patients will have what type of skin cancer?
>60% of patients will have what internal malignancy?
- Caused by mutations in mismatch repair genes including MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2
- Twenty-five percent of patients with MTS also have keratoacanthomas
- More than 60% of patients will have associated colorectal adenocarcinoma
KRT1 and KRT10 mutations cause what skin disease?
Epidermolytic ichthyosis, in which the pathology is not characterized by acantholysis but rather epidermolytic hyperkeratosis
What gene mutation and organelle is involved in Darier disease (keratosis follicularis)?
What gene mutation and organelle is involved in Hailey-Hailey disease (familial benign chronic pemphigus)?
- Darier disease (keratosis follicularis) → ATP2A2 mutation, encoding the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase
- Hailey-Hailey disease (familial benign chronic pemphigus) → ATP2C1 gene, which encodes the Golgi-associated Ca2+ ATPase
Think of the disease names, mutations, and organelles involved in ALPHABETICAL order. And the organelles involved are just one letter away from the first letter of the name!!
You are called by the neurology team to perform a skin biopsy for the workup of cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy. You perform a 4-mm punch biopsy of the arm.
In what medium do you place the specimen?
Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is a neurologic disorder caused by mutations in NOTCH3. Patients with CADASIL have migraines, recurrent strokes, and progressive dementia. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of a skin biopsy is the gold standard to detect pathologic findings.
Placing the skin specimen in the correct medium, glutaraldehyde for TEM, is critical for accurate diagnosis.
What media should be used for preservation of gout crystals or for fat immunostaining?
Alcohol
What media should be used for immunofluorescence studies? (2)
Michel transport medium or normal saline
EBS with pyloric atresia (EBS-PA) is caused by what genetic mutation?
Mutations in PLEC1 leading to a defective plectin 1 protein
The split described is intraepidermal, which is characteristic of epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS).
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) with pyloric atresia is caused by what genetic mutation?
The split is within the lamina lucida.
Ectodermal dysplasia skin fragility syndrome can be caused by what genetic defect?
PKP1 gene defects lead to dysfunctional plakophilin 1 and ectodermal dysplasia skin fragility syndrome.
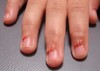
In addition to the clinical findings in the Figure, you see granulation tissue around the mouth, the nape of the neck, and fingernails.

Excessive granulation tissue is a characteristic finding of the Herlitz subtype of junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB). This feature is not seen in other inherited epidermolysis bullosa disorders. JEB has a cleavage plane in the lamina lucida.
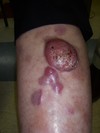
A 65-year-old man has a pink papule on the right side of the abdomen that has been slowly enlarging over one year. A shave biopsy is performed, and the histopathologic findings are shown (Figure).

Fibroepithelioma of Pinkus (FeP) is an uncommon follicular neoplasm that clinically presents as a fleshy pink papule or small plaque, typically on the trunk.
Like BCC, the majority of FeP cases demonstrate diffuse expression of the proto-oncogene Bcl-2 as well as androgen receptor.
The majority of trichoblastomas demonstrate peripheral expression of _____ and absence of _____ receptor and stromal _____expression.
The majority of trichoblastomas demonstrate peripheral expression of Bcl-2 and absence of androgen receptor and stromal CD34 expression.
Lacazia loboi can be identified using what fungal stain?
Gomori methenamine silver
A 50-year-old man comes to the office for evaluation of 2- to 5-mm papules on the face and neck. A biopsy of a characteristic lesion is performed (Figure).
Which three of the following options are most likely associated with this disorder?

Histopathologic examination demonstrates a fibrofolliculoma, characterized by epithelial strands extending from the undersurface of the epidermis into the underlying dermis with follicular differentiation and a surrounding fibroblast-rich sclerotic stroma.
This may be associated with Birt-Hogg-Dube (BHD) syndrome, which is caused by a mutation in the BHD gene. Renal cell carcinoma and spontaneous pneumothoraces are strongly associated with BHD syndrome.

Immunofluorescence antigenic mapping is an effective technique for the diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa (EB). Immunomapping with antibodies to BPAg1 and collagen IV allows for differentiation between the major types of EB.
In junctional EB, where do BPAg1 and collagen IV localize to - the roof or the floor?
What about in EBS?
What about dystrophic EB?
Type IV collagen is present in the lamina densa of the basement membrane zone, whereas BPAg1 localizes to the hemidesmosomes of basal keratinocytes. The split in junctional EB is in the lamina lucida, which is below the hemidesmosomes and above the lamina densa. Therefore, BPAg1 would localize to the roof, whereas collagen IV would localize to the floor.
In epidermolysis bullosa simplex, both antigens localize to the floor. In dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa, both antigens localize to the roof.
An 18-year-old woman has multiple slowly growing papules on her face, including her cheeks and forehead. A biopsy showed a proliferation of basaloid cells forming multiple small nests, lobules, and small folliculocystic structures containing keratin material. No significant cytologic atypia, mitotic activity, or infiltrative features were identified.
What is the most likely diagnosis for this tumor?
The histologic findings describe a benign follicular neoplasm composed of basaloid cells forming small nests, lobules, and folliculocystic structures, findings typical of trichoepithelioma.
_____ is the most common drug-induced cause of pemphigus vulgaris.
Penicillamine
What is pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia (PEH)?
Epidermal acanthosis, papillomatosis, and hyperkeratosis that can mimic squamous cell carcinoma

True or false: a three-week course of systemic steroids will not affect DIF results.
Deposited immunoglobulin (Ig) must undergo several half-lives (21 days for IgG) to clear completely. As such, a short course of less than 4 weeks of systemic steroids will likely not affect direct immunofluorescence (DIF) test results.
____ and ____ stains are useful for metastatic small cell carcinomas of the lung, as they are typically positive for both of these markers.
_____ and _____ are the best stains for confirming the diagnosis of a metastatic adenocarcinoma of gastrointestinal tract origin, especially lower gastrointestinal tumors, which are usually positive for both of these markers.
CK7 and TTF1 stains are useful for metastatic small cell carcinomas of the lung, as they are typically positive for both of these markers.
CDX2 and CK20 are the best stains for confirming the diagnosis of a metastatic adenocarcinoma of gastrointestinal tract origin, especially lower gastrointestinal tumors, which are usually positive for both of these markers.
Is dermatitis herpetiformis positive or negative on IIF? What about PCT?
Both DH and PCT are IIF-negative.
What is the DIF pattern of PCT?
IgG perivascular “donut” like accentuation and increased signal along the basement membrane zone (BMZ)
What are the optimal location and timing for immunofluorescence testing of discoid lupus erythematosus?
Lesional skin more than 4 to 6 weeks old
Lesional skin is the preferred site to look for immunoreactants in discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE). Deposition of the classic granular band of immunoreactants takes some time and biopsies of lesions less than 4 to 6 weeks old may yield false-negative results.
In bullous pemphigoid and EBA on salt-split skin, do the antibodies bind to the epidermal or dermal side of the salt-split skin? Are the autoantibodies to components of the hemidesmosomes or the anchoring fibrils?
- BP → linear deposition of IgG to the epidermal side (Ab against components of hemidesmosomes)
- EBA → dermal side of salt split skin (Ab against anchoring fibrils)
What are the most common underlying neoplasms associated with paraneoplastic pemphigus?
The most commonly associated neoplasms are non-Hodgkin lymphoma (40%), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (30%), Castleman disease (10%), malignant and benign thymomas (6%), sarcomas (6%), and Waldenström macroglobulinemia (6%).
Figures 1 and 2 show patient skin (left) and normal control skin (right) incubated with mouse anti-human laminin 332 (beta chain).
What is the diagnosis?

In the normal human skin (Figure 1), there is linear deposition of anti-human laminin332 to endogenous laminin332 along the basement membrane. In the patient’s skin, there is some background artifact staining of the epidermis and stratum corneum but linear staining at the basement membrane is not seen, indicating an absence of endogenous laminin332 and the diagnosis of junctional epidermolysis bullosa, Herlitz type.
In cicatricial pemphigoid, whether the autoantibody is laminin332 or BPAg2, endogenous laminin332 is present and binding of an exogenous incubated anti-laminin332 antibody will be detectable.