Clostridium tetani Flashcards
what is the appearance in the microscope for c. tetani?
they look like tennis rackets
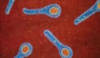
where are c. tetani spores found in?
in the soil and rusty nails
what is the most common form of acquiring c. tetani?
give 2 examples…
Traumatic implantation of spores into tissues with low oxygenation *
- Puncture wound
- Non-sterile surgeries or deliveries
what happens after the c. tetani spore is implanted?
it germinates and releases tetanospasmin
what is tetanospasmin?
a potent neurotoxin
what can tetanospasmin, released by c. tetani, cause?
- Painful muscular contractions (Opisthotonus)
- risus sardonicus
what type of toxin is tetanospasmin?
A-B toxin
how does tetanospasmin work?
Blocks release of inhibitory neurotransmitters glycine and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) causing unrestrained excitation of motor neurons*
what 2 clinical forms of c. tetani can be found?
- Generalized tetanus:*
- Neonatal tetanus:*
Generalized tetanus will cause these symptoms?
lockjaw
risus sardonicus
opisthotonus
Drooling, sweating, irritabililty
Neonatal tetanus:* occurs due to what?
- improper umbilical care
- local infection of umbilical stump becomes spreads
what individuals are at risk of c. tetani?
- those that are not vaccinated
- neonates born to unvaccinated mothers (no passive immunity towards baby from mother) *
how do you treat c. tetani?
metrodinazole
toxoid tetanus


