CH 9 The Immune System Flashcards
Parts of the immune system:
- Bone marrow
- Spleen and lymph nodes
- Thymus
- Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
- Leukocytes
- Bone marrow: Produces white blood cells (leukocytes)
- Spleen and lymph nodes: Where B-cells are activated
- Thymus: Site of T-cell maturation
- Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT): includes the tonsils and adenoids
- Leukocytes: white blood cells

Innate Immune System:
Phagocytes:
- Macrophages MHC-1, and MHC-2
1. Macrophages: ingest pathogens and present them on major histocompatibility complex (MHC), and secrete cytokines (cell signaling molecules.
- MHC-1: Found in all nucleated cells and displays endogenous antigen to cytotoxic T-Cells (CD8+)
- MHC-2: is on antigen-presenting cells (macrophages, dendritic cells, B-cells) and displays exogenous antigen to helper T-cells (CD4+)
Innate Immune System:
- Dendritic cells
- Natural Killers cells
- Granulocytes:
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Mast Cells
- Dendritic cells: Antigen-presenting, identify pathogens, and activate other immune cells
- Natural Killers cells: attack cells not presenting MHC molecules. i.e cancer cells by promoting apoptosis
-
Granulocytes:
- Neutrophils: Ingest bacteria marked with antibodies, can follow them using chemotaxis (kill themselves after)
- Eosinophils: Used in allergic reactions. Release histamine to cause inflammatory response
- Basophils: Large purple granules, involved in allergic responses
- Mast Cells: smaller granules, exist in tissues, mucosa, and epithelium. Release histamine for inflammation.
The adaptive immune system
Humoral Immunity:
- B-cells (B-lymphocyte):
* Memory and effector B-cells - Types of antibody attacks upon antigen binding:
- Opsonization
- Agglutination
- Neutralization
- Plasma Cells
- Hypermutation
Humoral Immunity:
- B-cell: originate and mature in the bone marrow. All cells contain different antibody variations to attack antigen.
- Once its antibody binds to the antigen that fit, it begins to divide
- Some become memory cells and other effector B-cells. Effector B-cells being producing and releasing free antibodies.
- Types of antibody attacks upon antigen binding:
- Opsonization: mark them for destruction
- Agglutination: clumping that makes it easier for macrophages to find and digest
- Neutralization: block binding sites (pathogen cant attach to your tissues)
Hypermutation: To improve specificity of antibody produces, signals to switch isotypes of antibody (IgM, IgD, IgG, IgE, IgA)
Plasma cells Involved in the production of antibodies from the B-cells which are activated in the spleen and lymph nodes and mature in the bone marrow
The adaptive immune system
Cell-mediated (cytotoxic) immunity
- T-cells
- Helper T-cells
- Cytotoxic T-cells
- Suppressor (regulatory T-cells)
- Memory T-cells
- Positive and negative selection
- T-cells: originate in bone marrow but mature in the thymus
- Helper T-cells (Th or CD4+): respond to MHC-2, Starts secreting cytokines, Th1 cells activate macrophages by secreting interferon-gamma, Th2 activate B-cells so they can make more antibodies.
- Cytotoxic T-cells (Tc, CTL, or CD8+): respond to antigen in MHC-1., and can secrete enzymes to start apoptosis
- Suppressor (regulatory T-cells): Tone down the immune response.
- Memory T-cells:
- Positive and negative selection: Thymosin promote T0cell development and are matured in the thymus by positive selection (only the ones that can react with antigen on MHC) and negative selection (cause apoptosis in self-reactive t-cells)
The lymphatic system
where does it connect to the cardiovascular system?
It is connected via the thoracic duct in the posterior chest.
Equalized fluid distribution (collect excess interstitial fluid), transports fats and fat-soluble compound in chylomicrons, and provides sites for immune response

Active vs passive immunity

Immune system cell type and function
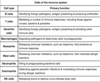
Antibodies:
Parts
- Parts: have two identical heavy and two identical light chains. Have a constant region, and a variable region (the tip antigen-binding region

