Central Nervous System Flashcards
What does the myelin sheath wrapping around the axon do?
Insulates Faster impulse conduction along the axon Eg: Destruction of the myelin sheath (as in multiple sklerosis) would result in impulses be conducted much slower or not at all.
Movement, behaviour, memory, speech, learning, planning, reasoning is controlled by what lobe in the brain?
frontal

the parietal lobe is responsible for what?
sensory perception

vision is controlled by what lobe?
occipital
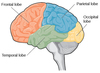
hearing, language, taste, smell is controlled by what lobe?
temporal
blood pressure is controlled by the
medulla oblongata
respiratory control is controlled by the
pons and medulla
startle reflexes are controlled by the
midbrain
memory is controlled by the
limbic system
maintaining alertness is controlled by the
reticular formation
balance and posture is controlled by the
cerebellum
protective layers of connective tissue coverings the central nervous system are called?
meninges
The junction between an axon terminal and a muscle is called a:
neuromuscular junction
The dorsal root ganglion:
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons outside the CNS.
Problems in balance may follow injury to which nerve?
vestibularcochlear nerve

