Autolysis Flashcards
Autolysis
自體溶解:self-digestion or degradation of cells and tissues by the hydrolytic enzymes(水解酶) normally present in those tissues
Putrefaction
腐敗:postmortem bacterial metabolism and dissolution of host tissues (postmortem decomposition的細菌對宿主組織進行分解利用) 結果:color and texture changes, gas production, and odors
Rigor mortis
屍僵: (1) 死後1-6小時肌肉產生強力收縮,通常持續1、2天直到用完所有ATP軟掉 (2) 若生物生前cachexia(惡病體質)、營養不良,則死後可能不會產生屍僵,因為沒有存夠足夠的ATP (3) 動物死亡後細胞內殘存的ATP與因全身性缺氧導致膜通透性改變,Ca2+大量流入細胞,繼續作用在肌肉(actin與myosin)上面使肌肉不正常收縮,而後因ATP的耗盡使myosin無法自actin上脫離,導致屍僵
Algor mortis
屍冷:死後循環消失,導致體溫逐漸流失。可藉體溫判斷動物死亡多久 不能用在爬蟲類
Livor mortis (hypostatic congestion)
屍斑:gravitational force –> 將血液往側躺方向拉產生紅色,而重量的壓迫產生白色,故會有紅白相間的屍斑,可幫助判斷死者的死亡姿勢,對法醫學第一現場的判斷很重要

Chicken fat
Result of postmortem clotting血液凝集:
- 死後血液裡RBC與plasma成分紅白分明的凝集塊,一抽出來就斷裂,為其中一個區分柱塞的方法,又稱為chicken fat clot
- 正常健康的心臟,在死前一刻會急遽收縮擠出血液,使心臟內殘留的血液很少,不易產生chicken fat,假如死後有明顯的chicken fat產生,代表動物生前生理狀態差、身體虛弱,心臟無法強力的收縮,心臟內殘留的血液很多,因此出現在心臟的chicken fat clot對動物的死亡分析是有意義的。
- 反觀,出現在血管中的則是沒意義的,為正常死後變化

hemoglobin imbibition
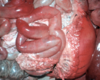
血紅素浸透:
- pinkish to reddish coloration imparted to tissues due to the lysis of red blood cells.
- beginning some hours after death
- 不會用肉眼確認是否病變或死後變化,會在切片下確認
- especially the heart and arteries (particularly evident in the aorta) and veins
bile imhibition

- 動物死後幾個小時之內,膽汁會開始穿透膽囊並將周圍組織染黃,並逐漸轉為棕綠色
- 右肝藏呈棕綠色
Pseudomelanosis
偽黑病變
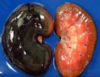
致屍體呈現藍綠色的iron sulphide,因為:
(1) Fe in the Hemoglobin released by lysed erythrocytes reacts with
(2) H2S(硫化氫) generated by腐敗菌 (putrefactive bacteria) on the animal
* 不是因黑色素(melanin)所導致
bloating
鼓脹
- 動物死後體內的細菌(尤其在GI tract)持續發酵產氣導致的結果,草食性動物相較於肉食性動物在死後鼓脹的較快也較嚴重
- 在死掉的反芻動物與馬的胃腸中,細菌會持續進行發酵,故死後不久因不會噯氣肚子鼓漲,為明顯的腹內postmortem decomposition,而在太陽照射下會加快bloating現象。
- 判斷是否為死後鼓脹,可由觀察食道或氣管上的鼓脹線來做為依據。
(i) 若為死前的鼓脹,屬於急性的變化,氣管或食道的後段會因腹壓擠壓而壓破血管,使血液受阻,呈現缺血後較白色的顏色,胸腔則因還有血液,黏膜會是正常因此呈現紅色

Pale foci subserosally
漿膜下蒼白小點- 發生在肝臟
- 因腹腔內壓(intraabdominal pressure)上升,將血液擠壓出去
- bacterial action:細菌將組織降解,切片下沒有細胞核像凝固樣壞死(coagulation necrosis),沒有炎症反應且出現很多細菌,可判斷為死後變化
- 外觀:使肝臟表面上出現白色小點區域,變得不圓滑

Mucosal sloughing
黏膜脫落Mucosal sloughing
保護腸道的黏液死後停止分泌,消化酵素開始分解腸道,使黏膜上皮細胞全面性脫落,屬死後自溶現象
lens opacity
Lens opacity occurs when the carcass is very cold or frozen. The change will reverse to normal transparency on warming, but it can be confused with cataracts in cold carcasses.
水晶體混濁lens opacity:因缺氧導致蛋白質變性,變得混濁可藉由水晶體的混濁程度判斷該動物死亡多久,死亡愈久,水晶體愈混濁。易與cataracts白內障混淆,要判斷為何者仍須透過切片儀器判讀

Atrophy and possible causes
萎縮
- decrease in size, amount of cell or tissue or organ
•Disuse atophy
- Overwork or persistent cell injury
- Loss of innervation (denervation atrophy)
- Loss of hormonal (trophic) stimulation
- Reduced blood supply / hypoxia
- Inadequate nutrition
- Compression
- Aging (senile atrophy)
- Starvation and malnutrition atrophy
What are the reversible cellular adaption?
Atophy, hyperplasia, hypertrophy, metaplasia
Serous atrophy of fat
when happens?
脂肪細胞的萎縮
- fat deposits are completely or partially depleted, and a clear or yellowish gelatinous material remains.
- indicate starvation

Involution
退化/生理性萎縮
- normal physiological atrophy
- eg Thymus, uterus after parturition
Hypertrophy
especially for what types of cells?
肥大
- for cells that undergo limited cellular proliferation/division, such as cardiac and skeletal muscle cells
- no increase in number of cells, but increase in size and number of organelles

Compensate hypertrophy
hypertrophy when
- loss of a part of an organ or one of the paired organs or
- from obstruction of the lumen of a hollow muscular organ.
Hyperplasia
- 增生: increase in number/layers of cells
- 增生是排列整層增生,沒有影響外觀
- Ability: Labile cells (epidermis, intestinal epithelium, and bone marrow cells)>Stable cells(bone, cartilage, and smooth muscle)> Permanent cells (neurons and cardiac and skeletal muscle myocytes)
Pituitary Cushing Syndrome vs Adrenal Cushing Syndrome
Pituitary Cushing Syndrome
tumor in anterior pituitary gland–> over production of ACTH
–> which in turns over stimulates adrenal gland to produce cortisol
- final result: adrenal gland 成個腎上腺cortex都變厚
Adrenal Cushing Syndrome
- tumor in adrenal gland causing over production of cortisol
- adrenal gland 變到好醜,亂長,難看到分界
Metaplasia
Give one example
化生: one adult cell type is replaced by another adult cell type of the same germ line
Example: Smoking causes the psedostratified epithelium of airways to undergo metaplasia into stratified squamous epithelium under chronic irritation.
–> loss of cilia, less protective against antigen
Example2: lack of vitamin A –> transitional epithelium in urinary tract, epithelium of mucous gland of esophagus into squamous epithelium

Dysplasia
異生dysplasia:腫瘤的前驅,細胞生長不固定方向且大小不一。在異生一開始時是有機會可逆的,此時basement membrane(基底膜)仍完整,若不改善則,一旦穿過basement membrane,終會走向腫瘤一途
Storage disease
genetic defeats in transportation, protein folding etc resulting in lack of critical enzyme in breaking down and removing the substances that accumultaes in the lysosome
Fatty change and the corresponding mechanisms in leading it
how is it in histology?
=hepatic lipidosis
Accumulation of triglycerides(三酸甘油), cholesterol (膽固醇)and phospholipids(磷脂) in the hepatocytes of liver
- Excessive delivery of free fatty acids either from the gut or from adipose tissue
- Decreased β-oxidation of fatty acids to ketones and other substances because of mitochondrial injury (toxins, hypoxia)
- Impaired synthesis of apoprotein (CCl4 toxicity, aflatoxicosis)
- Impaired combination of triglycerides and protein to form lipoprotein (uncommon)
- Impaired release (secretion) of lipoproteins from the hepatocyte (uncommon)
In histology, many haptocytes look like fat cells, and nucleus 會被擠到邊邊去,甚至看不到

Fatty infiltration
Proliferation/hyperplasia of adipocytes, not fatty acid
muscle cell atrophy may result in infiltration of adipocytes
Glycogen deposition
Excessive amounts of glycogen are present in animals in which glucose or glycogen metabolism is abnormal, such as diabetes mellitus, or in animals that have received excess amounts of corticosteroids.
- liver enlarged, 米黃色(beige to tan-white), non-greasy, do not float on formalin
histology: vacuoles present (but irregularly in shape with indistinct outline) , nucleus centrally located, 蜘蛛網狀

Proteinuria
蛋白尿
Russel bodies
- hyaline inclusion bodies present in plasma cell –> Matt cells
- large, eosinophilic, homogenous, amorphorus
- found in Spleen
Protective unfolded protein response

Crystalloid

Crystalloid: Crystalline protein 水晶狀蛋白質
- intracellular inclusion bodies 核內包含體
- 長條形在核中心
- accumulation of 老化了的蛋白質
The Splendore-Hoeppli Reaction
- caused by persistant infection by foreign antigen,尤其是黴菌與特殊細菌
- chronic(慢性)肉芽腫性inflammation response(炎症反應),產生許多抗體/補體和病原作用,形成immno complex(免疫複合體),稱Splendore-Hoeppli material

hyaline microthrombi
- 玻璃樣微血管血栓hyaline microthrombi:DIC (disseminated intravascular coagulation) 血管內不正常的凝集,所有身體裡的微血管因為特殊原因(毒素、細菌的內毒素和燒傷等)而全面病變,全身微血管發生血液凝集時,此生物便會馬上缺氧休克而死
腫脹的包氏囊,肉眼看不出,需切片染色,會造成動物急性death
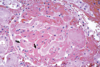
hyaline membranes of the alveolar
- 肺泡的玻璃樣膜hyaline membranes of the alveolar:專指肺泡微血管因病毒感染造成cytokine釋放造成肺炎,導致通透性過度增加,使蛋白質大量流出在肺泡表面堆積,造成呼吸困難,生物體最後因呼吸衰竭而死
Amyloid
類澱粉質
- 成分為摺疊不完全的蛋白質(misfolded proteins),因蛋白質上有醣基化修飾,滴入iodine(碘液)會呈現黑紫色如澱粉而得其名
- 會沉積在微血管末梢,如peripheral arteries(周末動脈)、glomerulus(絲球體)和sinuloid(竇狀隙),容易導致周遭血管物理性的堵塞或壓迫,導致atrophy、缺血進而壞死,堆積在絲球體的臨床症狀為蛋白尿proteinear
- 最常使用的特殊染色為剛果紅Congo Red,在偏光鏡polarized light帶有青蘋果螢光綠
- Amyloid產生其因細胞內β-sheet蛋白質不正常的產生,兩兩相遇後會polymerase越拉越長,形成長形絲狀物,與剛果紅特殊染色(可與DIC做區別)有關

Secondary Amyloidosis
- under chronic inflammation,
- 是動物最普遍的患病形式
- 這些amyloid可能會沈積在kidney/liver/spleen/lymph node
- 最重要為沈積在腎臟Kidney,因為過不到glomerulus(絲球體),一直沈積,造成物理性堆積,導致缺氧hypoxia,內皮細胞受損,蛋白質流出,導致動物的proteinuria(蛋白尿)
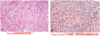
vasculitis
血管炎
Beta-amyloidosis
在人的病例中,胞外堆積amyloid-beta protein (Aβ)導致了Alzheimer’s disease(阿茲海默症);老狗腦中亦發現此堆積,有Aβ plaques,但在其中動物身上比較少見