Aspirin OD Flashcards
What is the chemical name for aspirin?
acetylsalicylic acid,
Define aspirin overdose
-
Salicylate poisoning is the result of ingestion of, or (rarely) topical exposure to:
- chemicals metabolised to salicylate
- poisoning can be due to acute or chronic aspirin exposure
- characterised by:
- acid-base disturbances
- electrolyte abnormalities
- CNS effects
Summarise the metabolism of aspirin
acetylsalicylic acid rapidly hydrolysed –> salicylate in the:
- GI tract
- liver
- bloodstream
When can
- acute
- chronic
poisoning occur (doses)
- acute = single dose of aspirin or equivalent of >150 mg/kg or >6.5 g
-
chronic = repeated exposure to high-dose aspirin or equivalent (150 mg/kg/day)
- particularly in pts with renal insufficiency
What is the aetiology of aspirin OD?
poisoning can be due to:
- accidental ingestion
- self-harm
- attempted suicide
- Incorrect salicylate dosing (children & older people)
- cutaneous absorption - rare
Other than prescribed aspirin, with OTC medications/therapies contain salicyclic acid?
- Alka-Seltzer XS
- Anadin and Anadin Extra
- Askit powders
- Aspro Clear
- Beechams powders
- Codis 500
- Disprin
- Many cold and influenza preparations
What is bismuth subsalicylate & where is it found?
- 50% aspirin equivalent
- found in some non-prescription antidiarrheal medications (Pepto-Bismol, Maalox Total Stomach Relief, and some formulations of Kaopectate
What are the risk factors for aspirin OD?
-
age:
- young (<3yrs)
- old (>70yrs)
- Hx of self-harm or suicide attempts
- ingestion of >recommended dose of aspirin, bismuth salicyclate, oil of wintergreen
Summarise the epidemiology of aspirin OD
- In the UK, deaths by suicidal overdose of analgesics, including salicylates, were reduced by 22% in the 1999
- (after the introduction in 1998 of legislation limiting the pack size of analgesics that could be purchased)
- all age groups
What are the presenting symptoms of aspirin OD?
-
CNS symptoms
- abnormal behaviour
-
Tinnitus/deafness
- is reversible
-
malaise
- early sign
-
dizziness
- early sign
-
movement disorders, asterixis
- depth correlates with level of poisoning
- seizures
-
GI symptoms:
- nausea
- vomiting
- epigastric pain
-
profuse sweating
- due to impaired production of energy and its release as heat
-
respiratory signs
-
SOB
- MAY BE THE ONLY PRESENTING SYMPTOM
- due to underlying metabolic acidosis and/or respiratory alkalosis
- tachypnoea
- hyperpnoea
-
Kussmaul’s respirations
- Salicylates directly stimulate the respiratory centre and cause tachypnoea. Respiratory alkalosis
-
SOB
What are the signs of aspirin OD O/E?
-
CNS signs
- coma, papilloedema
- confusion, delirium
- abnormal behaviour
-
GI signs
- haematemesis
-
Fever
- due to impaired production of energy and its release as heat
-
Respiratory symptoms
- tachypnoea
- hyperpnoea
- Kussmaul’s respirations
- Salicylates directly stimulate the respiratory centre and cause tachypnoea. Respiratory alkalosis
What are some uncommon signs of aspirin OD & what do they imply?
- rales + low O2 sats
- Indicates life-threatening non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema
- which can develop in both subacute and chronic poisoning
- with additional risk at high altitude
What are the primary investigations for aspirin OD?
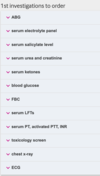
wWhat would the results of these primary investigations be in the case of aspirin OD?
-
ABG
- initially respiratory alkalosis;
- later concomitant metabolic acidosis
- (more prominent in children as they have less capacity to compensate with hyperventilation than adults)
- potentially with wide anion gap
BLOODS
-
serum electrolyte panel
- hypokalaemia, hypocalcaemia, and/or hypomagnesaemia
-
serum salicyclate
- Salicylate levels should be followed every 2-4 hours until they peak.
- Tx decisions are driven by clinical presentation rather than salicylate level
- but salicylate levels can help to determine whether the patient is still absorbing salicylate and so assist in decision-making.
-
urea & creatinine
- may show renal insufficiency (rare complication)
-
ketones
- may be positive (mainly in children) or negative
-
blood glucose
- may show hyperglycaemia due to derangement of carbohydrate metabolism
-
FBC
- WBC count may be elevated (but non-specific)
-
LFTs
- Direct hepatotoxicity can occur and is usually reversible
- However, most patients develop asymptomatic elevation of transaminases (AST. + ALT)
-
PT, activated PTT, INR
- coagulopathy may be present due to hepatoxicitity, but do not usually clinically manifest in the picture
- toxicology screen (bloods + urine for drugs of abuse)
IMAGING
-
CXR
- to exclude non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema
- requires urgent haemodialysis
-
ECG
- to exclude prolonged corrected QT interval (associated with severe ventricular dysrhythmias)
- may be life-threatening
What are some secondary investigations for aspirin OD?


