Math: the subject that turns mere mortals into caffeine-fueled problem solvers. Whether you're tackling calculus, algebra, or statistics, math is less about raw memorization and more about mastering skills over time.
But here’s the problem—our brains are wired to forget. That formula you learned last week? Gone. The shortcut to solving quadratic equations? Vanished.
Before you can solve math problems, the key values, formulae, notation, and concepts need to be solidly embedded in your memory for instant retrieval.
Enter spaced repetition: a learning technique so effective it feels like cheating (but isn’t). This cognitive hack helps you retain mathematical concepts longer, rendering your study sessions way more efficient.
Let’s take a closer look at how spaced repetition is essential for maximum efficiency in studying math.
TL;DR – Does spaced repetition help with studying math?
Oh, are you in a rush? That’s okay! Here’s the TL;DR of this article… but if you want more in-depth explanations, please keep reading!
- Yes, spaced repetition helps! It reinforces math concepts by systematizing their review at the perfect time intervals, right before you’re about to forget them.
- Flashcards are the perfect vehicle for spaced repetition because they make it easy to break subjects down into their individual concepts, which you can then repeat based on how well you know each one: more often if your understanding is weak and less often if it’s strong.
- Digital flashcard apps like Brainscape are the best tool for this kind of study because they have in-built spaced repetition study algorithms, which systematizes all of this FOR you!
- How can you use flashcards to study math? You can use flashcards to memorize your multiplication tables, formulas, equation methodologies, and theorems. You can also use them to prompt you to practice problem sets or solve equations by writing them out on the question side of the flashcard and then writing out the solution on the answer side.
In sum, practice makes perfect and spaced repetition is exactly that: practice in its most optimized form!
How do you use spaced repetition for studying math?
A spaced repetition system is like the Goldilocks of studying. It’s a method that shows you concepts not before you forget them; not after you forget them but juuuuuuust as you’re about to forget them. This ideal timing strengthens your memory and keeps your brain from chucking knowledge into the mental recycle bin.
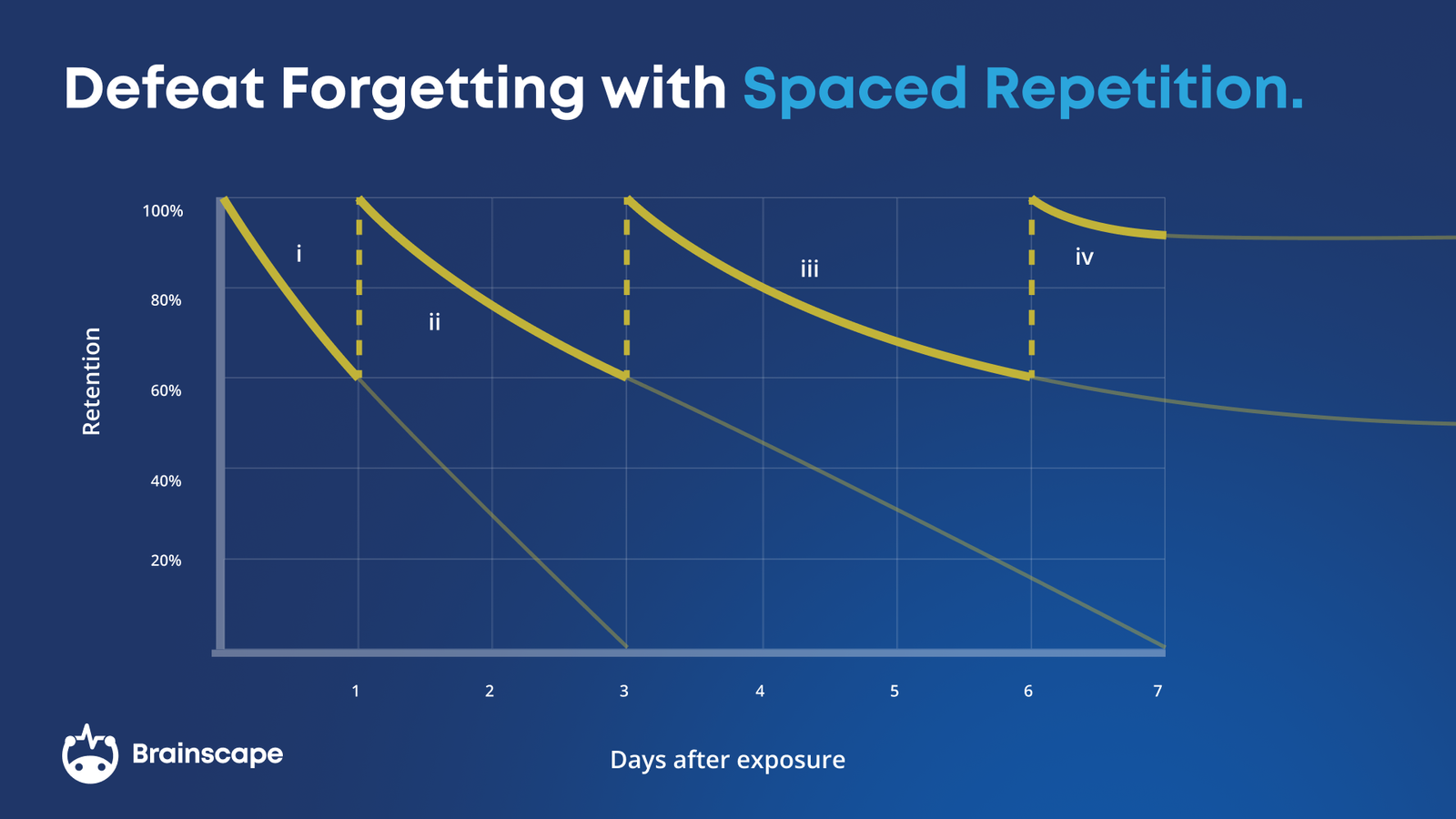
When it comes to studying math, spaced repetition helps you master formulas, theorems, and even tricky concepts by revisiting them in just the right intervals. For example, instead of memorizing the quadratic formula once (and forgetting it by next Tuesday), a spaced repetition system ensures that you refresh that knowledge regularly.
How does this system know how often to show you concepts again? Through your feedback! Brainscape's digital flashcards, which are delivered via a spaced repetition algorithm, require you to rate how well you knew the answer on a scale of 1 to 5 with 1 being "not at all" and 5 being "very well".
If you rate a concept a 1, the algorithm will show you that flashcard again within minutes. If you rated it a 5, you won't see that flashcard again for a long time: weeks or even months. Done this way, a flashcard app like Brainscape drills you on your specific weaknesses while saving you time reviewing the concepts you're already confident in.
And as a bonus, the very act of this self-reflection—this assessing how well you know what you know—improves your metacognition, which enhances your memory of each concept!
(PS This isn't just true for children. Spaced repetition is the best learning technique for adults too.)
How do you use active recall and spaced repetition in math?
Now that you know the “what,” let’s tackle the “how.” A spaced repetition app like Brainscape doesn’t just make math manageable—it helps you learn TWICE as fast.
1. Flashcards break down math concepts into bite-sized pieces
Math concepts often feel overwhelming, so it’s important to chunk them into smaller, digestible sections. Instead of creating a single flashcard that says, “Explain trigonometry,” flashcards quiz you on stand-alone concepts, such as “What is sin(30°)?”
This approach allows your spaced repetition system to focus on individual concepts, helping you master them incrementally.
2. Flashcards prioritize active recall
Math isn’t a spectator sport. To truly grasp it, you need to actively solve problems rather than passively review notes. One way you can do this is to write out a problem set on the question side of a flashcard and then provide the worked-out answer on the other side.
If you’re using a flashcard app like Brainscape, and your notation is particularly complex with lots of formulas and symbols, you can easily write them out with pen and paper, snap a shot with your phone, and upload those separate photos to the question and answer side of the flashcards. Alternatively, you can type your formula in LaTeX, and then upload a screenshot of that...

Then, you can use your flashcards to test you on your math problem sets. Once you’ve arrived at the answer, flip over the flashcard. If you easily got the answer right, you won’t have to repeat that flashcard again for a while. But if you struggled (and got it wrong), set it aside to work on it again soon.
Pro tip: When you get an answer wrong, don’t sweat it. Brainscape will serve that card up again soon, giving you more practice where you need it most and optimizing your learning efficiency.
3. Use multimedia for complex topics
Some math concepts—like 3D geometry or graphing functions—are tough to convey with plain text. That’s where digital flashcards shine. As we’ve just explained, Brainscape lets you include images and diagrams to visualize tricky ideas when studying math.
For instance, upload a graph of a sine wave or a step-by-step solution to an equation. These visuals make abstract concepts easier to understand and remember.
4. Take advantage of real-time feedback
What is the best schedule for spaced repetition? Brainscape automatically tracks your progress and drills you relentlessly on the concepts you’re weakest in. This is especially helpful for math, where building a strong foundation is crucial. Misunderstanding a basic concept can snowball into bigger problems later on.
5. Apply your memory to practice problems
You’ve memorized all the formulae, values, and steps using a spaced repetition system. Now, you take them for a test drive. Quiz yourself with practice questions, and enjoy your new, swift memory that has been trained to actively recall every fact it needs.
Want to see how the app works? Check out this handy sampler:
Why spaced repetition works so well for math
Let’s get nerdy for a second: studying math isn’t just about understanding—it’s about application. Spaced repetition excels here because it doesn’t let your brain off the hook.
- Reinforce problem-solving skills: The more you practice recalling a math concept—and practice the associated skills—the more it becomes second nature.
- Prevent knowledge decay: By practicing and revisiting concepts over time, spaced repetition strengthens neural connections, making it easier to recall formulas and problem-solving techniques.
- Boost confidence: Exam anxiety is real, but confidence grows when you repeatedly get little things right.
Why Brainscape is the best spaced repetition app for math
When I first started using Brainscape to study math, it honestly felt like a cheat code. Spaced repetition isn't just a buzzword; it's a real game-changer for actually remembering all those formulas, theorems, and problem-solving techniques that math loves to throw at you.
Here’s why I think Brainscape is the perfect tool for tackling math:
- It adapts to you. Brainscape has this amazing algorithm that knows when to show you a card based on how well you’re doing. Let’s say you’re struggling with trig tables—those cards will keep showing up until you’ve got them locked down. It’s like having a personal tutor who actually pays attention.
- You can create your own decks. Whether you’re learning multiplication tables or you’ve made it to college-level matrix transformations, you can build flashcards for the exact concepts you need. That way, you’re not wasting time on stuff you already know.
- There are pre-made decks too. Brainscape has thousands of already-made flashcards on dozens of math topics crafted by fellow learners and professional educators, covering everything from high school geometry to advanced calculus. They're an amazing place to start if you're short on time!
- It fits into your life. You can study anywhere—on the bus, in the library, or while waiting for your coffee to brew. Brainscape is fully mobile, so it’s super easy to squeeze in quick sessions wherever you are, even if you have virtually no time to study.
Seriously, if math feels overwhelming, spaced repetition with Brainscape might be the exact system you need to make everything click. It helped me go from barely remembering formulas to actually feeling confident walking into exams.
Conclusion: study math smarter and faster
Studying math doesn’t have to feel like scaling Mount Everest. With the right tools—like a flashcard app that uses spaced repetition—you can master formulas faster, practice problem sets, drill yourself on theorems, and even (dare we say it?) enjoy the process.
So, are you ready to revolutionize how you study math? Download Brainscape today and discover how spaced repetition can make math your new favorite subject.
Your future self (and your GPA) will thank you.
Sources
- Bjork, R. A., & Bjork, E. L. (2020). Desirable difficulties in theory and practice. Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition, 9(4), 475–479.
- Ebbinghaus, H. (1913). Memory: A contribution to experimental psychology. New York: Teachers College, Columbia University.
- Karpicke, J. D. (2012). Retrieval-based learning: Active retrieval promotes meaningful learning. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21(3), 157-163.
- Lally, P., & Gardner, B. (2013). Promoting habit formation. Health Psychology Review, 7(sup1), S137-S158.
- Sadler, P., & Good, E. (2006). The impact of self- and peer-grading on student learning. Educational Assessment, 11(1), 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326977ea1101_1
